Method for roasting high-temperature drought premature tobacco leaves
A curing method and technology of tobacco leaves, applied in the fields of tobacco, tobacco preparation, application, etc., can solve the problems of tobacco malnutrition, difficulty in dehydration, large loss, etc., and achieve the goal of improving the quality of tobacco leaf curing, reducing the loss of curing, and reducing the proportion Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
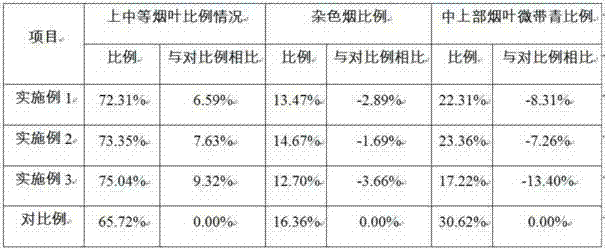
Embodiment 1
[0022] In the early stage of yellowing: after the tobacco leaves are loaded into the furnace and ignited, the temperature rises rapidly, and the dry bulb temperature is raised to 32°C at a heating rate of 2-3°C / h, and the wet bulb temperature is controlled at 32°C, and the temperature is stabilized for 4 hours; after that, the temperature is raised at a rate of 1°C / h Speed up the dry bulb temperature to 35°C, keep the wet bulb temperature at 32°C, and stabilize the temperature for 2 hours. This stage is mainly moisturizing and yellowing. The tobacco leaves are heated and sweat, and the tip of the leaf becomes soft. The tobacco leaves in the high temperature layer germinate and turn yellow, and 1 / 3 of the tip of the leaf turns yellow.
[0023] Mid-yellowing stage: raise the dry bulb temperature to 37°C and the wet bulb temperature to 32°C at a heating rate of 1°C / h, and keep the temperature stable for 12 hours; then keep the dry bulb temperature at 38°C and the wet bulb temper...
Embodiment 2
[0031] In the early stage of yellowing: after the tobacco leaves are loaded into the furnace and ignited, the temperature rises rapidly, and the dry bulb temperature is raised to 34°C at a heating rate of 2-3°C / h, and the wet bulb temperature is 32°C, and the temperature is stabilized for 4 hours; after that, the temperature is raised at a heating rate of 1°C / h The dry bulb temperature rose to 36°C, the wet bulb temperature was maintained at 32°C, and the temperature was stabilized for 2 hours. This stage is mainly moisturizing and yellowing. The tobacco leaves are heated and sweat, and the tip of the leaf becomes soft. The tobacco leaves in the high temperature layer germinate and turn yellow, and 1 / 3 of the tip of the leaf turns yellow.
[0032] Mid-yellowing stage: raise the dry bulb temperature to 37.5°C and the wet bulb temperature to 32°C at a heating rate of 1°C / h, and keep the temperature stable for 8 hours; then keep the dry bulb temperature at 38°C and the wet bulb te...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Early stage of yellowing: Tobacco leaves heat up rapidly after the furnace is ignited, and the dry bulb temperature is raised to 32°C at a heating rate of 2-3°C / h, and the wet bulb temperature is 32°C, and the temperature is stabilized for 2 hours; then the temperature is raised at a heating rate of 1°C / h Raise the dry bulb temperature to 34°C, wet bulb temperature to 32°C, and stabilize the temperature for 2 hours; then raise the dry bulb temperature to 36°C at a heating rate of 1°C / h, keep the wet bulb temperature at 32°C, and stabilize the temperature for 2 hours. This stage is mainly moisturizing and yellowing. The tobacco leaves are heated and sweat, and the tip of the leaf becomes soft. The tobacco leaves in the high temperature layer germinate and turn yellow, and 1 / 3 of the tip of the leaf turns yellow.
[0041] Mid-yellowing stage: raise the dry bulb temperature to 38°C and the wet bulb temperature to 32°C at a heating rate of 1°C / h, and keep the temperature sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com