Delay tolerant network energy-efficient routing scheme based on social attribute forwarding
A social attribute and delay-tolerant network technology, applied in the field of computer networks, can solve problems such as long network delay, limited node power, and influence of delay-tolerant network routing performance, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of forwarding times and reducing average energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
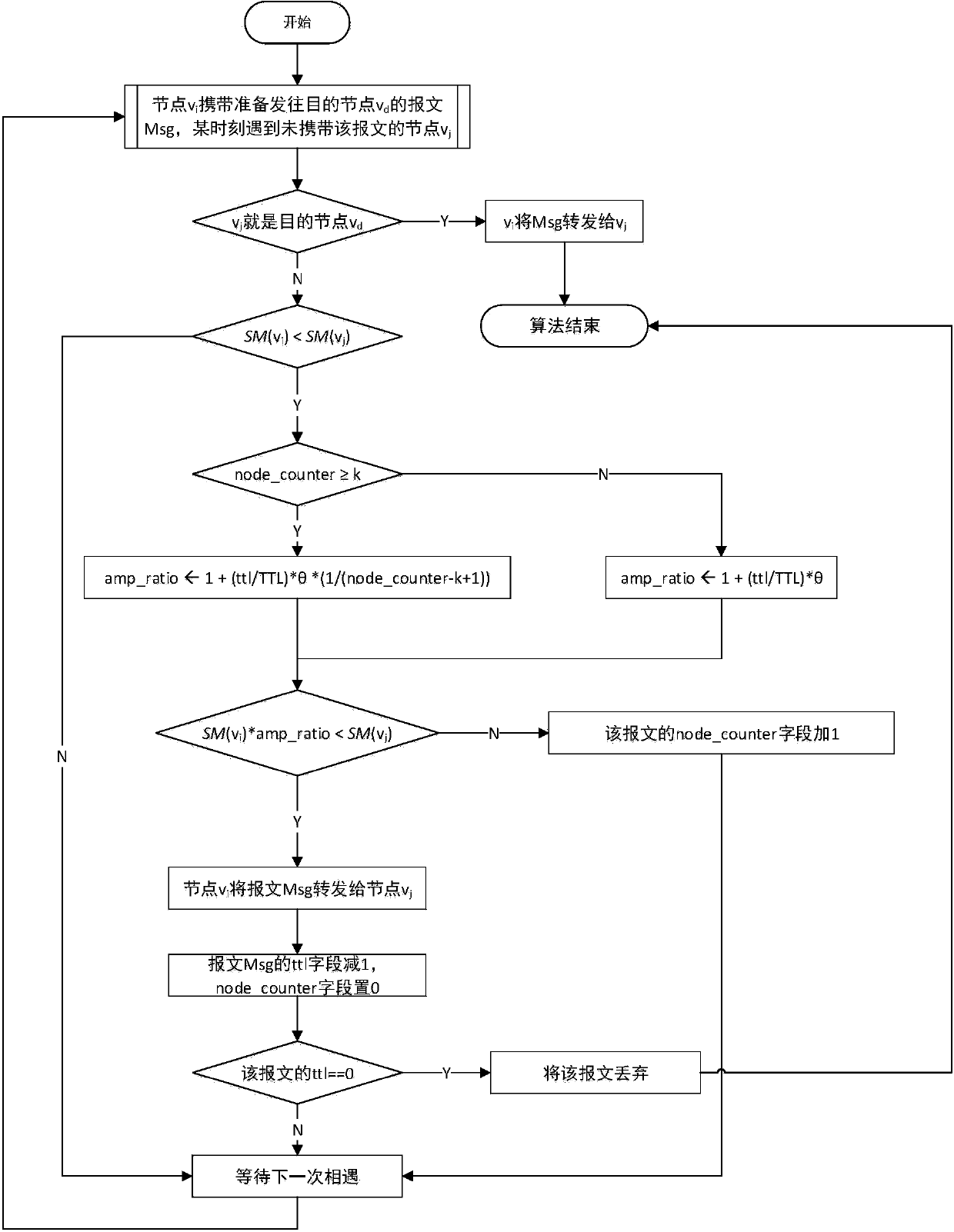
[0043] The content of the method of the present invention will be specifically described below in conjunction with theory and accompanying drawings.
[0044] In many applications of latency-tolerant networks, more and more mobile communication devices are carried and used by people, and their behavior can be well characterized by their social attributes. The energy-saving routing method based on social attribute forwarding proposed by the present invention is a method of selecting a relay node for message forwarding according to the social attribute of the node itself and the social relationship between the nodes in the delay-tolerant network.
[0045] The traditional routing method based on social attributes is to calculate the social index SM (Social Metric) of the node through the social attributes of the node itself and the social relationship between nodes. The social index here can be the SimBet value in the SimBet routing method, or It can be social energy in the SEBAR ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com