Q-and-PB (quenching and partitioning in bainite zone) heat treatment process for preparing 30 GPa%-grade complex-phase steel
A complex phase steel and process technology, applied in heat treatment equipment, heat treatment process control, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of high production cost, not higher than 20%, and limit the wide application of second-generation automotive steel, and achieve improved performance. The effect of elongation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
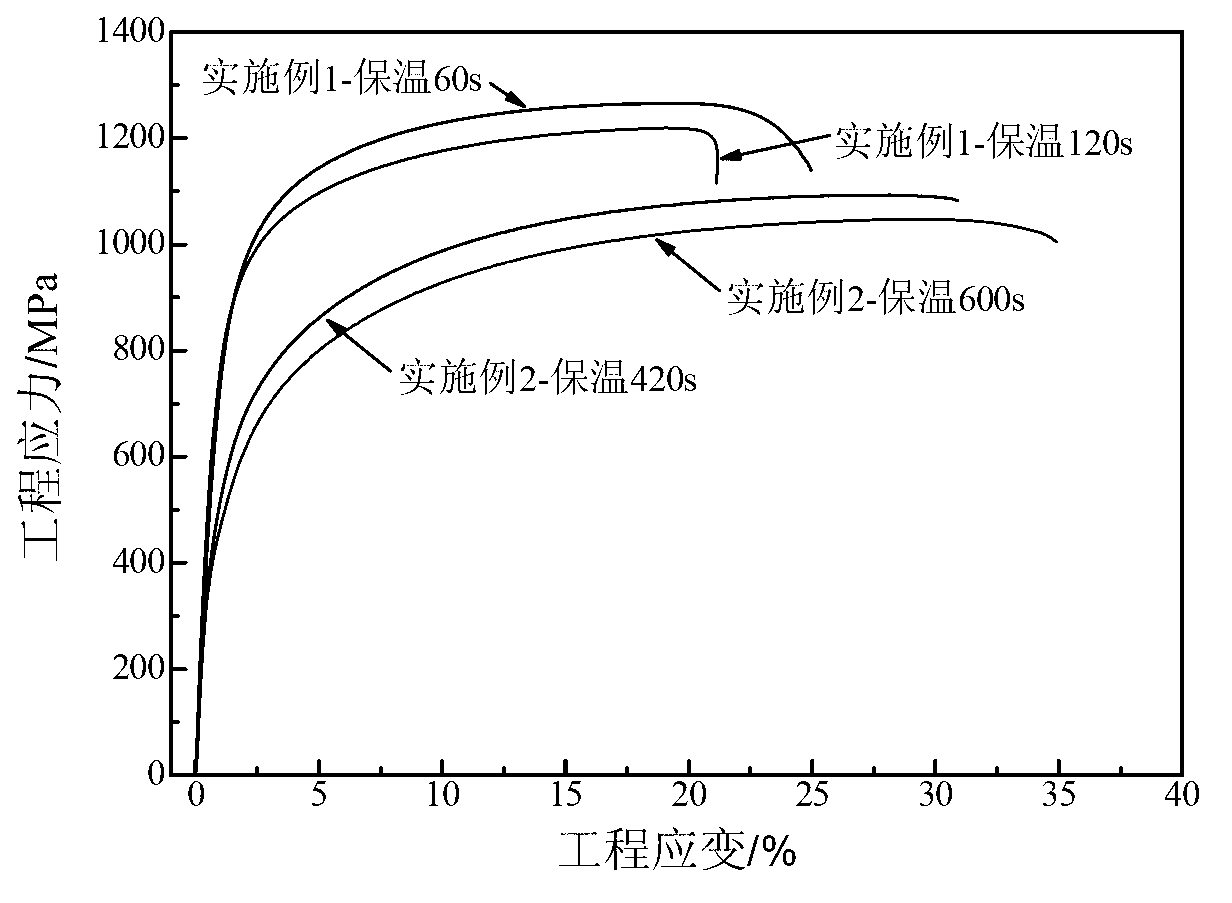
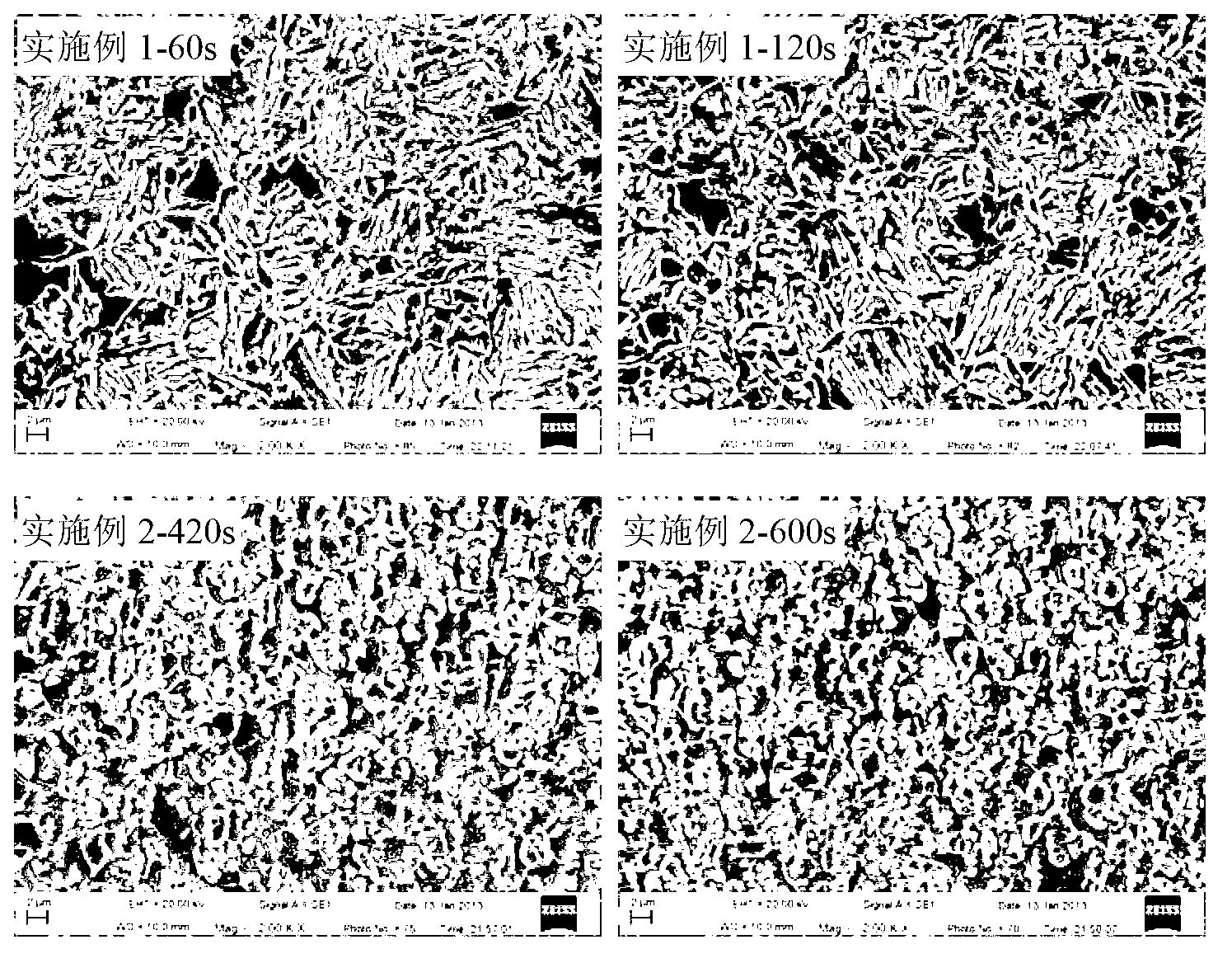
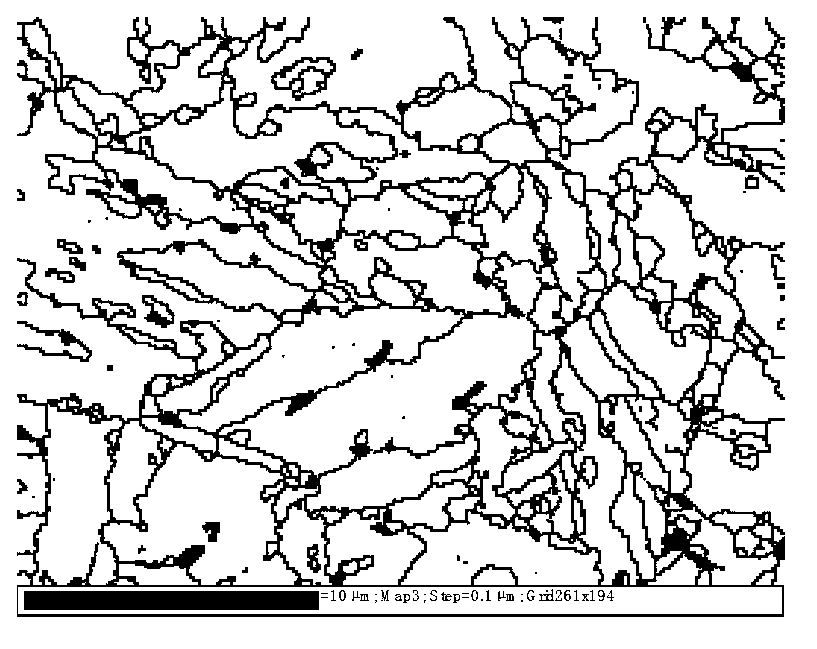
[0018] The mass fraction of each component of the cold hard plate: C: 0.23%, Si: 1.53%, Mn: 2.07%, P: 0.010%, Al: 0.03%, S: 0.004%, the rest is Fe and unavoidable impurities, according to experience According to the formula, the starting temperature of martensite transformation and the optimum quenching temperature are 368°C and 230°C, respectively. The Q&PB heat treatment process is as follows: heat the sample to 850°C for 1-2min, quench to 270°C for 5s, according to the relationship between the quenching temperature and the amount of martensite V m =1-exp[-0.011(M s -T q )] The calculated martensite content obtained by the quenching temperature is 66%, and the austenite content is 34%. Then the temperature was raised to 400°C for 60s and 120s, and finally quenched to room temperature. The obtained room temperature structure included martensite, retained austenite and bainite, as shown in Figure 1. The test results of mechanical properties are that the yield strength, tens...
Embodiment 2
[0020] The mass fraction of each component of chilled hard board: C: 0.26%, Si: 1.61%, Mn: 2.1%, P: 0.013%, Al: 0.03%, S: 0.006%, Mo: 0.21%, Nb: 0.059%, and the rest It is Fe and unavoidable impurities. According to the empirical formula, the martensitic transformation temperature and the optimal quenching temperature are 354°C and 234°C, respectively. The Q&PB heat treatment process is as follows: heat the sample to 850°C for 1-2min, quench to 270°C for 5s, according to the relationship between the quenching temperature and the amount of martensite V m =1-exp[-0.011(M s -T q )] Calculate the martensite content obtained by the quenching temperature to be 60.3%, and the austenite content to be 39.7%. Then the temperature was raised to 400°C for 420s and 600s, and finally quenched to room temperature. The obtained room temperature structure included martensite, retained austenite and bainite, as shown in Figure 1. The test results of mechanical properties are that the yield s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strong plastic product | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strong plastic product | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com