Laser direct ablation with picosecond laser pulses at high pulse repetition frequencies
一种脉冲重复频率、激光直接的技术,应用在激光焊接设备、焊接设备、焊接/焊接/切割物品等方向,能够解决增大图案密度、影响产能等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] I. Overview
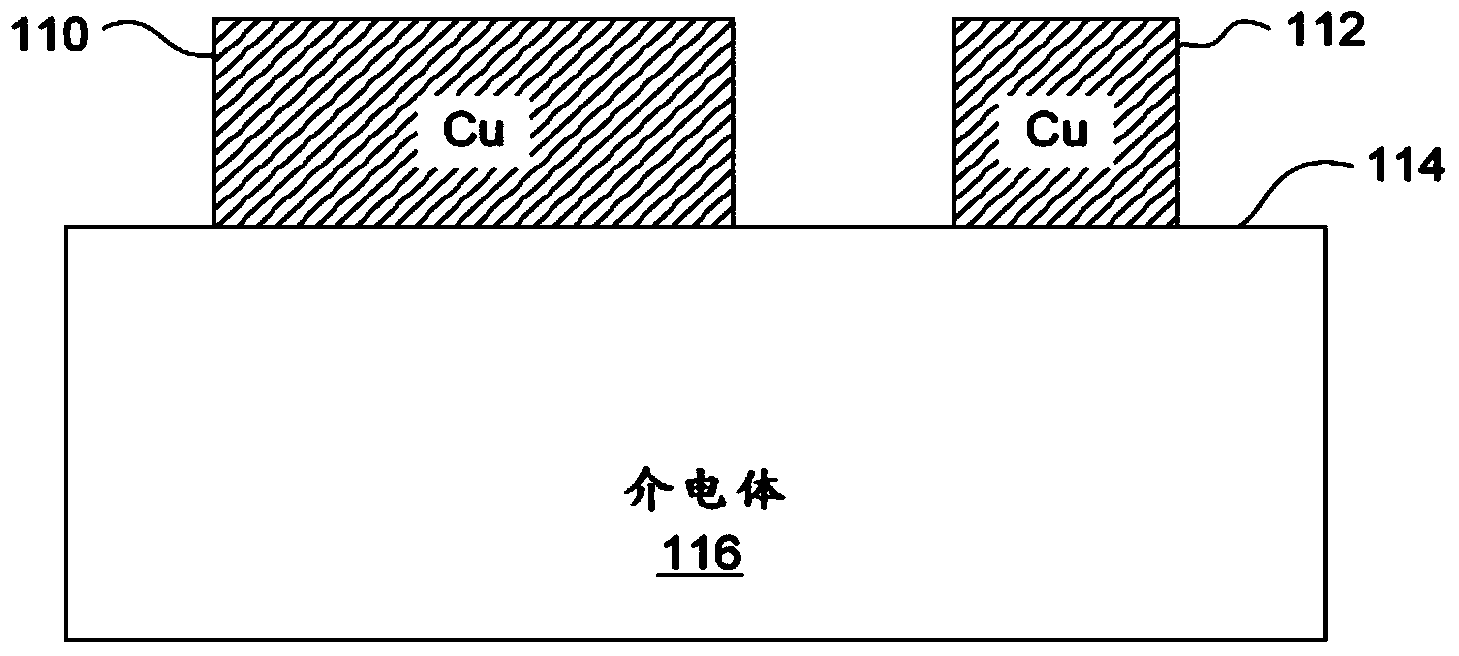
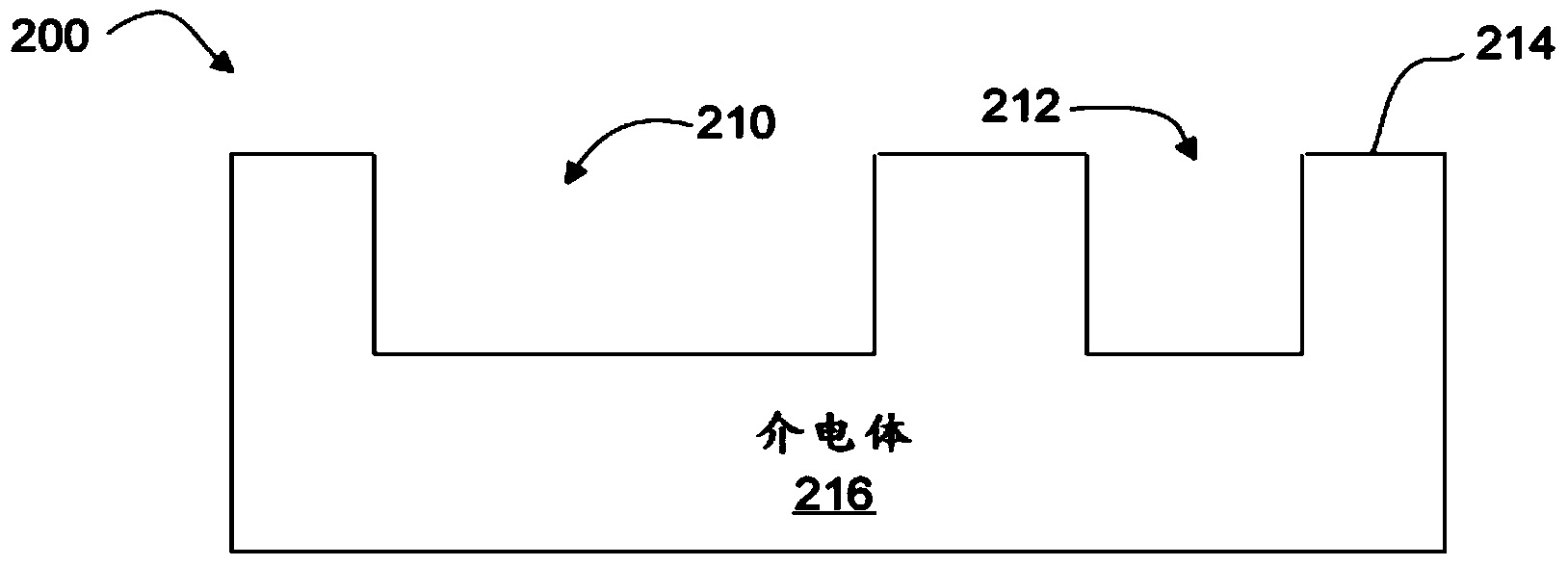
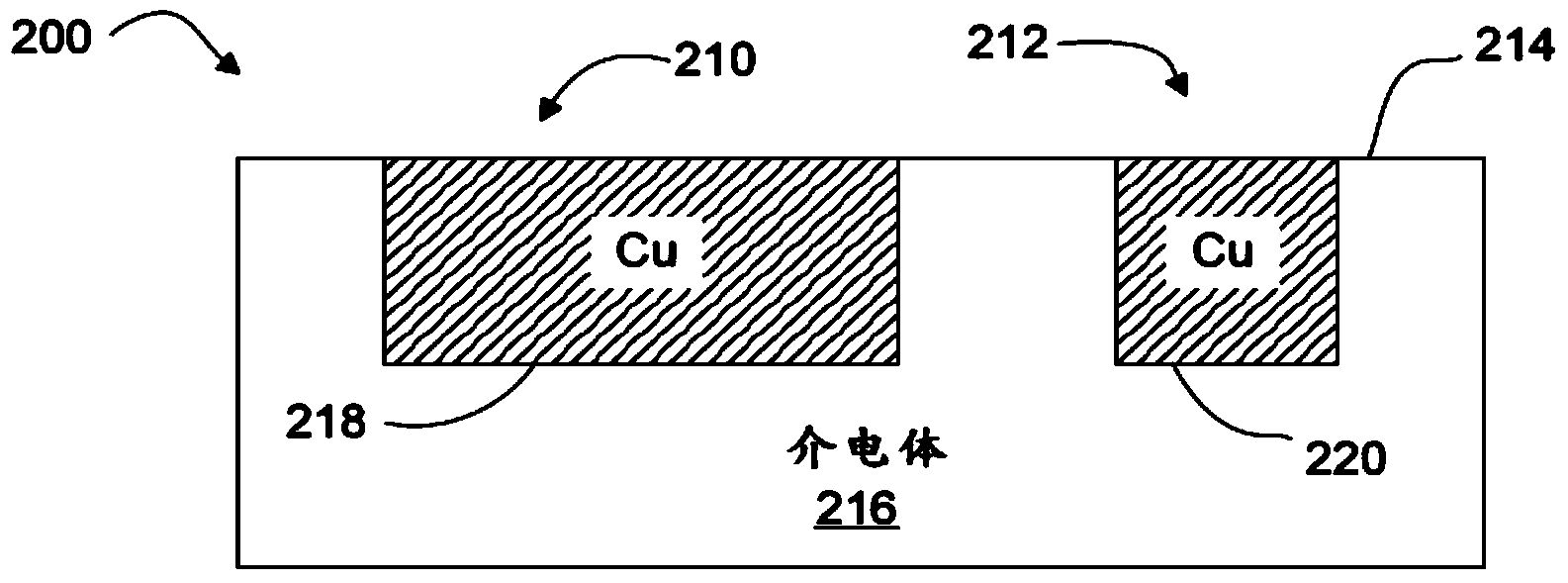
[0024] Systems and methods provide high throughput processing with high throughput (eg, using vector scanning methods) in laser direct ablation (LDA) applications. High-speed beam positioning and high pulse repetition frequency (PRF) provide sufficient continuous laser pulse overlap to control the uniformity and character of kerf cuts in dielectric materials. Known electroplating processes can then be used to form electrical paths in the cutouts with desired signal propagation characteristics (eg, impedance, resistance, and capacitance).
[0025] In certain embodiments, a high-speed beam positioning scheme is used in conjunction with a mode-locked laser. With the development of beam positioning technology, the pulse repetition rate of the laser source becomes the limiting factor. For example, the erosion size (one laser spot and The distance between one laser spot) is 10 μm or more. Therefore, in this example, there is no pulse overlap, and the laser b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com