Methods of making tissues and organs
A production method and organ technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, tissue regeneration, tissue culture, etc., can solve the problems of not yet clearly established human tissue-organ remodeling method, organ transplant rejection, and non-existing methods, etc. Achieving the effect of high manufacturing technology value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0103] [Example 1] Fabrication of organs using undifferentiated organ cells
[0104] 〔experimental method〕
[0105] 【(1) Production of human liver endoderm cells】
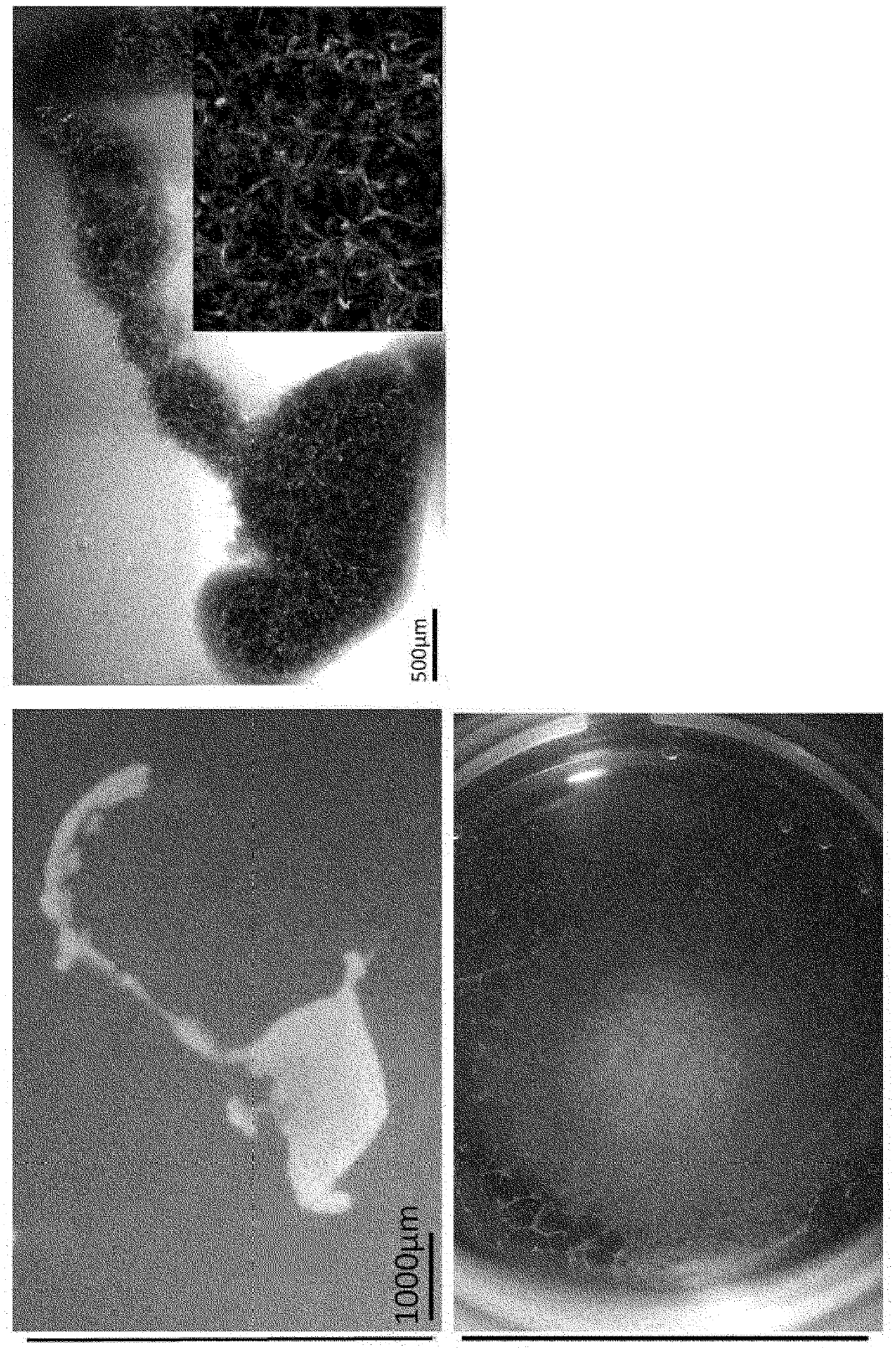
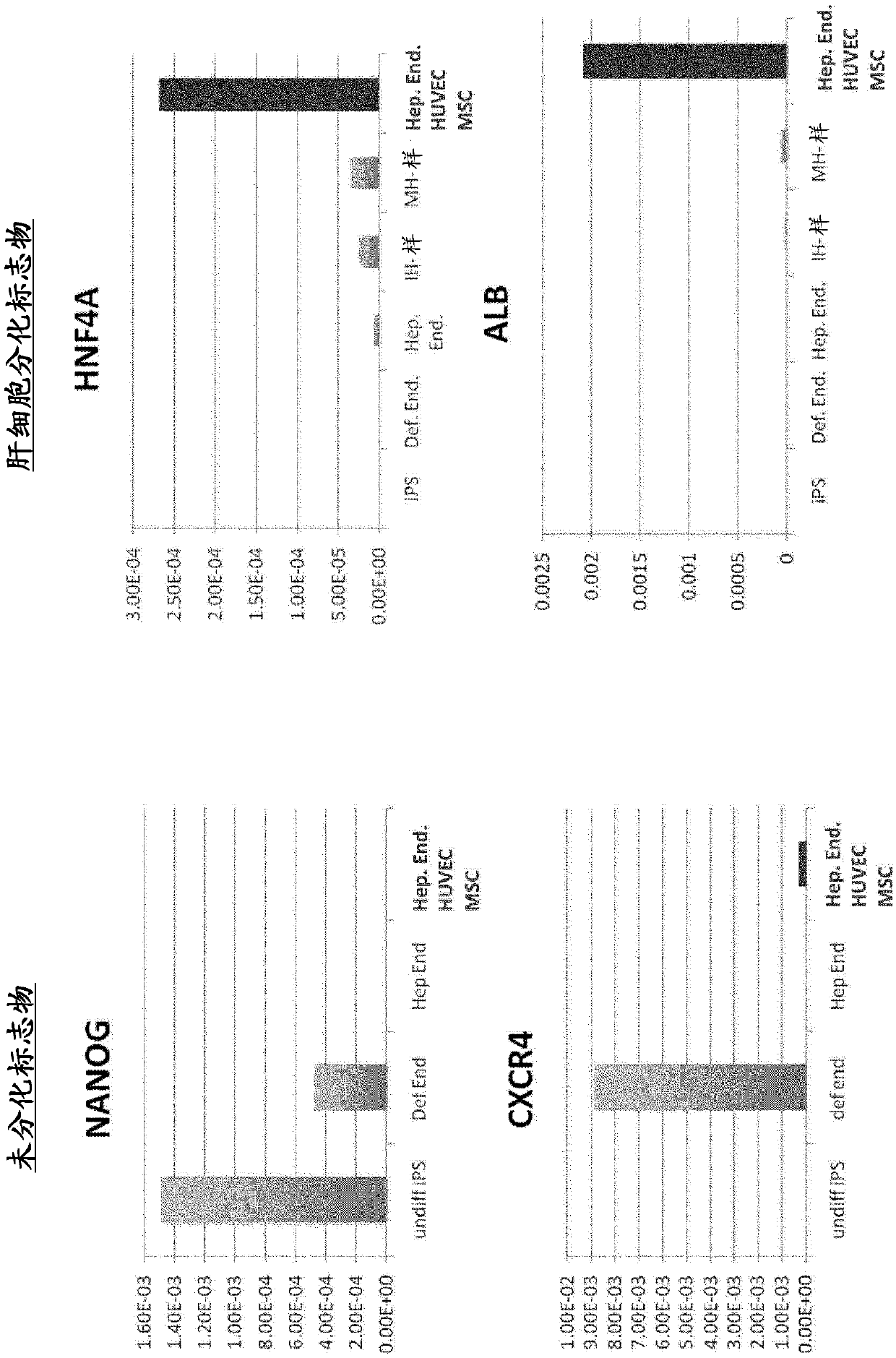
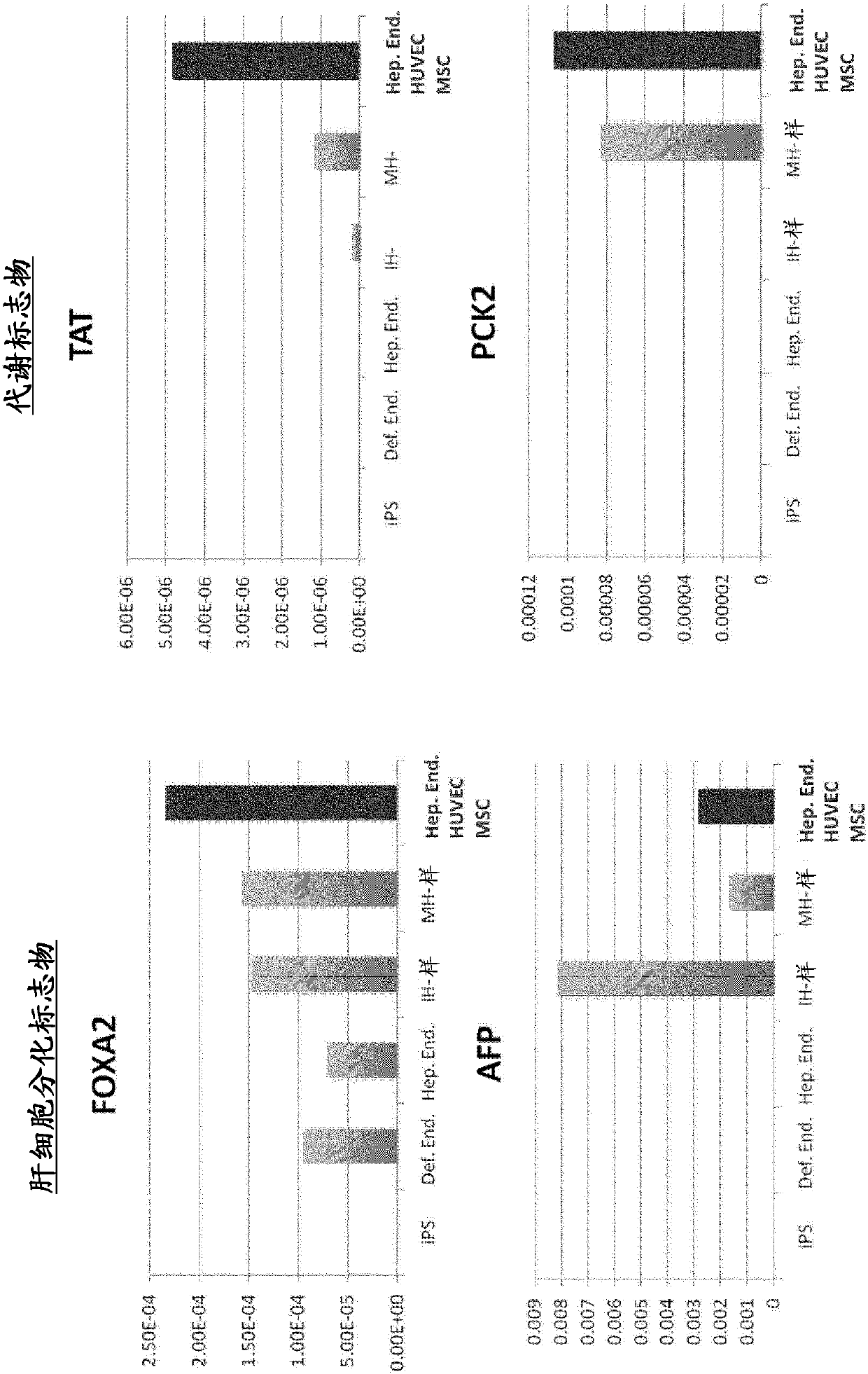
[0106] Human iPS cells (human skin-derived TkDA3hiPSC clone (gifted from Koji Eto and Hiromitsu Nakauchi)) were cultured in a serum-free medium by adding activin to induce CXCR4- and E-cadherin-positive endoderm cells. By adding BMP4 and FGF2 to the obtained endoderm cells and culturing them for 2 days, a CXCR4-negative HNF4α-positive hepatic endoderm group was obtained. The expressions of CXCR4 and HNF4α were confirmed by immunostaining and gene expression analysis according to the description in Hepatology, 51(1), 297-305, 2010.
[0107] 【(2) Production of human liver buds】
[0108] The obtained hepatic endoderm cells were combined with vascular endothelial cells (human umbilical cord blood-derived venous endothelial cells) (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells (human mesenchymal s...
Embodiment 2
[0122] [Example 2] Fabrication of organs using differentiated organ cells
[0123] 〔experimental method〕
[0124] Mix pancreatic beta cell line (MIN6) with vascular endothelial cells (human umbilical cord blood-derived venous endothelial cells) and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells (human mesenchymal stem cells) at a ratio of 5:5-10:2 for co-culture . For the pancreatic β-cell line (KO) and vascular endothelial cells (EGFP), cells labeled with each fluorescent marker were used. For co-cultivation, the cell suspension was inoculated on a culture dish immobilized with matrigel (BD pharmingen) diluted 2 times from the stock solution. In addition, no three-dimensional structure was formed when embedded in matrigel, or in a non-coated or type 1 collagen-coated culture dish. As a culture medium, endothelial cell culture medium kit-2: EGM-2BulletKit (product code CC-3162: Lonza) was used.
[0125] Perform short-term (3-10 days) culture to produce three-dimensional structures. T...
Embodiment 3
[0135] [Example 3] Production of functional vascularized human liver transplanted from artificial pluripotent stem cell-derived organ buds
[0136] Donor organs are significantly scarce for the treatment of end-stage organ failure, using patient-derived artificial pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) 1,2 The need to make organs is increasing. Although multiple papers report functional cell differentiation 3-7 , there is no successful example in the preparation of an organ having a three-dimensional vascular network such as the liver. We have succeeded in generating functional human liver tissue with vascular structures by transplantation of in vitro produced hiPSC-derived liver buds (hiPSC-LBs). In addition to endothelial cells and mesenchymal cells 8Furthermore, iPS cell-derived hepatic endoderm cells self-organized with 3D hiPSC-LBs while promoting organogenesis. As a result of immunostaining and analysis of expressed genes, similarity was confirmed between hiPSC-LBs grown in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com