Distributed resilient network interconnection-based service bearing method and device
An elastic network and service bearing technology, applied in the communication field, can solve problems such as traffic interruption, reduce the impact of services and improve user experience.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
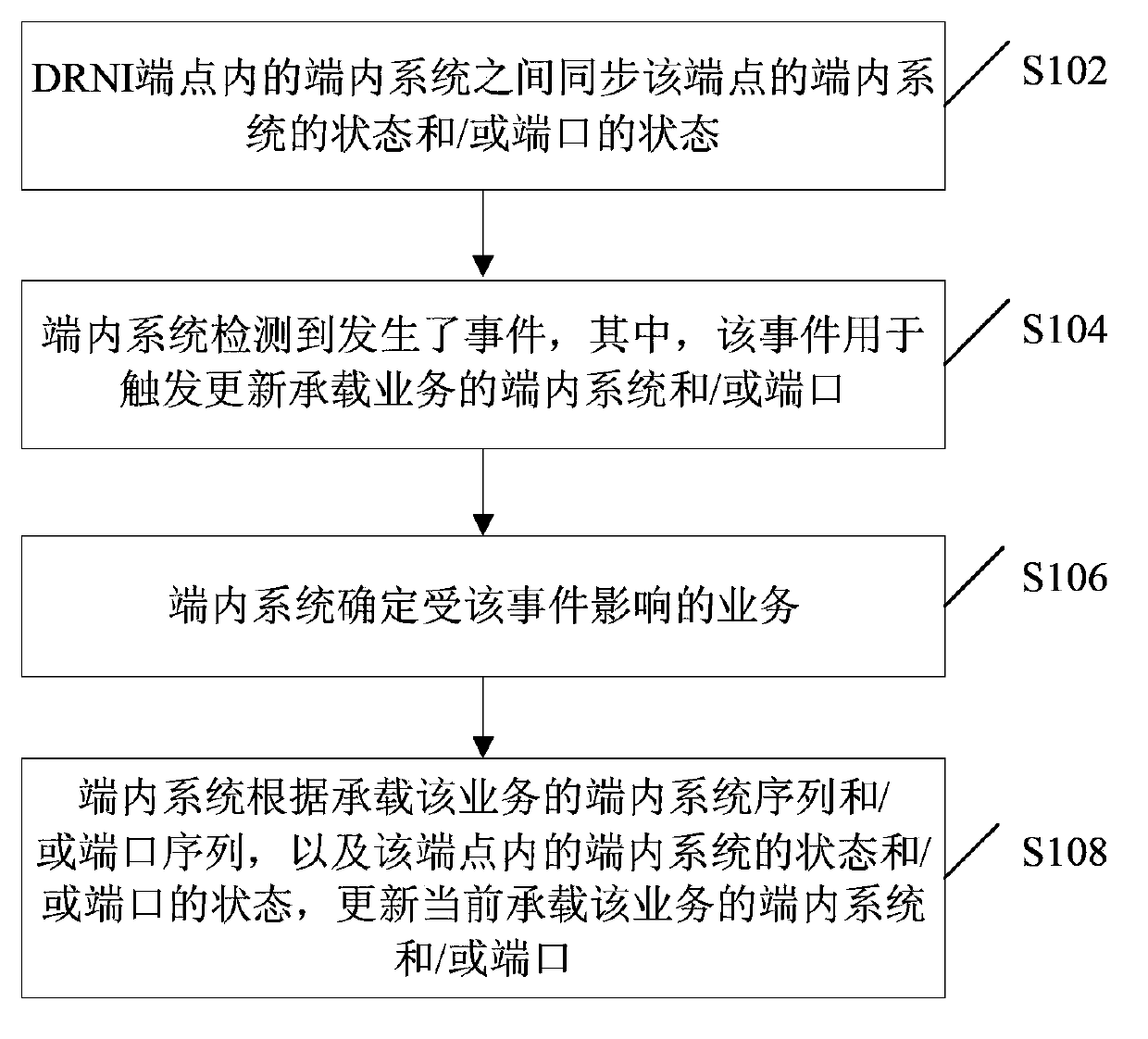
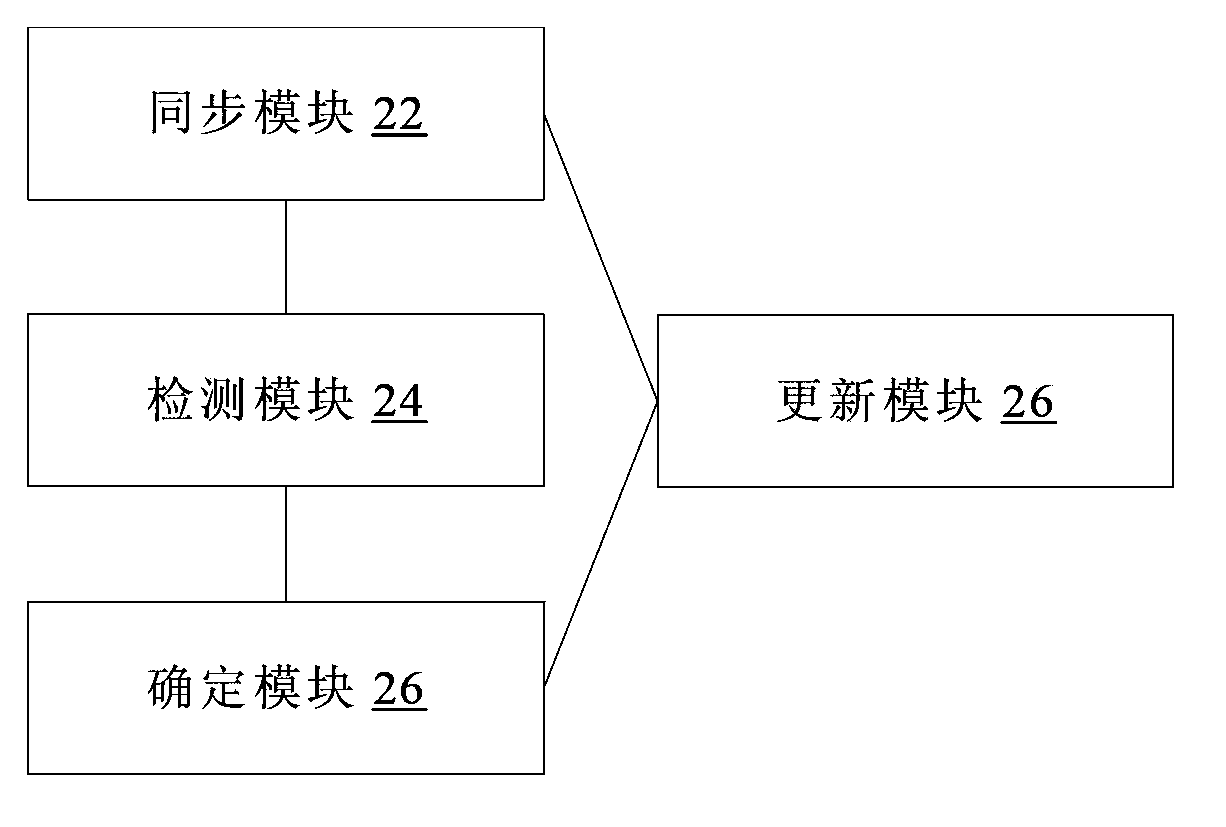
[0086] The implementation scheme of negotiating service bearer in DRNI in this preferred embodiment includes:
[0087] In step 1, the in-device system notifies the status of the synchronization port to other in-device systems of the local end point through the Distributed Relay Control Protocol (DRCP for short).
[0088] Wherein, the port status information is carried in the DRCP protocol message in the form of TLV, and the port status is periodically synchronized between the internal systems. In addition, when the state of the port changes, it is triggered to notify other internal systems of the change of the port state, so that the port states between the internal systems are synchronized.
[0089] The above-mentioned port status TLV may carry information such as aggregation port status and aggregator status. Wherein, the notification triggered when the state of the aggregation port changes may be: when the distribution enabling state of the aggregation port changes, the no...
Embodiment 2
[0127] In this preferred embodiment, the description is made by taking the port negotiated and updated between the internal systems at one end of the DRNI as a physical port as an example. Figure 14 is a schematic diagram of networking according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, such as Figure 14As shown, the two ends of the aggregation group are composed of 1 endpoint, and each endpoint is composed of 2 in-end systems. Among them, endpoint 1 is composed of in-end systems A and B, and endpoint 2 is composed of in-end systems C and D. . Link 1, link 2, link 3, and link 4 between endpoint 1 and endpoint 2 are aggregated into a distributed LAG. The information exchange and service forwarding of each end system in Endpoint 1 will be described below, and the processing method of each end system in Endpoint 2 is the same as that of Endpoint 1.
[0128] Step 1, the intra-end systems A and B in the endpoint 1 are configured and negotiated to obtain a global service port ta...
Embodiment 3
[0171] In this preferred embodiment, the description is made by taking the port negotiated and updated between the internal systems at one end of the DRNI as a physical port as an example. Figure 16 is a schematic diagram of a terminal system failure according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, as shown in Figure 16 As shown, on the basis of Embodiment 2, when the internal system fails, the processing process is as follows:
[0172] When end-end system A fails, end-end system B detects that the connection information of end-end system A is lost, and end-end system B still keeps joining the aggregation group. End-end system B obtains the services affected by the fault as "001, 002, 005, 006" from the saved port service table (such as Table 3) or aggregator service table (such as Table 4) of end-end system A. At the same time, update the aggregator and port status information of the end-end system A, and set the aggregator and port status of the end-end system A as una...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com