Low-modulus medical implant porous scaffold structure
A porous scaffold and low modulus technology, applied in scaffolds, bone implants, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of unsupported bone cells, complex processing technology of porous metal materials, doping, etc., to relieve pain and eliminate stress Blocking effect, effect of increasing service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
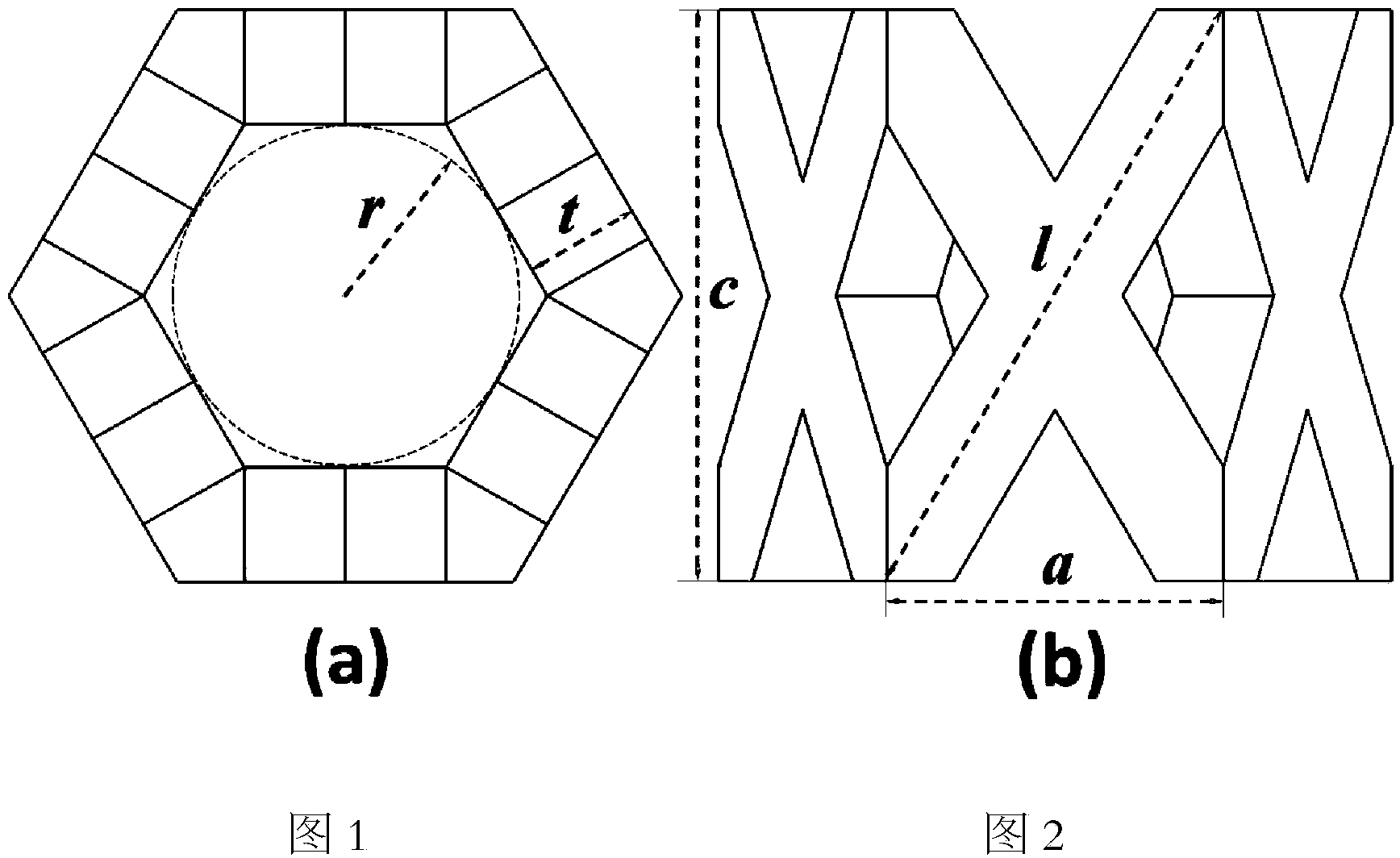
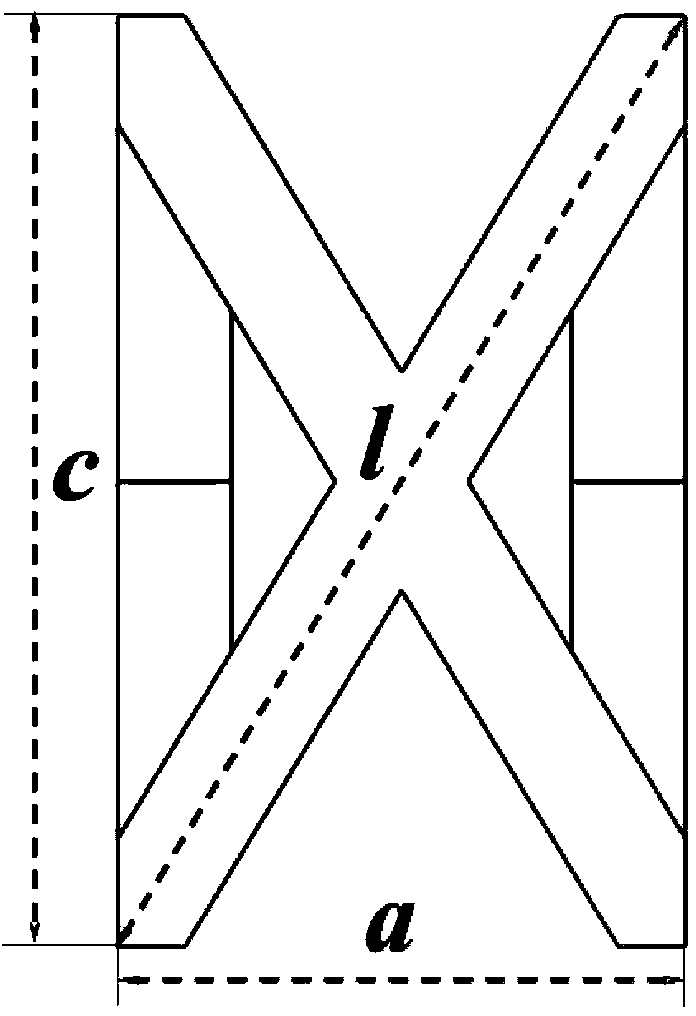
[0067] For the hexagonal prism basic unit, when the material of the implant is α-Ti (E=110GPa, ν=0.33), as image 3 Shown: The relationship between the relative modulus of the scaffold material and the relative density of the scaffold can be obtained by using the finite element method. The results showed that η 1 The value range is selected at 1.0-2.5, η 2 When the value range is selected to be 0.10-0.50, and the inscribed circle radius r of the through hole is selected to be in the range of 150 μm-750 μm, the relative modulus of the scaffold material will be lower than 30 GPa, which meets the range of human cortical bone modulus.
Embodiment 2
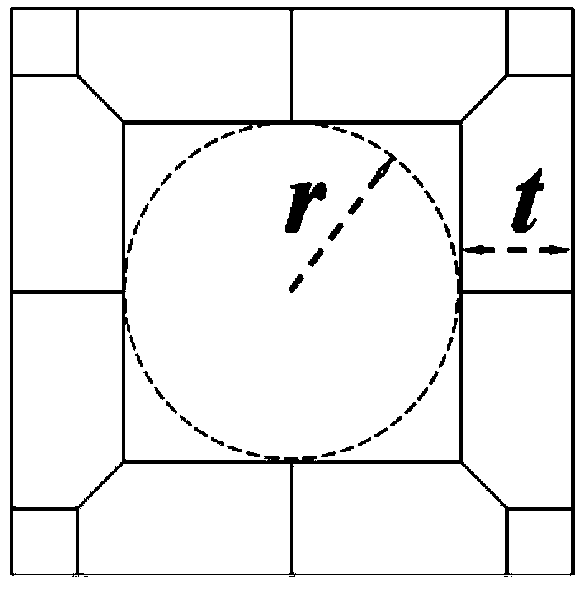
[0069] For the basic unit of quadrangular prism, when the material of the implant is α-Ti (E=110GPa, ν=0.33), as Figure 4 Shown: The relationship between the relative modulus of the scaffold material and the relative density of the scaffold can be obtained by using the finite element method. The results showed that η 1 The value range is selected at 1.0-2.5, η 2 When the value range is selected to be 0.1-0.35, and the radius r of the inscribed circle of the through hole is selected to be in the range of 150 μm-750 μm, the relative modulus of the scaffold material will be lower than 30 GPa, which meets the range of human cortical bone modulus.
[0070] Mg Example Group
Embodiment 3
[0072] For the basic unit of the hexagonal prism, when the material of the implant is Mg (E=44GPa, ν=0.26), as image 3 Shown: The relationship between the relative modulus of the scaffold material and the relative density of the scaffold can be obtained by using the finite element method. The results showed that η 1 The value range is selected from 1-2.5, η 2 When the value range is selected to be 0.1-0.5, and the radius r of the inscribed circle of the through hole is selected to be in the range of 150 μm-750 μm, the relative modulus of the scaffold material will be lower than 30 GPa, which meets the range of human cortical bone modulus.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com