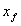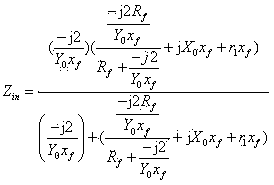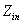Pi-type equivalent circuit based direct current earth electrode line fault location method
A distance measurement method and equivalent circuit technology, which can be applied in directions such as fault locations, can solve problems such as accurate location of ground electrode line faults, and achieve the effect of simplified calculation and easy on-site implementation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: A method for fault location of a DC grounding electrode line based on a π-type equivalent circuit, 800kV DC grounding line such as figure 2 shown. The line parameters are as follows: the total length of the line is 80km, the line impedance is: 0.0231+j0.001273237Ω / km, and the pole resistance is 0.2Ω. The data sampling rate is 6.4kHz. Ground electrode line l 2 A ground fault occurs 3km away from the measuring end, and the transition resistance is 0.2Ω. The line from the fault point to the measurement end is equivalent to a π-type equivalent circuit, and the equivalent input impedance is calculated by using the single-ended voltage and current. According to the input impedance equal to the equivalent impedance of the line from the fault point to the measurement end, the fault location function is determined. The fault distance is calculated by solving the fault location function.
[0028] The specific steps of the ranging method are as follows:
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: A method for fault location of DC grounding electrode lines based on π-type equivalent circuits, 800kV DC grounding line such as figure 2 shown. The line parameters are as follows: the total length of the line is 80km, the line impedance is: 0.0231+j0.001273237Ω / km, and the pole resistance is 0.2Ω. The data sampling rate is 6.4kHz. Ground electrode line l 2 A ground fault occurs 30km away from the measuring end, and the transition resistance is 4Ω. The line from the fault point to the measurement end is equivalent to a π-type equivalent circuit, and the equivalent input impedance is calculated by using the single-ended voltage and current. According to the input impedance equal to the equivalent impedance of the line from the fault point to the measurement end, the fault location function is determined. The fault distance is calculated by solving the fault location function.
[0040] The specific steps of the ranging method are as follows:
[0041]...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: A method for fault location of a DC grounding electrode line based on a π-type equivalent circuit, 800kV DC grounding line such as figure 2 shown. The line parameters are as follows: the total length of the line is 80km, the line impedance is: 0.0231+j0.001273237Ω / km, and the pole resistance is 0.2Ω. The data sampling rate is 6.4kHz. Ground electrode line l 2 A ground fault occurs 50km away from the measuring end, and the transition resistance is 20Ω. The line from the fault point to the measurement end is equivalent to a π-type equivalent circuit, and the equivalent input impedance is calculated by using the single-ended voltage and current. According to the input impedance equal to the equivalent impedance of the line from the fault point to the measurement end, the fault location function is determined. The fault distance is calculated by solving the fault location function.
[0052] The specific steps of the ranging method are as follows:
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Full length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com