Method for obtaining retained austenite in ferrite heat resistant steel T91
A retained austenite, T91 technology, applied in the field of high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel production, can solve problems such as applications that cannot be considered and have not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
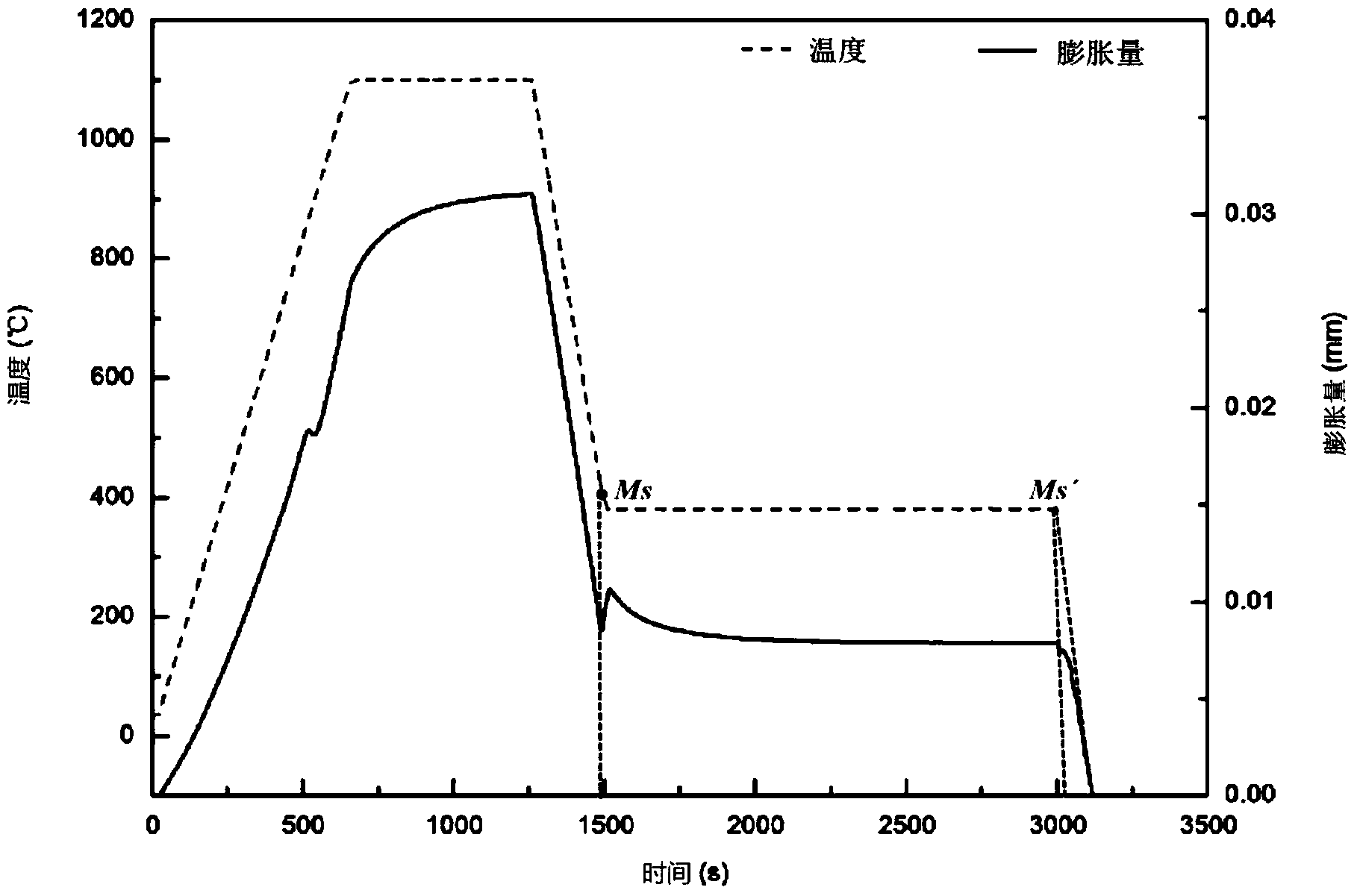
[0022] Process the T91 steel pipe into a cylindrical sample of Φ5×10mm, and perform the following heat treatment on the DIL805A / D linear dilatometer: heat at 4°C / s to 1100°C, keep it for 10 minutes; then continuously cool to room temperature at 3°C / s . Determine the starting temperature of martensitic transformation (M s ) is 406°C, the martensitic transformation end temperature (M f ) to 210°C.
[0023] Take three new Φ5×10mm cylindrical samples of ferritic heat-resistant steel T91, heat them at 4°C / s to 1100°C, and keep them for 10 minutes; then, cool them at 3°C / s to 380°C (210°C≦380 ℃≦406℃), keep warm for 10min, 25min and 45min respectively, and then continue cooling to room temperature at 3℃ / s.
[0024] figure 1 It is the heat treatment process curve and the curve of linear expansion with time in Example 1. It can be seen from the figure that when the sample is cooled from the austenitizing temperature to 406°C, the martensitic transformation begins to occur; When , ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Process the T91 steel pipe into a cylindrical sample of Φ5×10mm, and perform the following heat treatment on the DIL805A / D linear dilatometer: heat at 4°C / s to 1100°C, keep it for 10 minutes; then, continuously cool at 3°C / s to room temperature. According to the obtained linear expansion curve with temperature, the starting temperature (Ms) of martensitic transformation in the continuous cooling process of the above heat treatment of T91 steel is determined to be 406°C, and the end temperature (Mf) of martensitic transformation is 210°C.
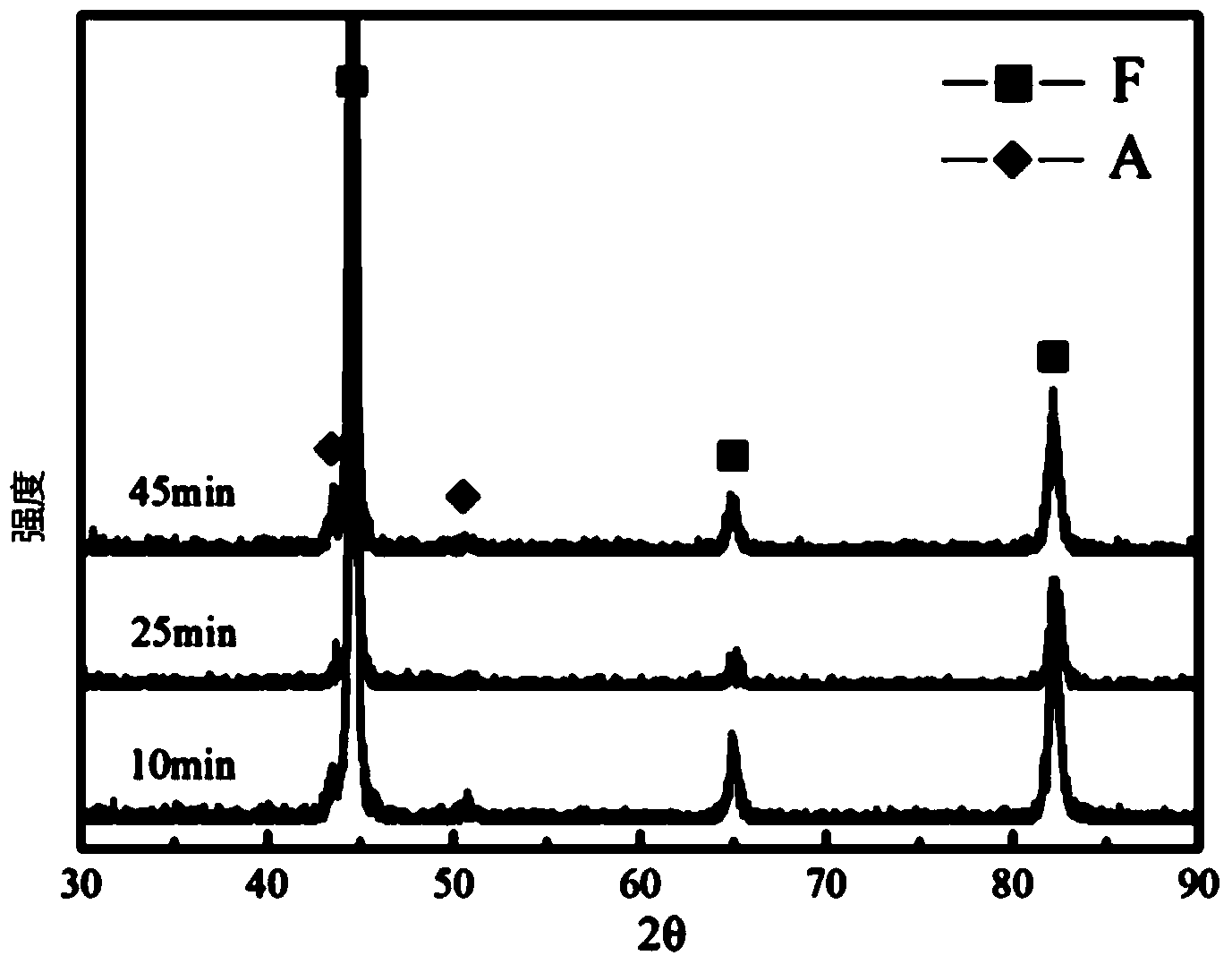
[0027] Take three new ferritic heat-resistant steel T91 samples and heat them up to 1100°C at 4°C / s and hold for 10 minutes; then cool them to 380°C, 365°C and 350°C at 3°C / s Between 210°C and 406°C), keep it warm for 25 minutes, and then continue to cool to room temperature at 3°C / s.
[0028] Figure 4 It is the XRD pattern of the sample after heat treatment. It can be seen that the presence of retained austenite can be detected in...
Embodiment 3
[0030]Take three Φ5×10mm cylindrical T91 samples and conduct the following heat treatment on an online dilatometer: heat at 4°C / s to 1100°C, hold at 1150°C and 1200°C for 15 minutes each; then continuously cool to room temperature at 3°C / s. According to the obtained curves of linear expansion with temperature, the starting temperature (Ms) and the end temperature (Mf) of martensitic transformation of the three T91 samples during the continuous cooling process of the above heat treatment were respectively determined.
[0031] Take three new ferritic heat-resistant steel T91 samples and heat them at 4°C / s to 1100°C, 1150°C and 1200°C for 15 minutes; then cool at 3°C / s to any one between Ms and Mf. temperature, keep warm for 25min, and then continue to cool down to room temperature at 3°C / s. By detecting the generation of retained austenite during the above heat treatment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com