Method for making a composite material, composite material and end product
A composite material, the final technology, applied in the direction of synthetic resin layered products, layered products, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of reducing in-plane strength, increasing weight and cost, increasing material weight and cost, etc., to achieve Increased damage resistance, reduced weight, and increased structural weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The composite material according to the present invention comprises a multilayer component with one layer on top of another layer. Each layer of components includes one group (m) of parallel strips on top of the other group.
[0042] It should be pointed out that "a layer (group) on top of another layer (group)" should not be understood only literally, because adjacent multilayer components are interlaced and adjacent groups of stripes are interlaced Yes, as you can see from below.
[0043] Each group will be made by a specific method of placing parallel bars in batches.
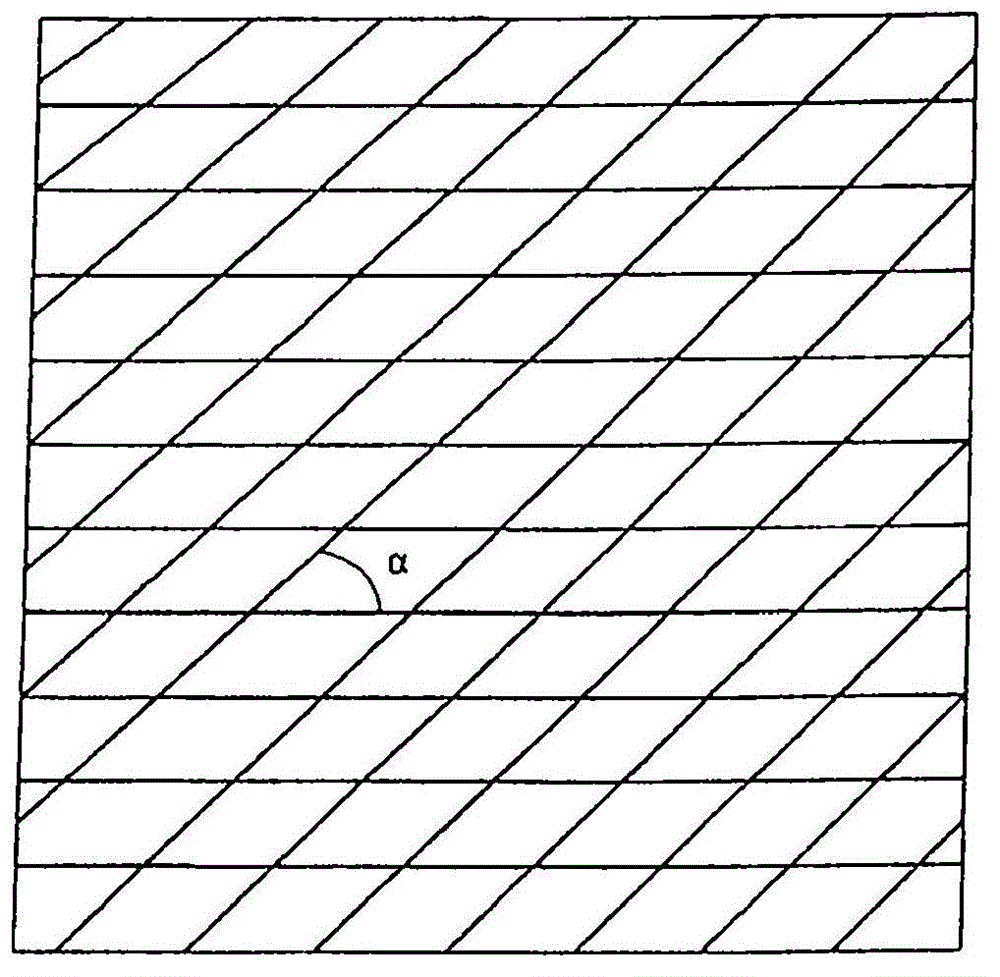
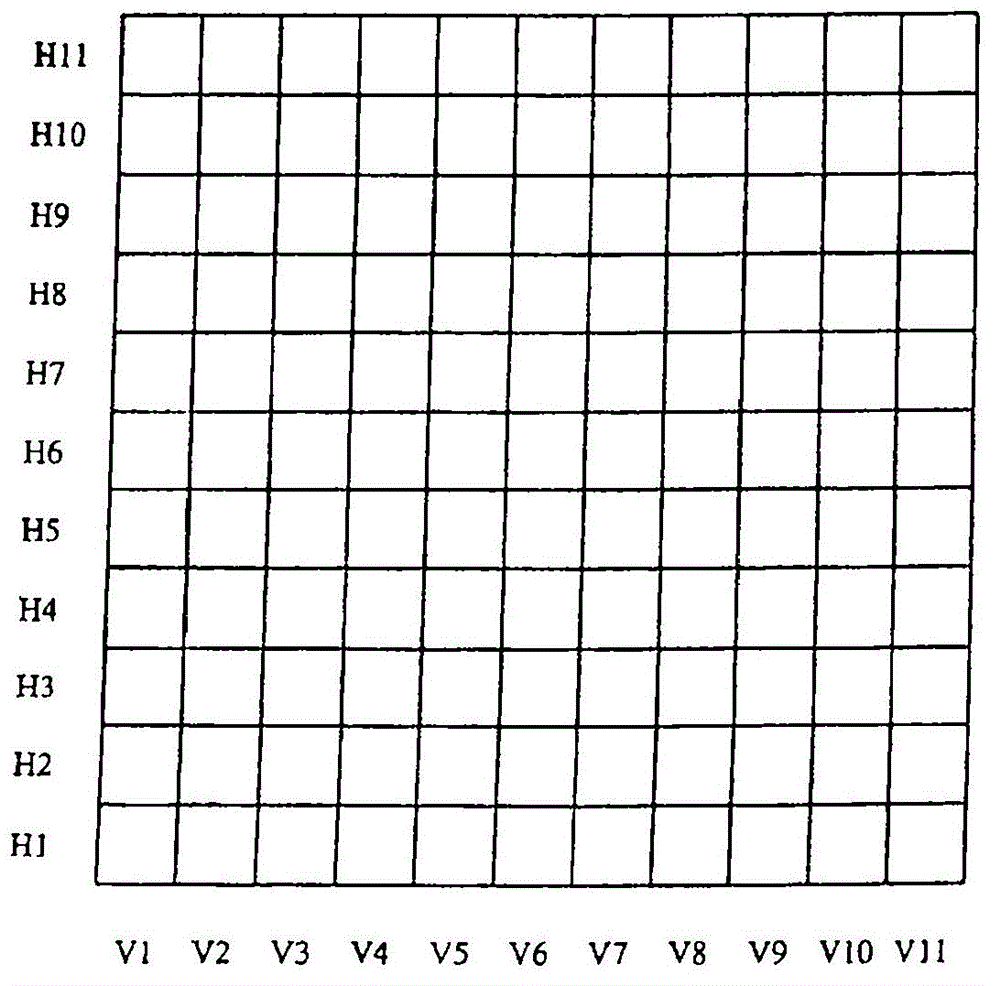
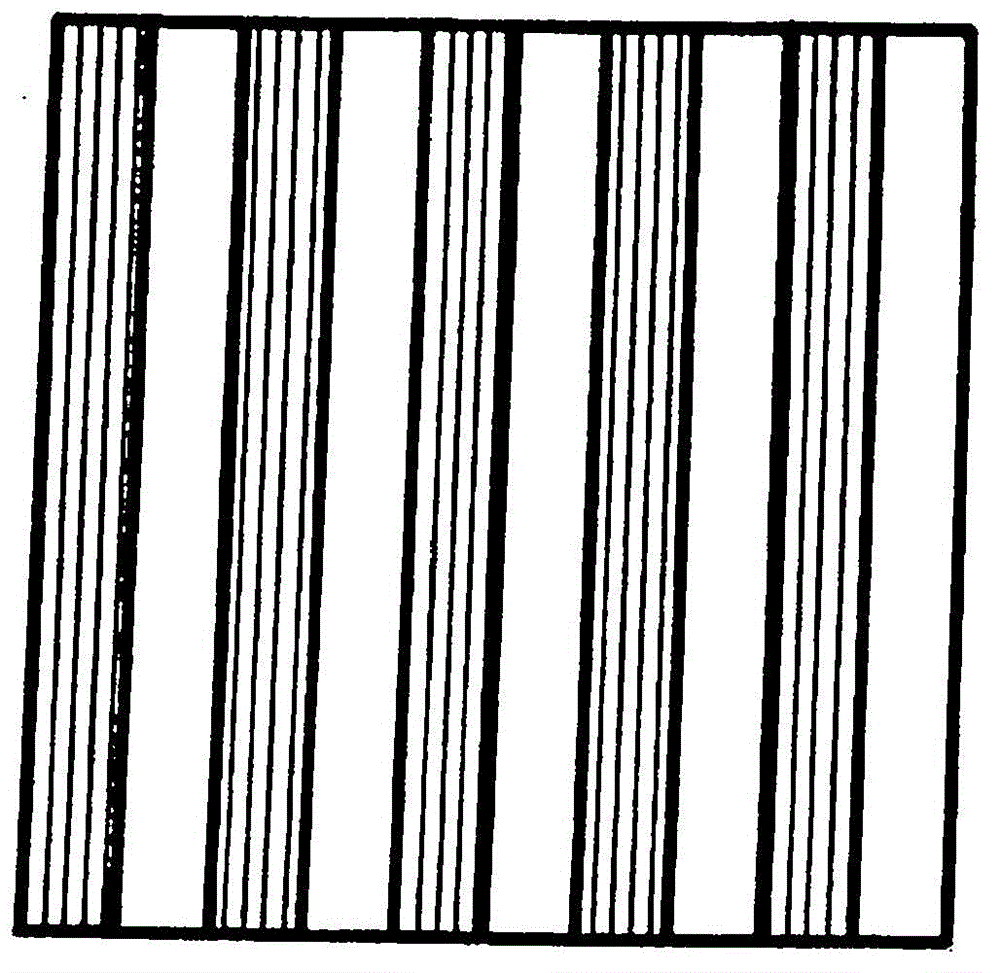
[0044] figure 1 A schematic diagram with a horizontal array H1-H11 and a vertical array V1-V11 pattern is shown. The angle between the horizontal and vertical arrays is 90°. The figure 1 Used together with Figure 2 to explain how two (m=2) sets of strips can be used to make a layer of components.
[0045] For the basic manufacturing of a one-layer module, first, according to the vertical arrays V1, V3, V5,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com