Method for creating finite element three-dimensional entity based on terrain remote sensing data
A technology for remote sensing data and three-dimensional entities, which is applied in image data processing, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., and can solve problems such as distortion and deviation of numerical simulation results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0023] Operating environment: Linux
[0024] Software support: FWTools, GMT, Cubit
[0025] Scripts: convert.pl, block_DEM.py
[0026] Data source: from http: / / srtm.csi.cgiar.org Download the terrain remote sensing data package srtm_12_03.zip and decompress it. The range of latitude and longitude is Latitude min: 45 N max: 50 N, Longitude min: 125 W max: 120 W.
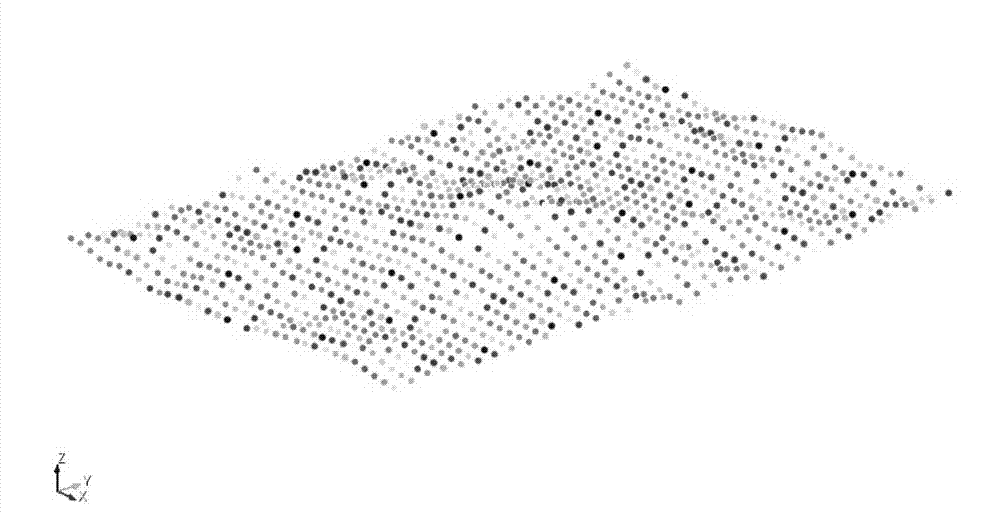
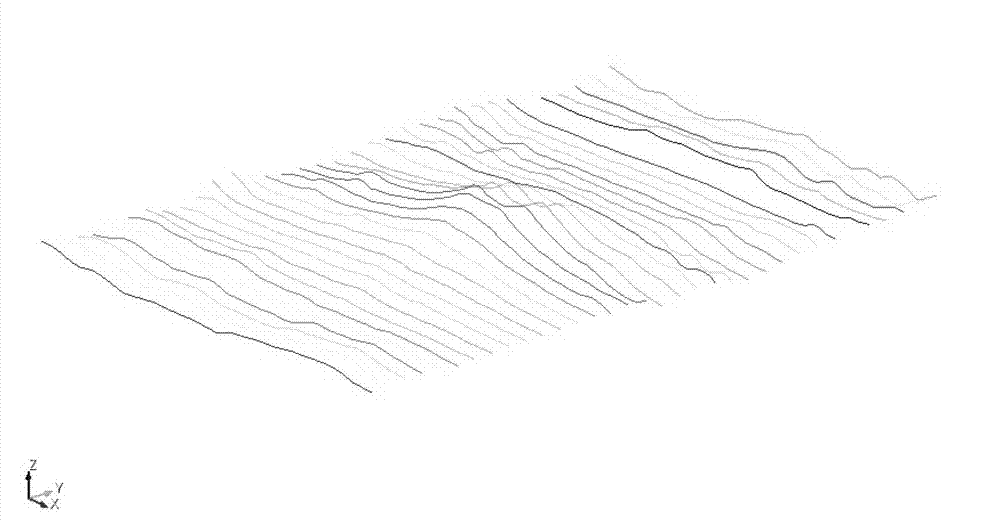
[0027] 1. Use the FWTools-2.0.6 software package to extract vector data from the terrain remote sensing data package, that is, to extract the text format vector data from the remote sensing image Geotiff format, and the obtained data file contains latitude, longitude and elevation information.
[0028] Specific operation: run in the linux terminal
[0029] FWTools-2.0.6 / bin_safe / gdal2xyz.py srtm_12_03.img > srtm_12_03.xyz
[0030] Suppose the research area is Latitude min: 46.1 N max: 46.3 N Longitude min: 122.1 W max: 122.3. You need to use the GTM software package to extract from Latitude min: 45 N max: 50 N Lo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com