Crosslinking agent composition, anti-fibrillation solution spun cellulose fiber and method for their preparation
A technology of cellulose fiber and cross-linking agent, applied in the field of fiber processing, can solve the problem of easy fibrillation of solution-spun cellulose fibers, and achieve the effect of improving the fibrillation performance of fiber antigens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
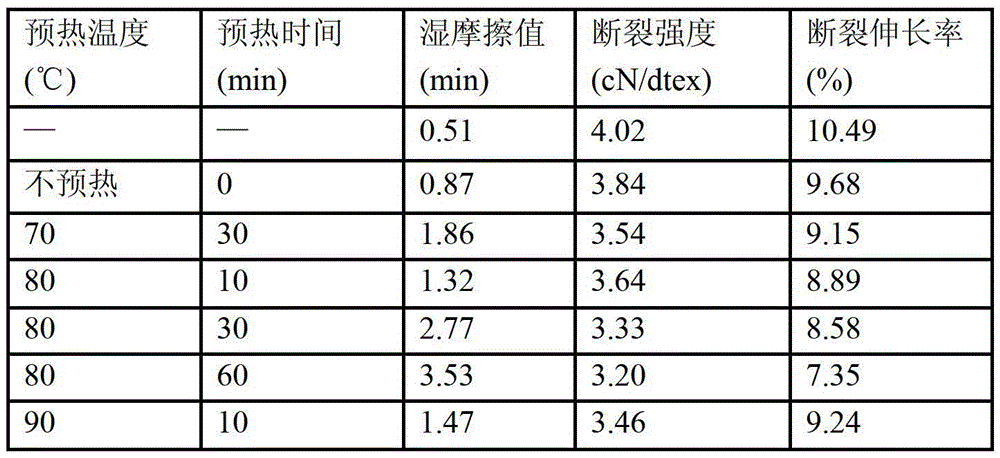
[0056] Dissolve PMA, CA and SHP with a molecular weight of 600 in distilled water at a weight ratio of 2:5:3 at room temperature to obtain a cross-linking agent solution. The content of PMA in the cross-linking agent solution is 40g / L and the content of CA is 100g / L, SHP content is 60g / L. The cellulose fiber is immersed in the above-mentioned crosslinking agent solution for 10 minutes to obtain a mixed fiber. The mixed fiber is preheated, and the preheating temperature is controlled to 70, 80, and 90 ℃ respectively, and then the mixed fiber is heated at 170 ℃ for 8 minutes. Wash and dry. The wet friction value and mechanical properties of the obtained fiber are listed in Table 1.
[0057] Table 1
[0058]
[0059] It can be seen from the content in Table 1 that the post-crosslinking treatment of cellulose fibers using the crosslinking agent composition provided by the present invention can effectively improve the antigenic fibrillation properties of the fibers. Especially in th...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Dissolve PMA, CA and SHP with a molecular weight of 600 in distilled water at a weight ratio of 2:5:3 at room temperature to obtain a cross-linking agent solution. The content of PMA in the cross-linking agent solution is 40g / L and the content of CA is 100g / L, SHP content is 60g / L. The cellulose fiber is immersed in the above crosslinking agent solution for 10 minutes, and then the fiber is preheated at 80°C for 60 minutes, and then the fiber is heated at 160°C, 170°C, 180°C, and 190°C for a certain period of time. Wash and dry. The wet friction values and mechanical properties of the obtained fiber bundles are listed in Table 2.
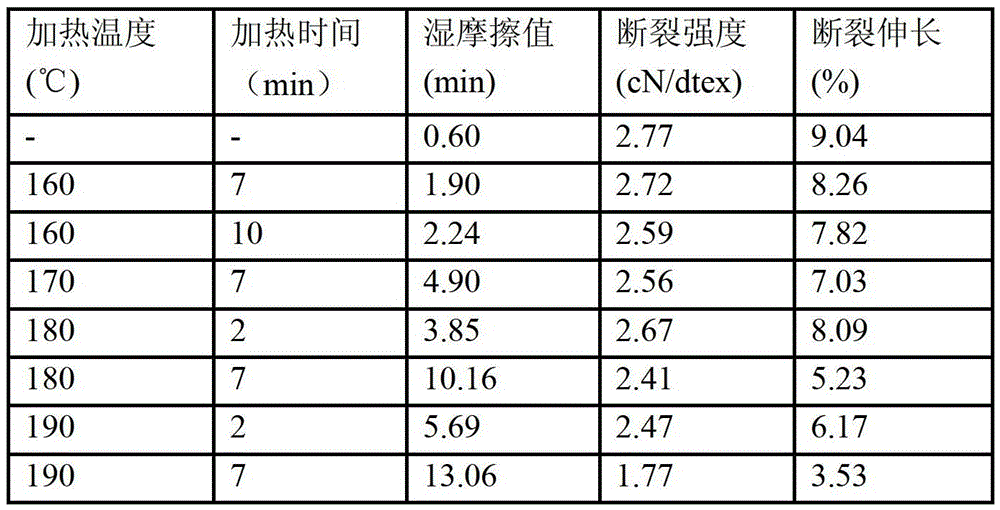
[0062] Table 2
[0063]
[0064] It can be seen from Table 2 that under other conditions, the increase in heating time and temperature in the post-treatment of cellulose fibers using the crosslinking agent composition provided by the present invention is beneficial to improve the wet friction of the fibers. The increase in temperature has a ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Dissolve the oligomeric polybasic acid with a molecular weight of 600, CA and SHP in distilled water at room temperature to obtain a crosslinking agent solution. The content of the oligomeric polybasic acid in the crosslinking agent solution is 5-60g / L and the CA content is 100g / L, SHP content is 60g / L. The cellulose fiber is immersed in the above-mentioned crosslinking agent solution for 10 minutes to obtain a mixed fiber, and then the mixed fiber is preheated at 80°C for 60 minutes, and then the fiber is heated at 170°C for 8 minutes, washed, and dried. The obtained fiber wet friction value, mechanical properties and fixed amount of chemical agent on the fiber are listed in Table 3.
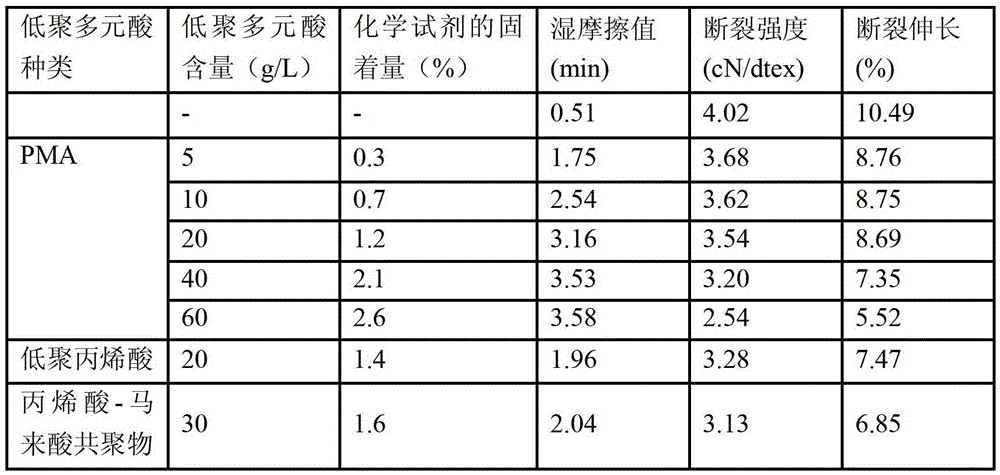
[0069] table 3
[0070]
[0071] It can be seen from Table 3 that in the crosslinking agent composition of the present invention, the content of PMA has a significant effect on the fibrillation performance of the fiber antigen. The higher the content of PMA, the higher the fiber wet fricti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com