Electroluminescent display and driver circuit to reduce photoluminescence
A technology for photoluminescence and display drivers, applied in circuits, static indicators, electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing photoluminescence, not applicable, not provided, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
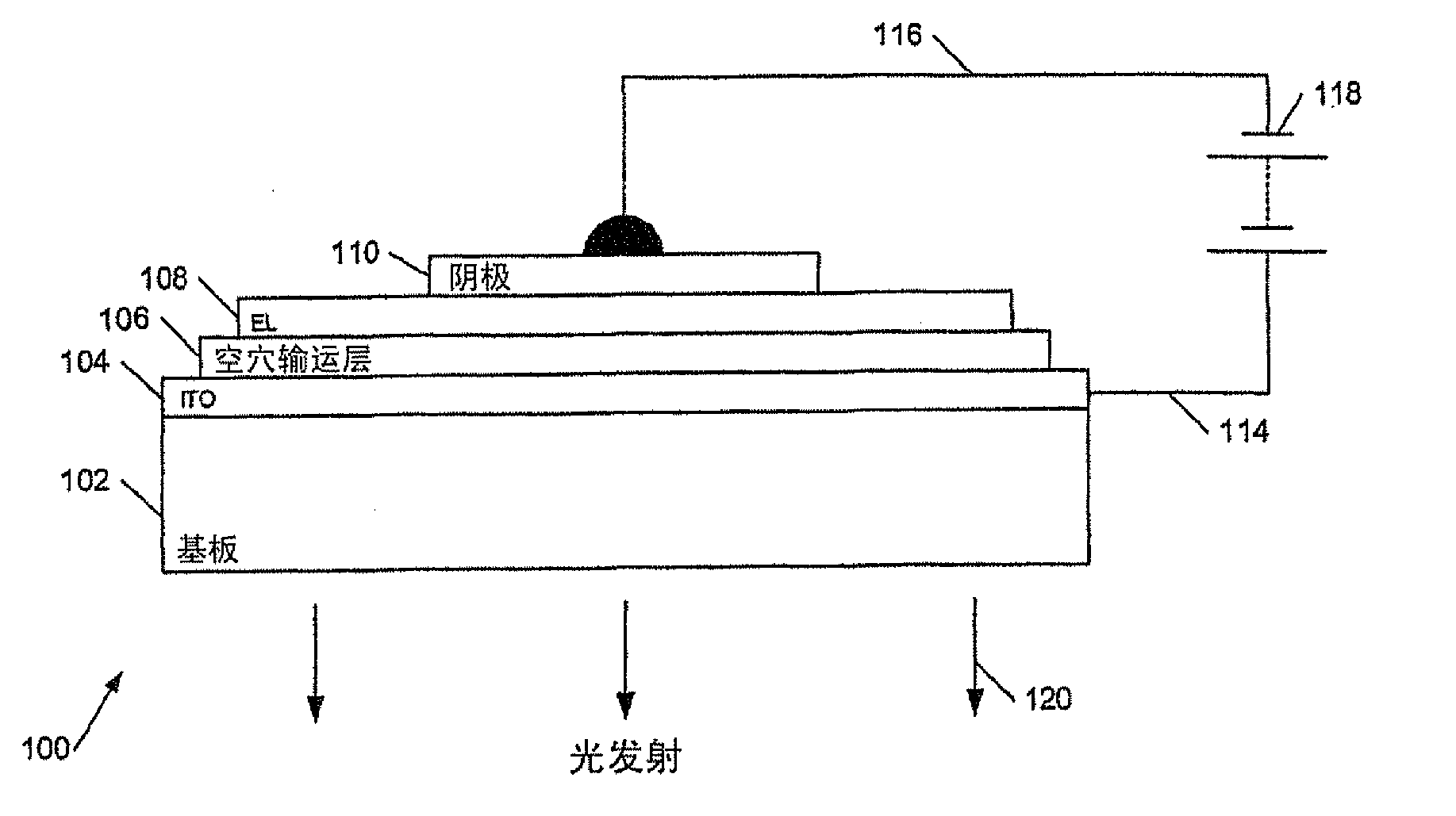
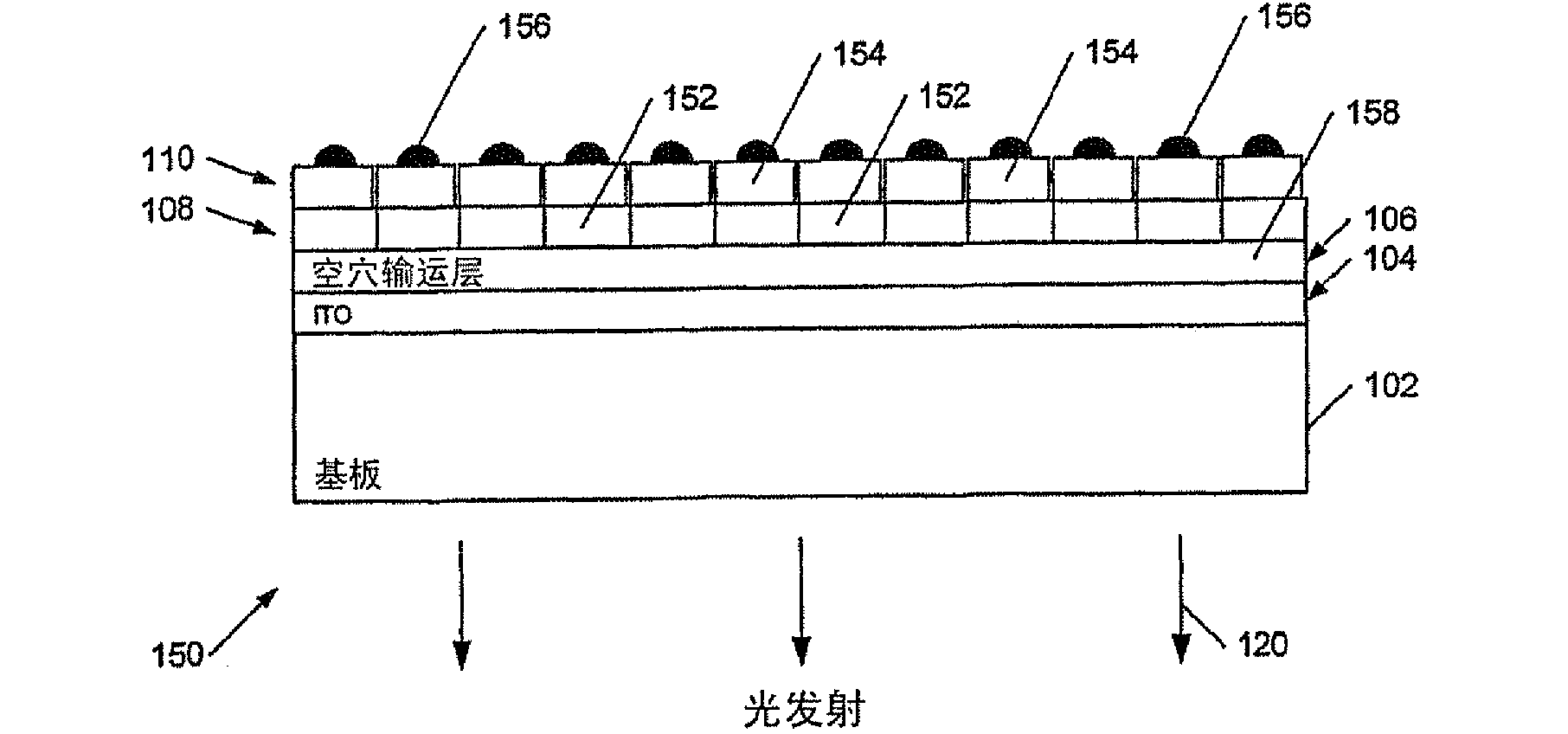
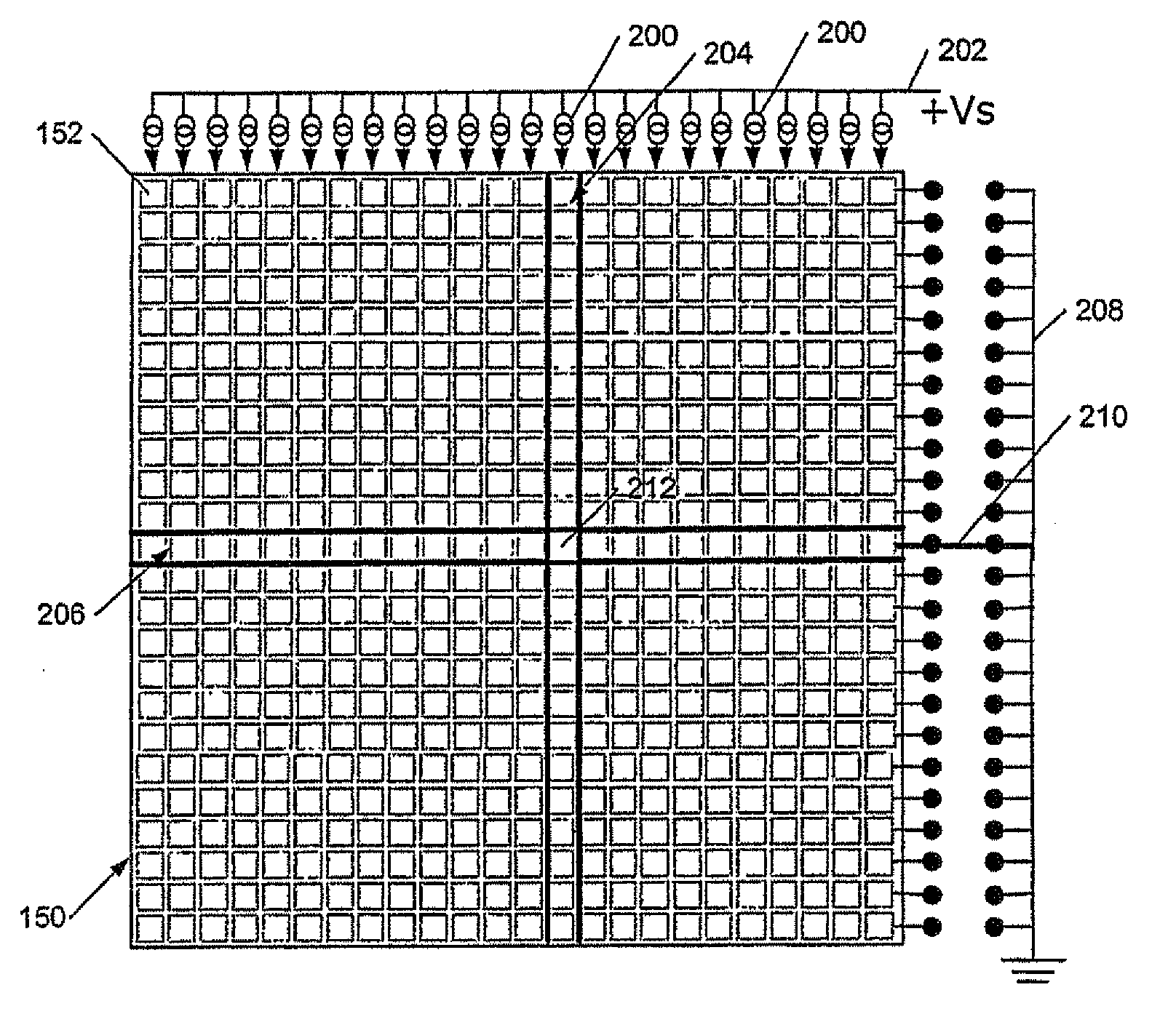
[0067] Applicants have realized that the contrast of light emitting diode based displays, eg passive or active matrix organic light emitting diode based displays, can be increased by reducing the contrast reducing photoluminescence. In the case of displays comprising light emitting diodes, especially organic light emitting diodes, this light can be reduced or quenched by reverse biasing a selected batch of light emitting diodes, i.e. those that are not emitting at any given moment Luminescence.
[0068] For example, consider a simple OLED display such as Figure 1a with 1b Display shown in , which is not forward biased or reverse biased. The apparent color of the (unlit) display is a combination of the color of the photoluminescence from the electroluminescent layer 108 of the display and the intrinsic color of said layer 108 and other modifying layers, especially the color of the cathode layer. Thus, for example, if the layer 108 is inherently colorless, and the photolumine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com