Anti-Potential Induced Degradation (PID) control method and control system
A control method and technology for a control system, which are applied in the field of back-EMF-induced decay control methods and control systems, can solve problems such as reducing the life of a bias power supply, PID devices that cannot be turned on and off intelligently, and energy consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
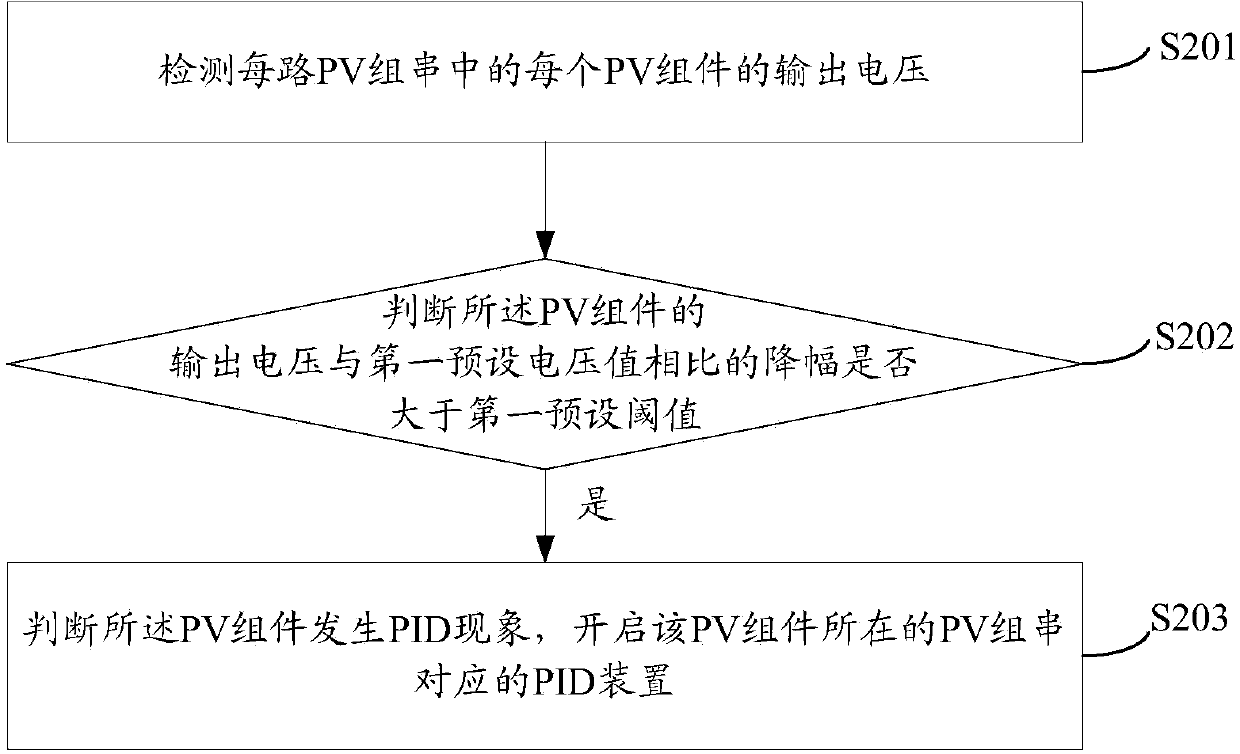
[0055] see figure 2 , which is a flow chart of Embodiment 1 of the method for controlling back EMF-induced decay provided by the present invention.
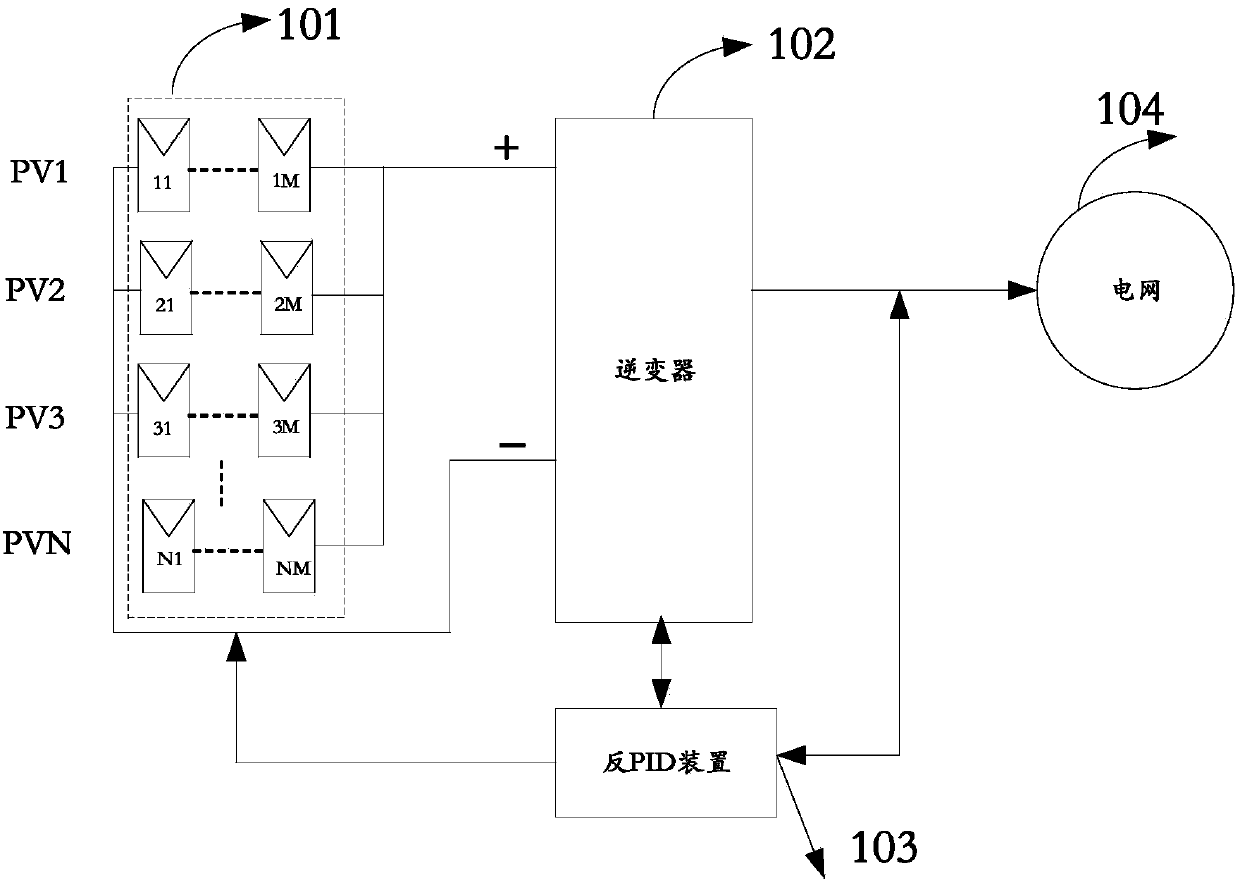
[0056] A method for controlling back-emf-induced attenuation provided in this embodiment is applied in a photovoltaic power generation system, where each PV string includes M PV modules connected in series; each PV string is configured with a back-emf-induced attenuation PID device;
[0057] Include the following steps:
[0058] S201: Detect the output voltage of each PV module in each PV string;
[0059] It should be noted that each PV module refers to each panel, that is, a PV string includes multiple panels connected in series.
[0060] In this embodiment, it is necessary to detect the output voltage of each battery board, so that it can be accurately judged whether to turn on the PID device. The battery board at the negative pole of the DC side is prone to PID phenomenon.
[0061] If the output voltage of the entire PV s...
Embodiment 2
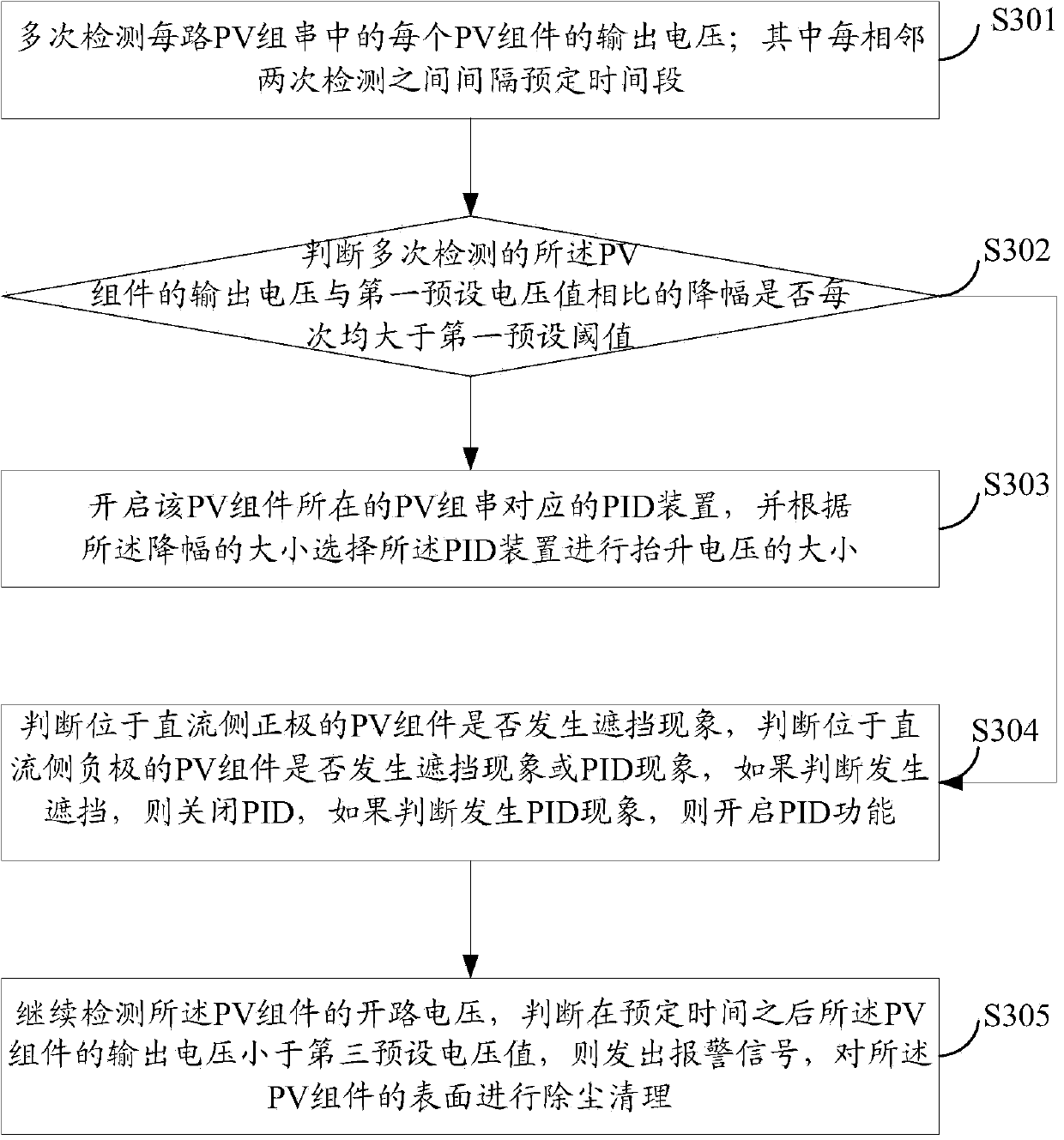
[0067] see image 3 , which is a flow chart of Embodiment 2 of the method for controlling back EMF-induced decay provided by the present invention.
[0068] S301: Detect the output voltage of each PV module in each PV string multiple times; wherein a predetermined period of time is separated between two adjacent detections.
[0069] It should be noted that, in order to accurately determine whether the PID phenomenon occurs, multiple detections can be performed in this embodiment, for example, the predetermined time interval is 1 day, and of course it can also be an integer multiple or a decimal multiple of 1 day, for example, 2 days, 0.5 days, or 1.5 days etc.
[0070] S302: Determine whether the output voltage of the PV module detected multiple times has a drop range greater than a first preset threshold each time compared with a first preset voltage value. If yes, execute S303, and if no, execute S304.
[0071] For example, sometimes the battery panel is blocked, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com