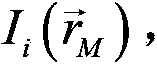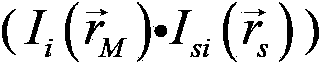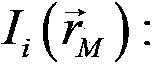Method and system for network secret key distribution based on calculation correlated imaging
A technology for associating imaging and network keys, which is applied in key distribution to achieve the effects of low system cost, good application prospect and low manufacturing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0059] Such as figure 1 The scheme diagram of the high-speed network key distribution method based on computational correlation imaging in the present invention is shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0060] 1) The legitimate user uses a part of the initial key to verify the identity of the server. These initial keys are distributed by the server to legitimate users through QKD or other methods. We assume that these keys are completely secure;
[0061] 2) The server uses n initial keys to obtain n light intensities I through the optical system i , and then send the n light intensities to legal users through the public channel.
[0062] 3) Legal users (A, B...N) receive n light intensities I from the server i , and then use the same n initial keys and n light intensities I i Image information is obtained by associative calculation.
[0063] 4) The legal user extracts the gray value of each pixel in the image, and then generates a binary number 0 or 1 accordin...
no. 2 example
[0082] In this embodiment, the scattering medium is used as the object. Figure 4 It is the image of the scattering medium when n=597. To obtain the key sequence, a total of 3582 pairs of data I i with Divided into 6 groups according to n=097, we can get 6 cards with Figure 4Similar pictures, a total of 152600 keys were extracted.
[0083] The key randomness test results are shown in Table 2. Among them, the amount of data is 152600 bits.
[0084] Table 2 The verification results of key sequences generated using scattering media as objects
[0085]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com