Common light chain mouse
A mouse and light chain technology, applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, peptides, anti-animal/human immunoglobulins, etc., can solve problems and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0084] Previous efforts to generate useful multispecific epitope-binding proteins (e.g., bispecific antibodies) have been hampered by multiple problems that often share a common paradigm: in vitro selection or manipulation of sequences for rational engineering, or by trying-and- - Errors (forms suitable for paired heterodimeric bispecific human immunoglobulins) were engineered. Unfortunately, most, if not all, in vitro engineering methods primarily provide for immediate localization of individual molecules, if any. On the other hand, in vitro methods employing complex organisms to select appropriate pairs capable of producing human therapeutics have not been achieved.
[0085] In general, naive mouse sequences are often not a good source of human therapeutic sequences. For at least this reason, generation of mouse heavy chain immunoglobulin variable regions paired with consensus human light chains is of limited practical utility. More in vitro engineering efforts will be spe...
Embodiment 1
[0111] Example 1. Identification of Human Heavy Chain Variable Regions Associated with Selected Human Light Chain Variable Regions
[0112] An in vitro expression system was constructed to determine whether a single rearranged human germline light chain could be co-expressed with a human heavy chain from an antigen-specific human antibody.
[0113] Methods for producing human antibodies in genetically modified mice are known (see, e.g., US 6,596,541, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, ). The technique involves producing a genetically modified mouse having a genome comprising human heavy and light chain variable regions operably linked to endogenous mouse constant region loci such that the mouse responds to an antigen Stimulation produces antibodies comprising human variable regions and mouse constant regions. encoded by The DNA of the variable regions of the heavy and light chains of antibodies produced by mice is entirely human. Initially, high affinity chimeric antibodies with...
Embodiment 2
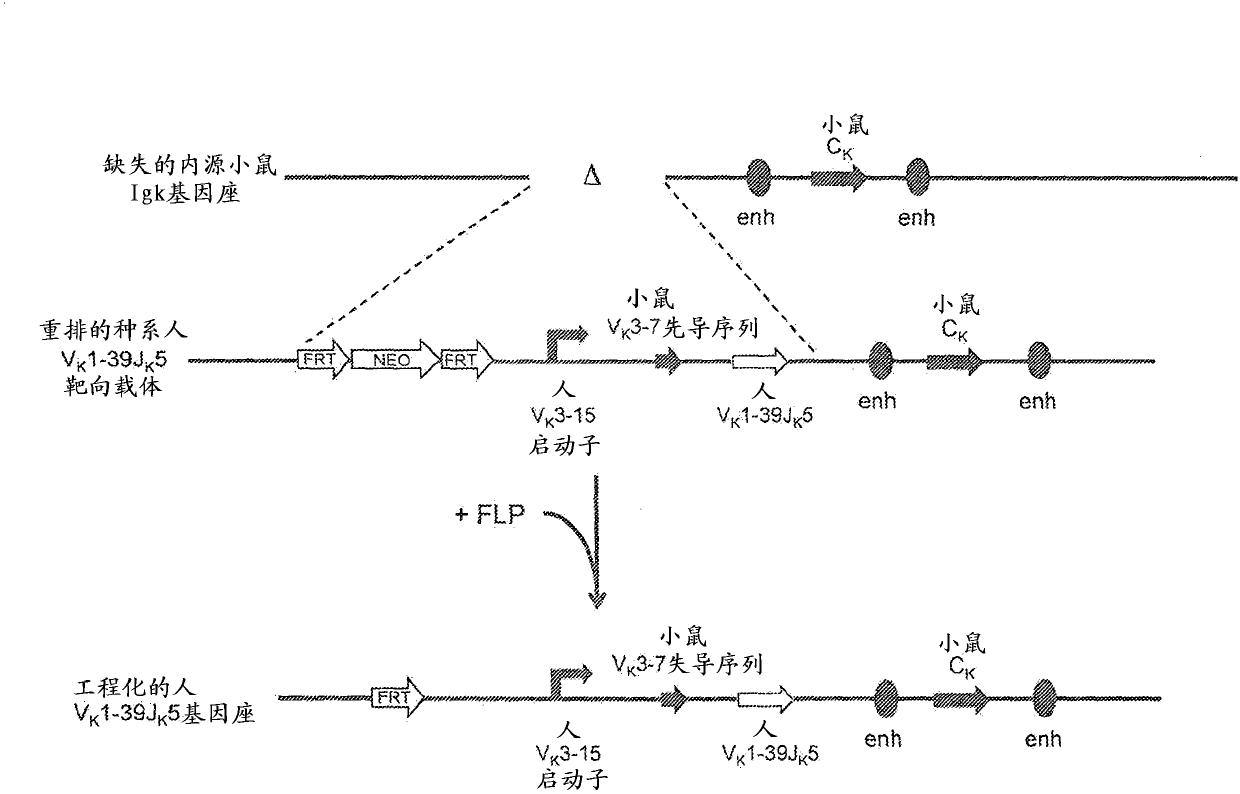
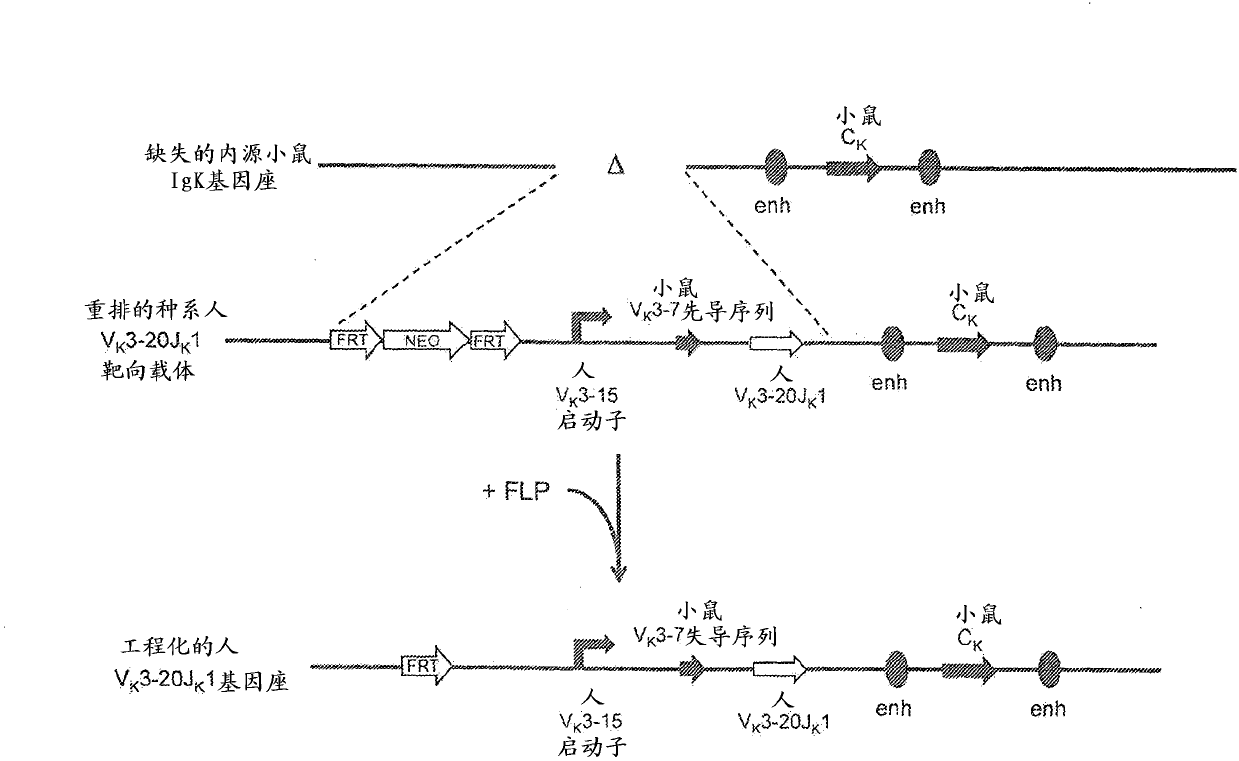
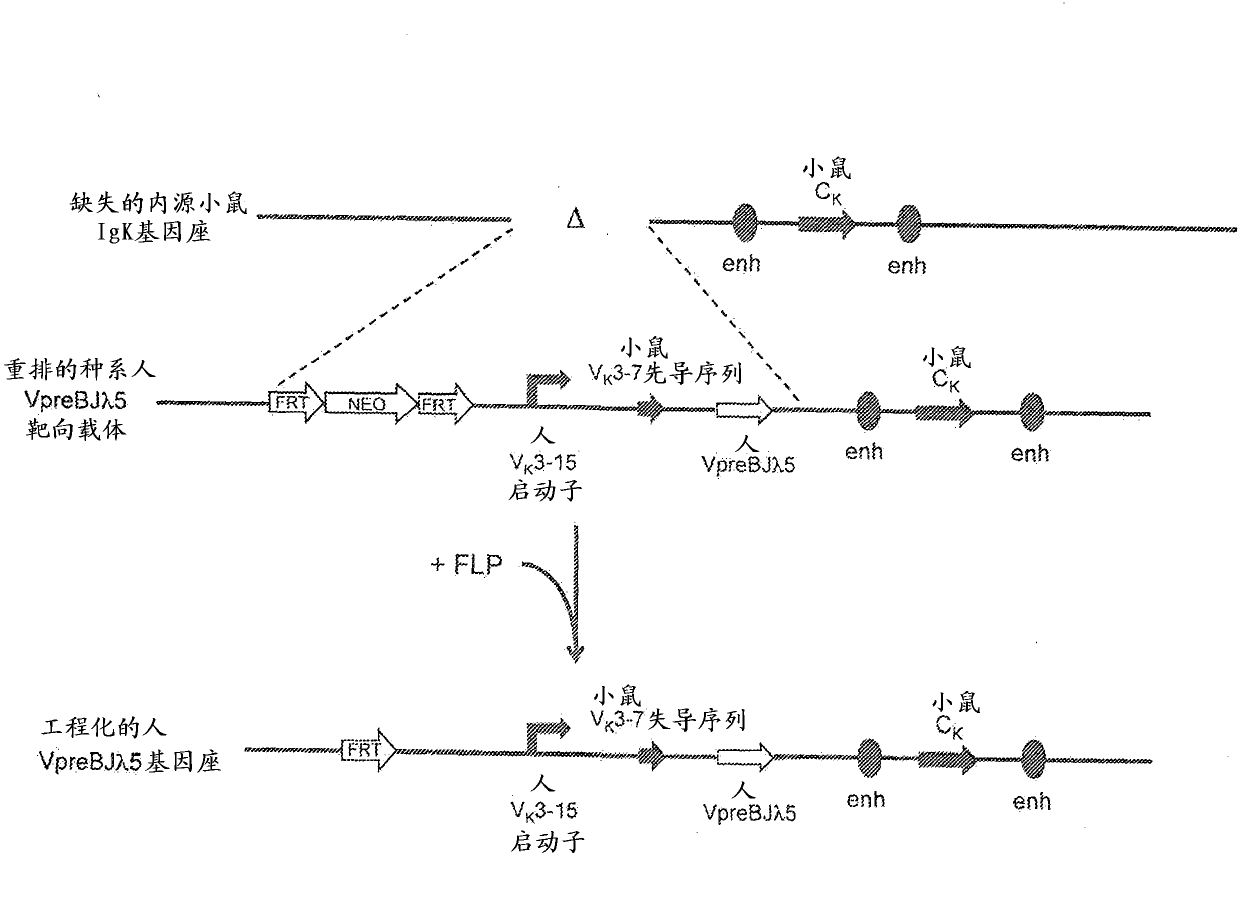
[0122] Example 2. Generation of rearranged human germline light chain loci
[0123] use technology (see, e.g., U.S. Pat. No. 6,586,251 and Valenzuela et al. (2003) High-throughput engineering of the mouse genome coupled with high-resolution expression analysis, Nature Biotech.21(6):652-659) prepared a variety of A row of human germline light chain targeting vectors was used to modify the mouse genome bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clones 302g12 and 254m04 (Invitrogen). Using these two BAC clones, a genomic construct was engineered to contain a single rearranged human germline light chain region and inserted into the endogenous kappa light chain locus preceded by Modified to delete endogenous kappa variable and linker gene segments.
[0124] A. Construction of rearranged human germline light chain targeting vectors
[0125] Three different rearranged human germline light chain regions were prepared using standard molecular biology techniques recognized in the art. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com