Axial Cutting Force Prediction Method for Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Grinding of Brittle Materials
A technology of cutting force prediction and ultrasonic vibration, which is applied to the control of parts of grinding machine tools, grinding/polishing equipment, and workpiece feed movement, and can solve problems such as not being able to reflect processing conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
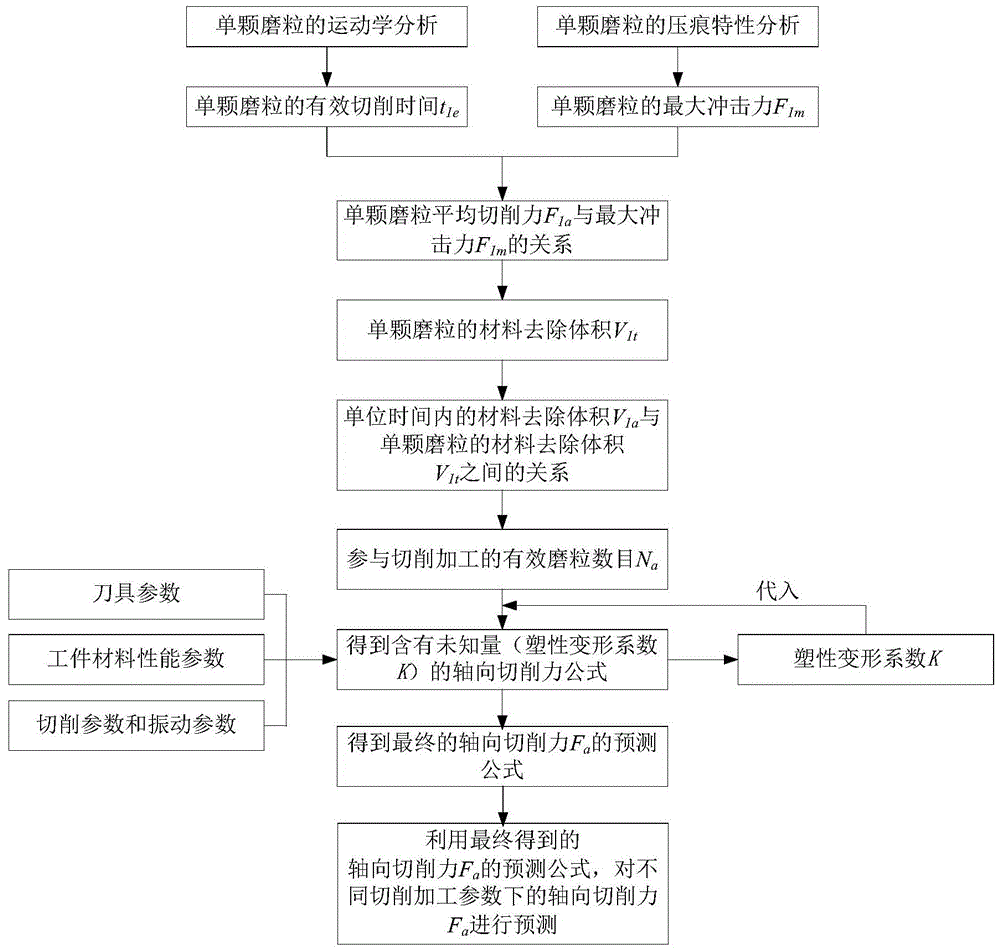
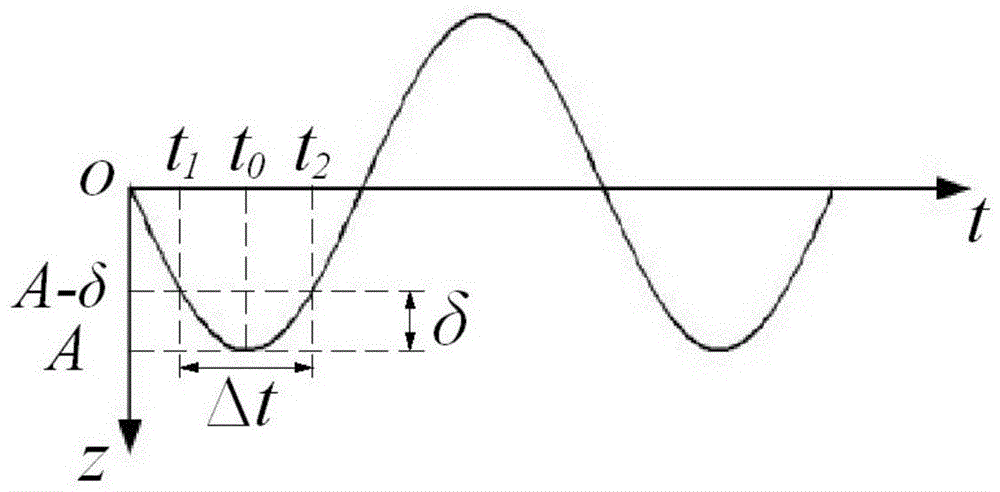
[0045] In order to better understand the technical content of the present invention, specific embodiments are given together with the attached drawings for description as follows.
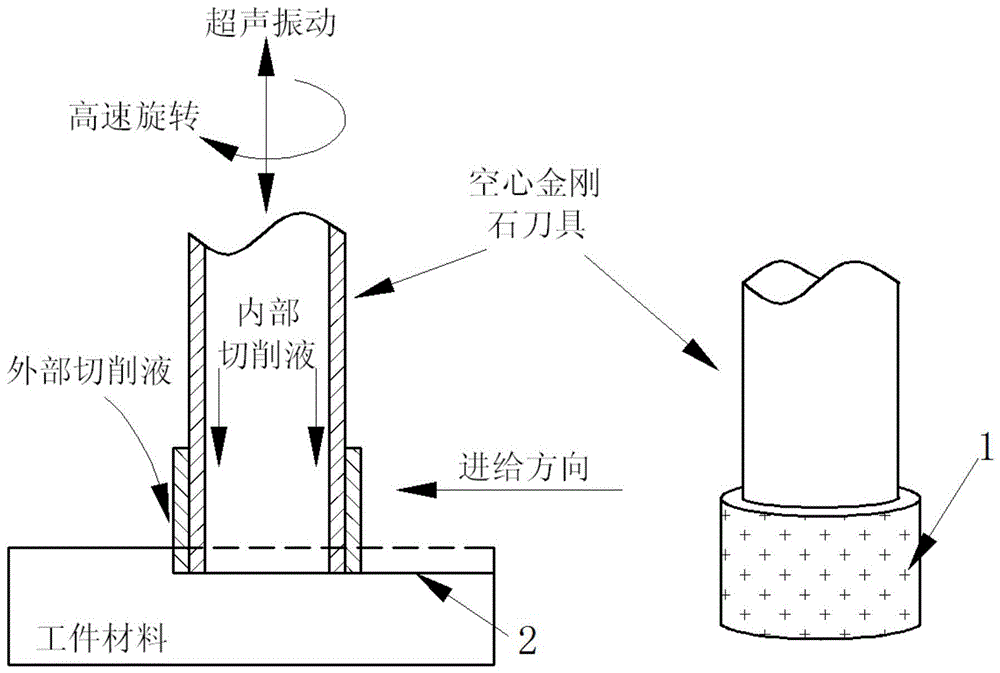
[0046] The axial cutting force prediction method for ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding of brittle materials of the present invention is suitable for ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding of brittle materials such as ceramics and glass. In this embodiment, the ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding of zirconia ceramics is used as For example, its processing form is as figure 2 As shown, the tool used is a hollow tool with diamond abrasive grains, the tool rotates with the spindle and vibrates at an axial ultrasonic frequency, and the tool performs a feed motion. In the figure, the number 1 indicates diamond abrasive grains, and the number 2 indicates the machined surface of the workpiece material. The specific parameters of diamond abrasive grain tools, the main performance parameters and vib...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com