System and method for cursor control based on brain-computer interface
A cursor control and brain-computer interface technology, applied in the field of brain science applications, achieves the effects of a large number of applicable people, high accuracy, and a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
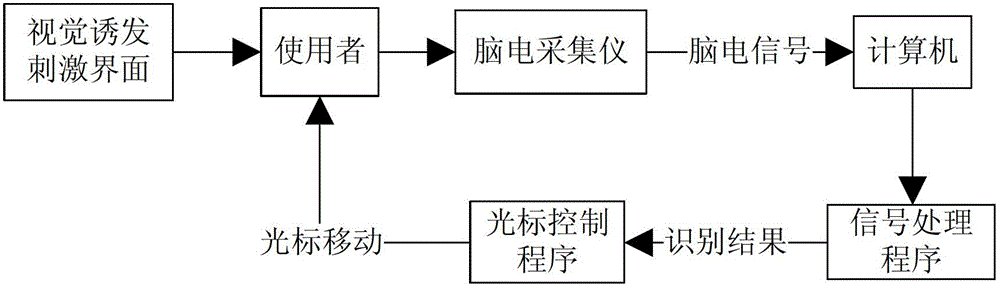
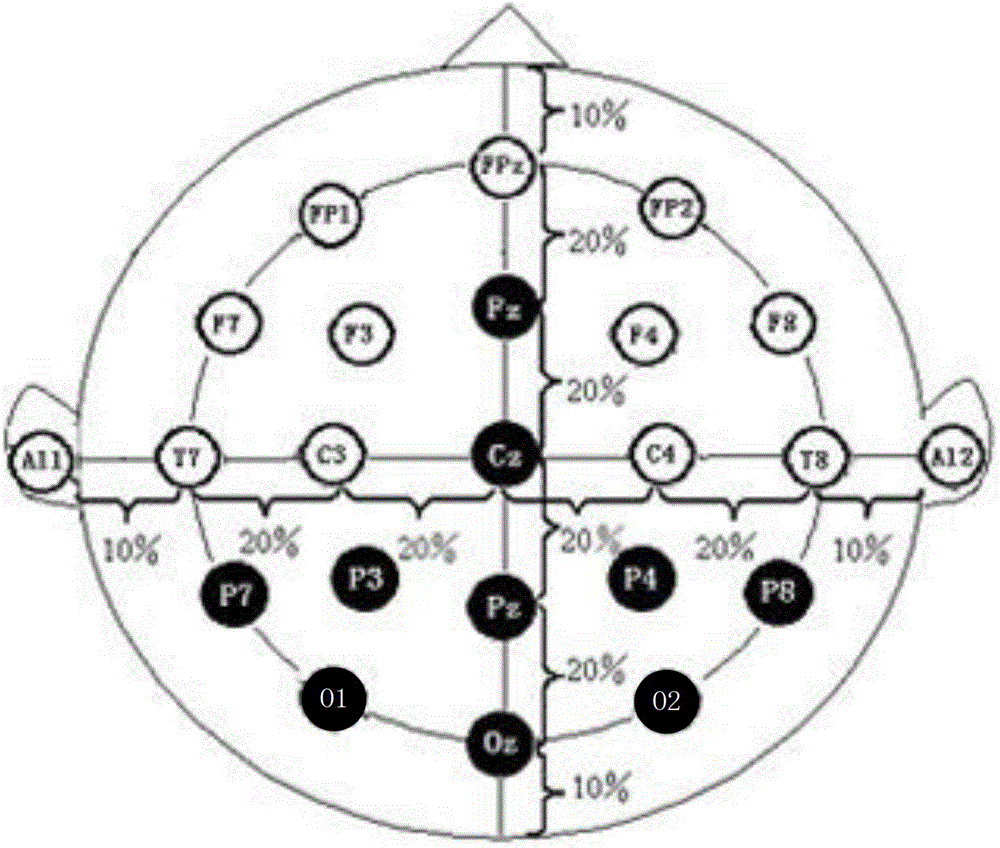
[0025] In the first embodiment of the present invention, a cursor control system based on a brain-computer interface is proposed, referring to figure 1 , the system includes a visually evoked stimulation module, an EEG collector and a processor. Wherein, the processor includes a signal processing module and a cursor control module. Wherein, the visually evoked stimulation module includes two stimulation modes of P300 evoked potential visual stimulation and SSVEP evoked potential visual stimulation, which are provided to users in the form of interface display.
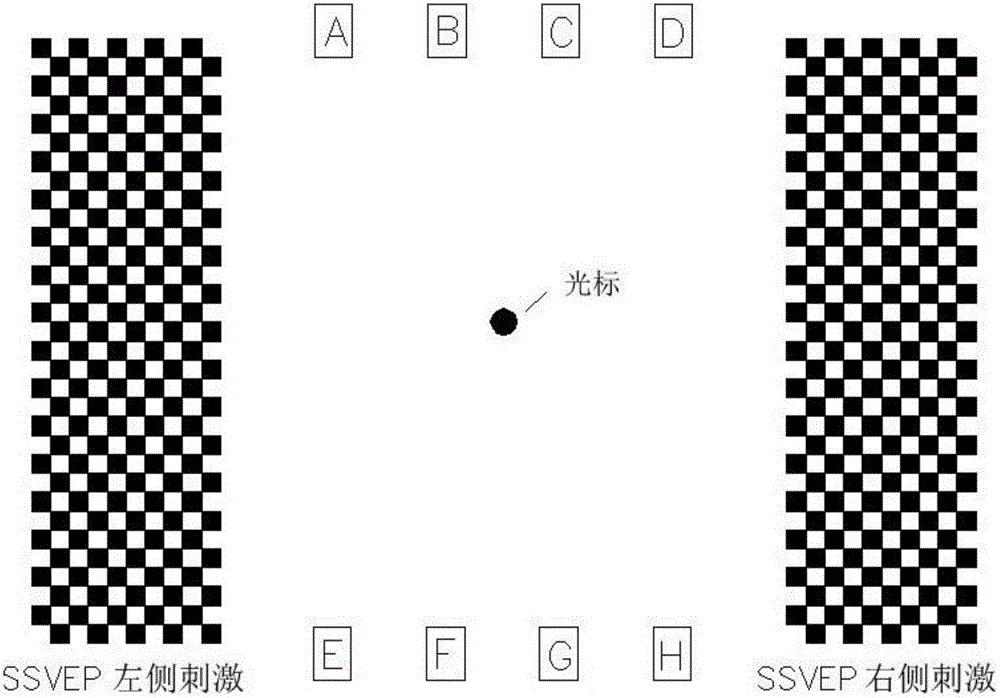
[0026] Among them, the P300-evoked potential visual stimulus and the SSVEP-evoked potential visual stimulus both contained several target stimuli. Among them, according to the existing P300 evoked potential technology, the P300 evoked potential visual stimulus was designed according to the Oddball paradigm, including eight flashing blocks A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H. According to the existing SSVEP evoked potential tec...
Embodiment 2
[0035] In the second embodiment of the present invention, a cursor control method based on a brain-computer interface is proposed, referring to figure 1 and Figure 8 , the method includes: step 1, providing the P300 evoked potential visual stimulus and the SSVEP evoked potential visual stimulus to the user in an interface display mode; step 2, collecting the EEG signal in real time and performing amplification and analog-to-digital conversion; step 3, the processor Receiving and processing the EEG signals to determine the user's control intention; step 4, controlling the cursor to move in a corresponding direction according to the control intention. Wherein, the distance of each movement in any direction is 50 pixels.
[0036] Wherein, step 3 includes: step 31, judge whether there is SSVEP evoked potential on a section of EEG signal collected in real time; The signal is reprocessed to determine whether the user has selected the P300 stimulus at the top of the screen or the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com