Method for separating sodium and magnesium from laterite-nickel ore smelting primary wastewater
A technology of laterite nickel ore and laterite ore, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, magnesium sulfate, alkali metal sulfite/sulfite, etc., can solve the problems of waste water utilization, etc., and achieve easy industrialization, increased economy, and easy operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
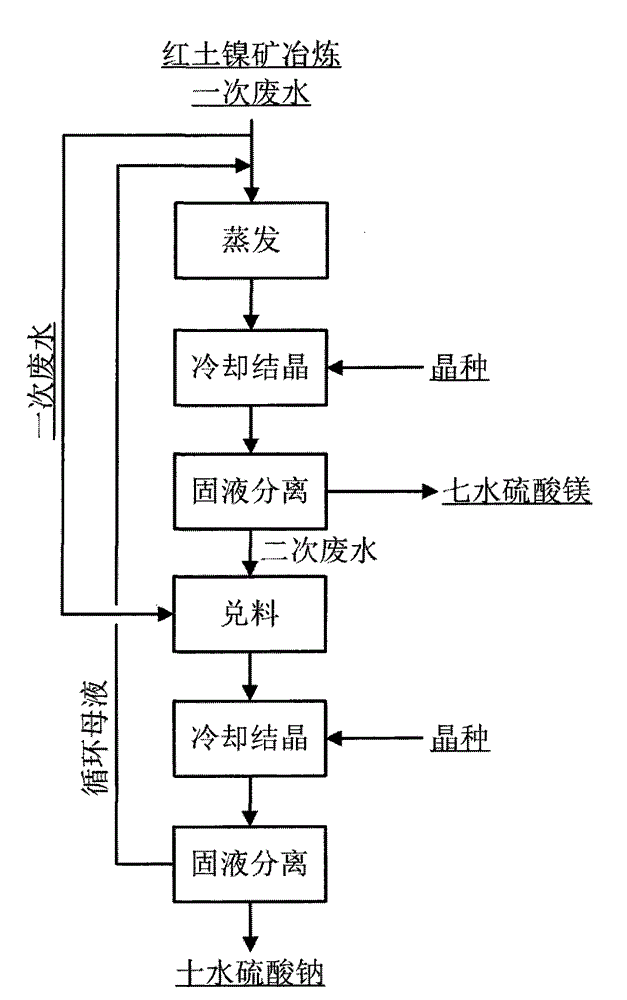
[0021] For the specific process flow of this embodiment, please refer to figure 1 .
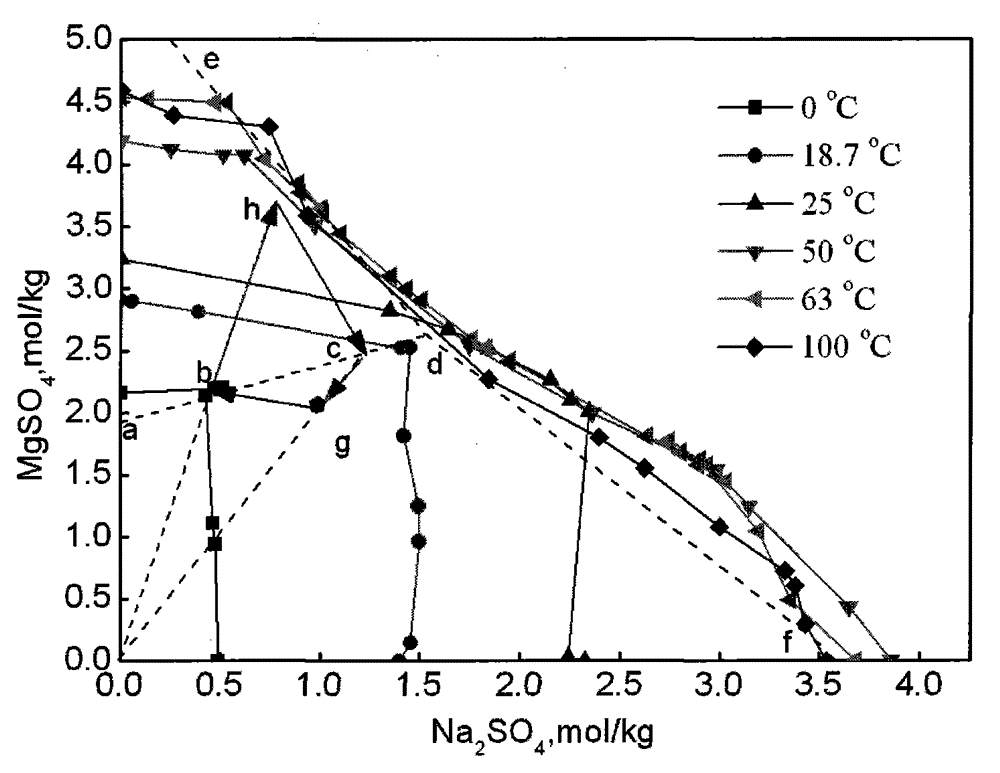
[0022] For a better description of this embodiment, figure 2 The process schematic diagram of this embodiment is given in . The raw waste water used in this example is the primary waste water produced in the hydrometallurgical smelting process of laterite nickel ore. The solution does not contain other cations except sodium and magnesium ions. The concentration of magnesium ions in the solution is 0.6mol / L, and the sodium ions are 0.15mol / L. Put 1000mL of primary waste water into the evaporator, and evaporate the solution in the boiling state until the concentration of magnesium ions reaches 3.5mol / L to obtain the mother liquor I. At this time, the corresponding solution composition point is figure 2 Middle h point; mother liquor I is transferred to the magnesium sulfate heptahydrate crystallization kettle, and it is cooled to 15 ℃, at this moment, the magnesium sulfate heptahydrate crys...
Embodiment 2
[0024] For the specific process flow of this embodiment, please refer to figure 1 .
[0025] The raw waste water used in this example is the primary waste water produced in the hydrometallurgical smelting process of laterite nickel ore. The solution does not contain other cations except sodium and magnesium ions. The concentration of magnesium ions in the solution is 2mol / L, and the concentration of sodium ions is 0.6 mol / L. Put 500mL of primary waste water into the evaporator, and evaporate the solution until the concentration of magnesium ions reaches 3mol / L in a boiling state; Add magnesium sulfate heptahydrate seed crystals to the magnesium sulfate heptahydrate crystallization kettle in an amount of 3 g / L, and continue to crystallize for 20 minutes while stirring to obtain slurry I; after filtering slurry I, the solid is dried to obtain heptahydrate with a purity of 95%. Magnesium sulfate 98g, the filtered mother liquor is the secondary waste water; add 10mL of primary w...
Embodiment 3
[0027] For the specific process flow of this embodiment, please refer to figure 1 .
[0028] The raw waste water used in this example is the primary waste water produced during the laterite nickel ore hydrometallurgical smelting process. The solution does not contain other cations except sodium and magnesium ions. The concentration of magnesium ions in the solution is 1mol / L, and the concentration of sodium ions is 0.3 mol / L. Put 1000mL of primary waste water into the evaporator, and evaporate the solution until the concentration of magnesium ions reaches 3mol / L under boiling state; Add magnesium sulfate heptahydrate seed crystals to the magnesium sulfate heptahydrate crystallization kettle in an amount of 2 g / L, and continue to crystallize for 90 minutes while stirring to obtain slurry I; after filtering slurry I, the solid is dried to obtain heptahydrate with a purity of 90%. Magnesium sulfate 100g, the filtered mother liquor is the secondary waste water; add 30mL of prima...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com