Solid state disk (SSD) and space management method thereof
A solid-state hard disk and space management technology, applied in the direction of memory address/allocation/relocation, etc., can solve the problems of low utilization rate of Flash resources, short service life of SSD, failure of the whole SSD, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
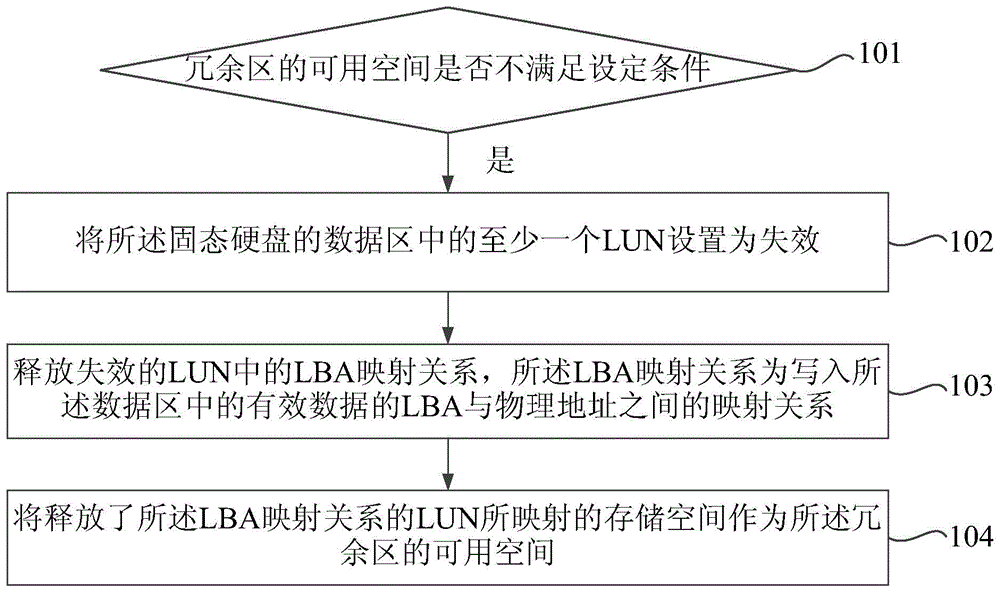
[0047] Figure 1a It is a flow chart of the solid-state hard disk space management method in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, such as Figure 1a As shown, the solid-state hard disk space management method may include:
[0048] Step 101, judging whether the available space of the redundant area of the solid state disk satisfies a set condition.
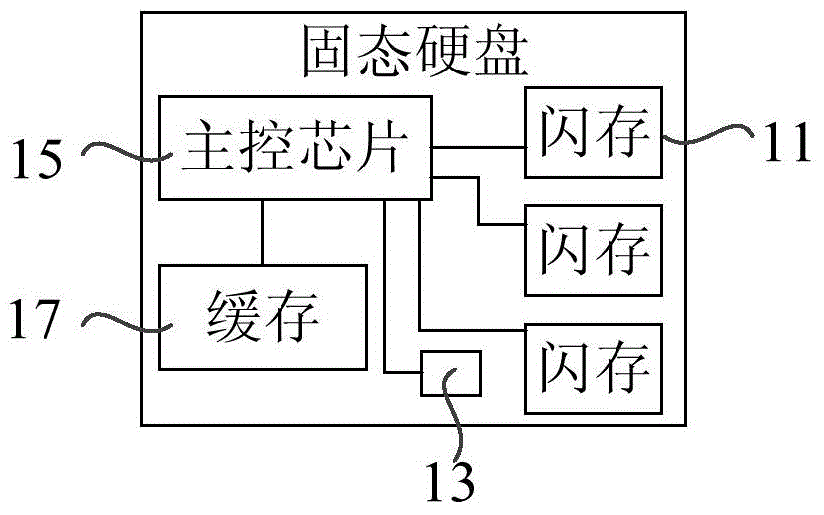
[0049] specifically, Figure 1b It is a schematic structural diagram of SSD in the solid-state hard disk space management method in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, as Figure 1bAs shown, a solid state disk (SSD) mainly includes a storage space composed of multiple flash memories (Flash) 11 , a main control chip 15 and a cache 17 . Among them, the storage space composed of flash memory (Flash) 11 can realize the functions of system area, data area and redundant area, and the main control chip 15 can control and execute corresponding control commands to control various SSD functions such as data writing and garbage collec...
Embodiment 2
[0060] figure 2 It is a flow chart of the solid-state hard disk space management method in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, figure 2 and Figure 1a Steps with the same numbers have the same functions, and for the sake of brevity, detailed descriptions of these steps are omitted.
[0061] The main difference from the previous embodiment is that step 102 may specifically include the following steps:
[0062] Step 201, look up the LUN heat table of the system area of the solid-state hard disk, determine the LUN with the lowest access heat in the LUN heat table as the designated LUN, and the access heat is accessed by all the LUNs of the solid-state hard disk within a certain period The frequency is determined; the lower the access heat, the smaller the impact of the LUN failure on the overall storage performance of the SSD.
[0063] Step 202, setting the state of the specified LUN as invalid in the LUN list of the system area;
[0064] Step 203, delete the LBA mappin...
Embodiment 3
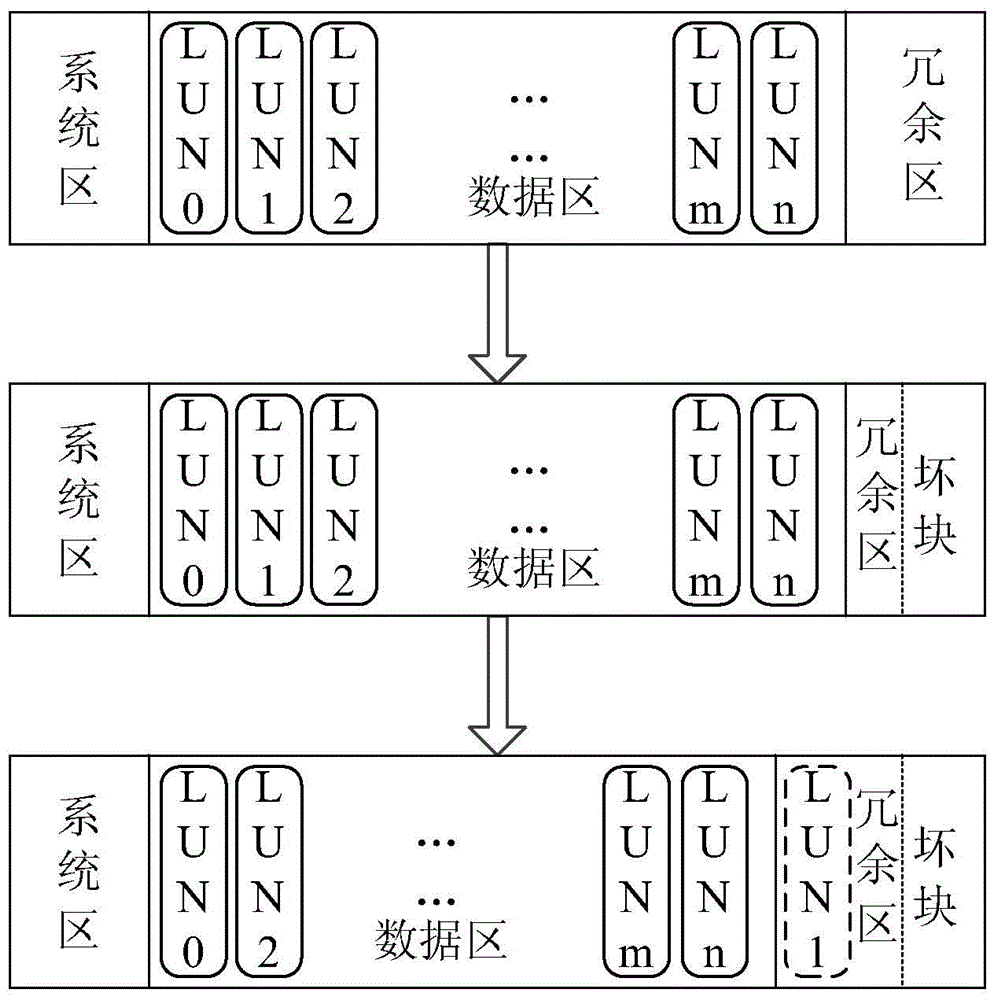
[0077] image 3 It is a structural block diagram of a solid-state hard disk in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, such as image 3 As shown, the SSD can include:
[0078] A judging module 31, configured to judge whether the available space in the redundant area satisfies the set condition;
[0079]A failure control module 33, configured to set at least one logical unit number LUN in the data area as invalid when the available space in the redundant area does not meet the set condition;
[0080] The release control module 35 is used to release the logical block address LBA mapping relationship in the failed LUN, and the LBA mapping relationship is the mapping relationship between the LBA of the valid data written in the data area and the physical address;
[0081] The space control module 37 is configured to release the storage space mapped by the LBA mapping relationship LUN as the available space of the redundant area.
[0082] Among them, see Figure 1b , the solid s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com