Sludge-type soil combined secondary dike-back pressure diking method
A technology of silt and sub-dykes, applied in construction, water conservancy projects, marine engineering and other directions, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of dam projects, restricting the construction progress of dam projects, and rising unit prices, and achieves high construction efficiency, fast construction speed, and construction cost. low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Embodiment 1, the embankment method of silty soil on both sides combined with sub-dike back pressure:
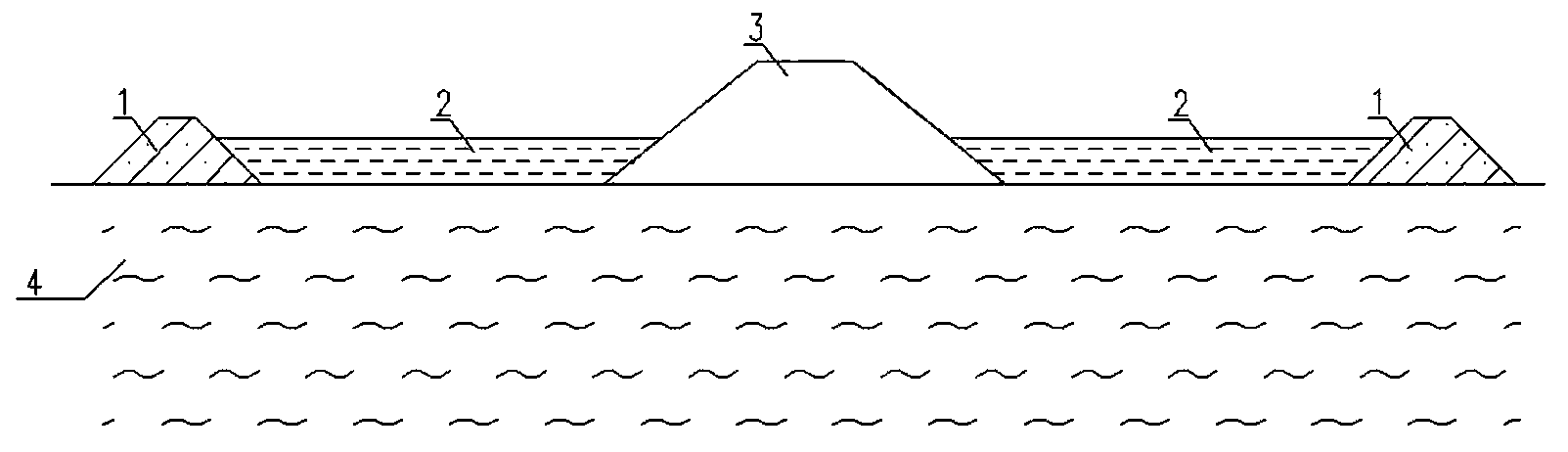
[0018] see figure 1 , sub-dikes 1 are arranged on both sides inside and outside the main dike 3 of the dam, and the distance between the main dike 3 and the sub-dikes 1 is generally 3 to 6 times the height of the main dike 3 . Between the main embankment 3 and the sub-dike 1, set up the silt soil counterpressure embankment core 2, whose top elevation does not exceed the top elevation of the sub-dike 1, and the sub-dike 1 top elevation is generally higher than the silt soil backpressure embankment core 2 top elevation 0~0.5m. The heights of the sub-dike 1 and the silty soil counterpressure embankment core 2 are generally not less than 1 / 3 of the height of the main dike 3 and not greater than 2 / 3 of the height of the main dike 3 . The silty soil backpressure embankment core is formed by dredging or backfilling, and the sub-dike 1 and the silty soil backpressure embank...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment two, the embankment method of one side silty soil combined sub-dike back pressure:
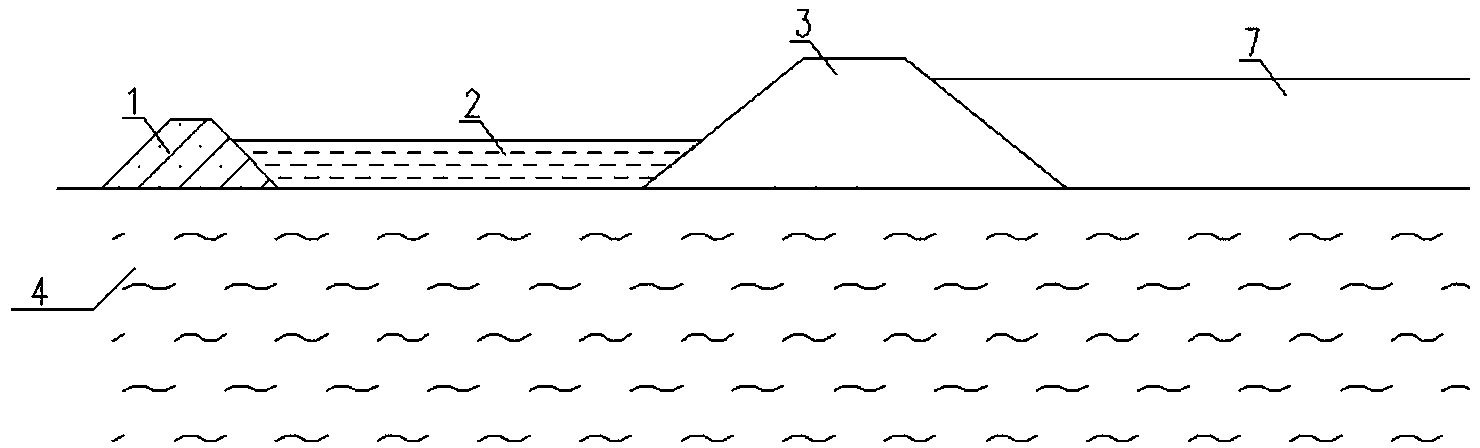
[0022] see figure 2 , a sub-dyke 1 of a certain height is set at a certain distance on one side of the main dyke 3 of the dam, and a silty soil backpressure embankment core 2, sub-dyke 1 and silty soil backpressure dyke are set between the main dyke 3 and the sub-dyke 1 The core 2 is combined to form a back pressure structure, which forms a back pressure on one side of the main embankment 3. On the other side of the main dike 3 of the dam, the dredging fill 7 is used as a back pressure structure to form a back pressure on the other side of the main dike 3 . All the other are the same as embodiment one.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Embodiment three, the embankment method of two-stage silty soil combined with two-stage sub-dyke back pressure:
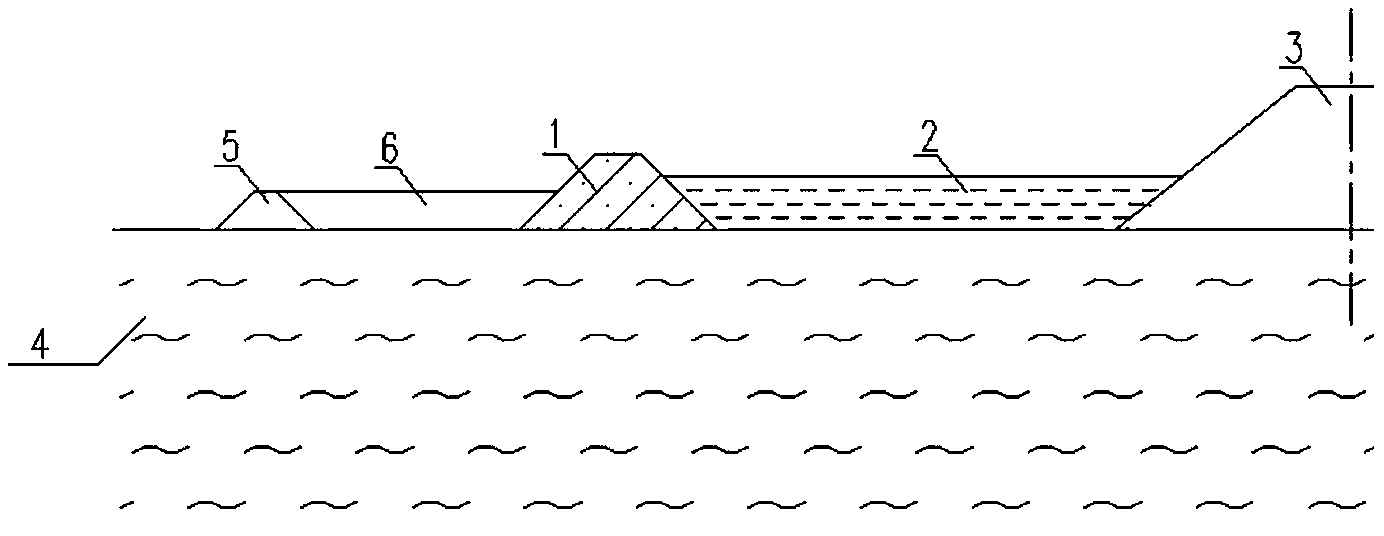
[0024] see image 3 , when the height of the main embankment 3 is relatively high or the soft soil foundation 4 is very weak, the two-stage backpressure structure formed by combining the two-stage sub-dike and the two-stage silt soil backpressure embankment core is used to improve the stability of the main embankment 3: in the sub-dike A second-level sub-dike 5 is set at a certain distance from the back main dike 3 side of the dike 1, and a second-level silty soil backpressure dike core 6 is set between the sub-dike 1 and the second-level sub-dike 5, and the second-level sub-dike 5 and the second-level backpressure structure formed by the combination of the second-level silty soil backpressure embankment core 6, thereby forming a two-level backpressure structure formed by the combination of two-level sub-dikes and two-level silt soil backpressure embankment ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com