Method quickly accessing internet in carrier-grade network address translation (CGN) network
An Internet and network technology, applied in the direction of network interconnection, data exchange network, data exchange through path configuration, etc., can solve the problem that the IPv6 rapid deployment solution cannot realize NAT traversal, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
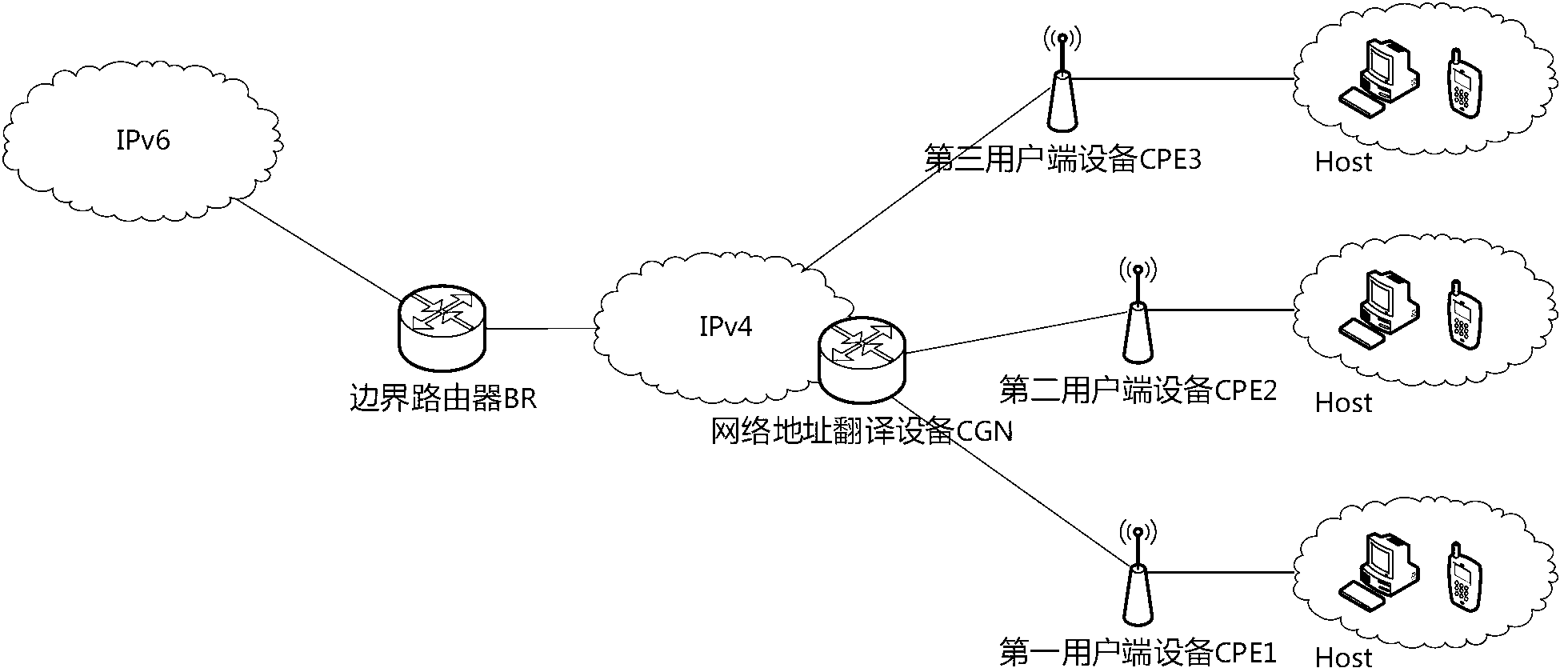
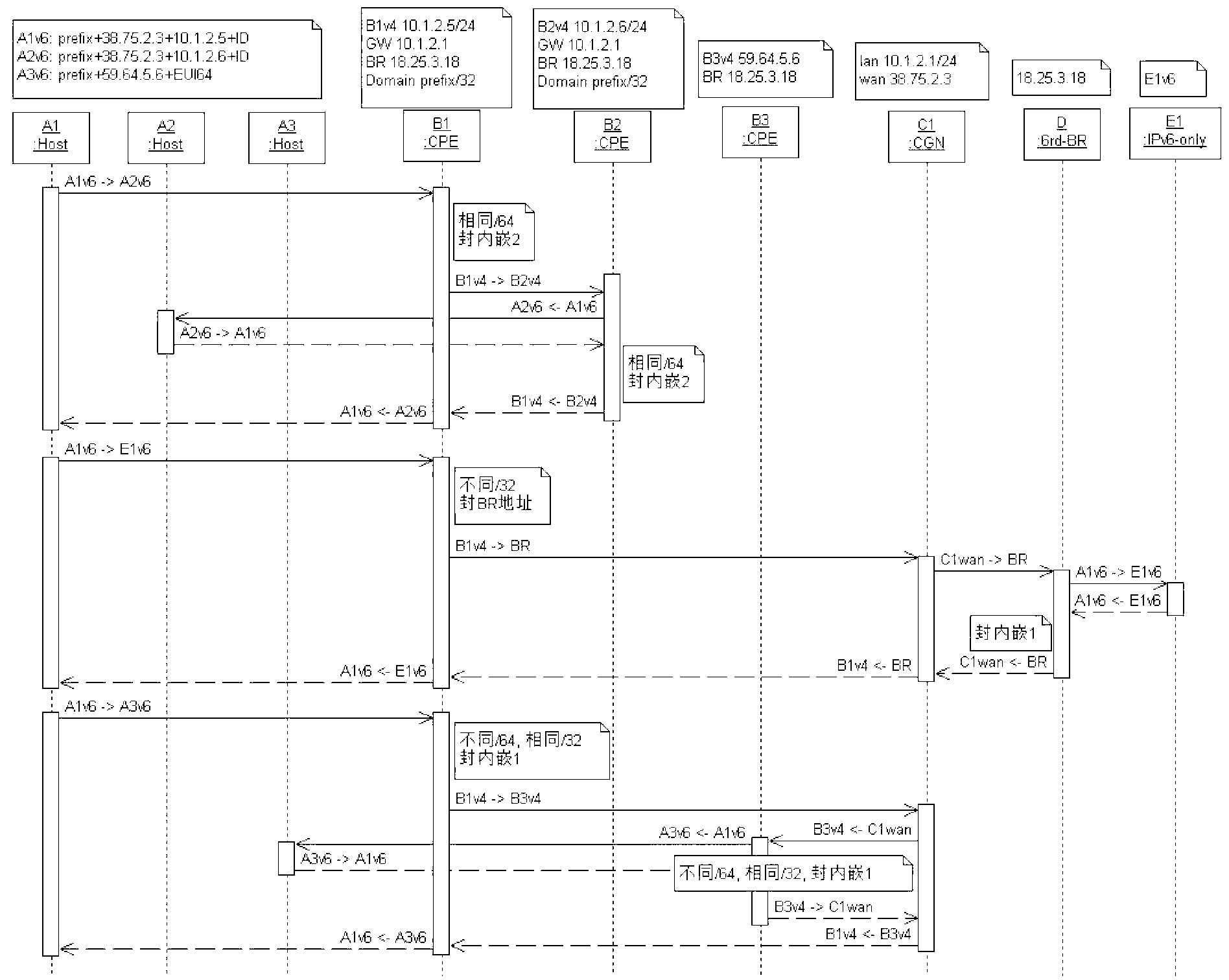
[0056] The client accesses the IPv6 site ipv6.google.com outside the 6rd domain (see image 3 A1v6-E1v6 part), at this time, the IPv6 data packet includes a destination address and a source address, and the source address includes: IPv6 prefix, CGN network WAN side IPv4 address, user end equipment CPE facing operator side IPv4 address and client ID, the destination address includes an IPv6 prefix.
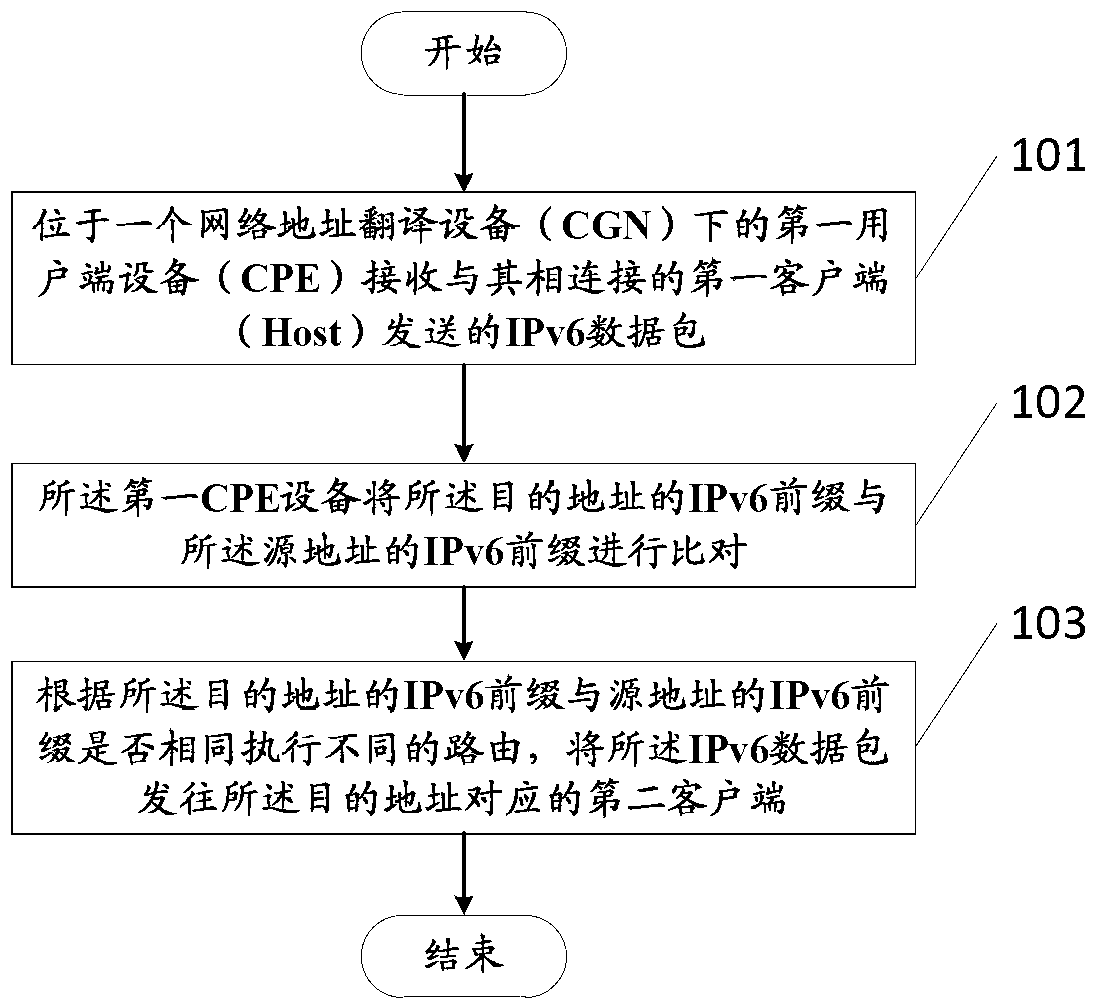
[0057] To this end, its upstream direction includes the following steps:
[0058] The user side equipment CPE1 located behind the network address translation equipment CGN equipment receives an IPv6 data packet initiated by the client host connected to it;
[0059] Among them, the data packet includes: the destination address corresponding to the destination website ipv6.google.com, the destination address includes an IPv6 prefix, the source address includes: the IPv6 prefix, the IPv4 address on the WAN side of the CGN network, and the operator-oriented Side IPv4 address and clie...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Clients access clients behind different CPEs in the same CGN network (see image 3 A1v6-A2v6 part)
[0067] To this end, its upstream direction includes the following steps:
[0068] The user side device CPE1 located behind a network address translation device CGN device receives an IPv6 data packet initiated by the client connected to it;
[0069] The CPE1 compares the prefix of the destination address of the IPv6 data packet with the IPv6 prefix provided by the operator, and finds that the first 32 digits of the IPv6 prefix are consistent, indicating that both belong to the same -6RD domain, and there is no need to traverse the BR at this time The device then further compares the embedded IPv4 address part, and finds that the embedded IPv4 address part is also consistent; it means that both belong to the same CGN network.
[0070] In this scenario, the composition of the destination IPv6 address is as follows:
[0071] 32-bit operator IPv6 prefix + 32-bit CGN WAN p...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Clients access clients directly behind CPE3 with IPv4 addresses (see image 3 A1v6-A3v6 part), wherein, its uplink direction includes the following steps:
[0078] The user side device CPE1 located behind a network address translation device CGN device receives an IPv6 data packet initiated by the client connected to it;
[0079] CPE1 compares the operator prefix in the prefix of the IPv6 destination address and finds that the 32-bit prefix is consistent. At this time, it means that the destination host is in the same 6RD domain, that is, accessing the destination host does not need to traverse the BR;
[0080] Next, the CPE1 compares the embedded IPv4 address part, and finds that the embedded IPv4 address part is inconsistent, which means that the two do not belong to the same CGN network.
[0081]At this point, the CPE1 needs to encapsulate the IPv6 data packet in the IPv4 packet, the source address of the IPv4 packet header is the IPv4 address of the port facing t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com