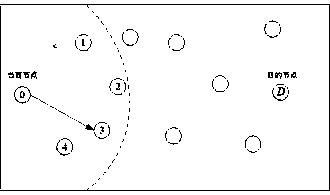
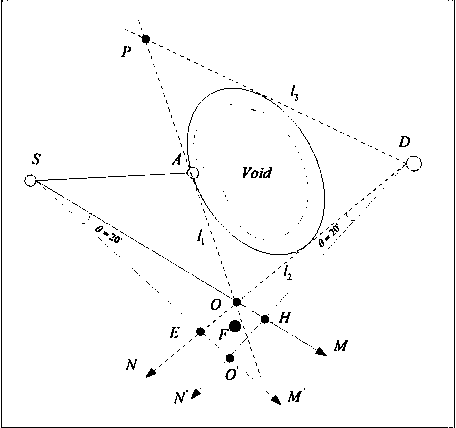
A predictive low-latency geographic routing method
A geo-routing and low-latency technology, applied in the field of geo-routing in wireless sensor networks, can solve the problems of high latency, uneven energy consumption, serious energy consumption and time consumption, and empty detours, so as to prolong life and reduce energy consumption. , The effect of balancing network load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
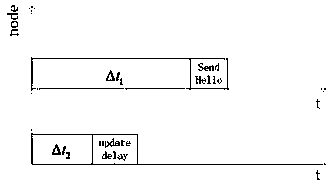
[0021] 1) Define the Hello protocol packet: add three new fields in the packet header, respectively carrying the average receiving rate of node data packets p in , the average packet sending rate p out and the node's current queue size Q cur_size Three messages; the node calculates the average receiving rate p of data packets in and the average sending rate p out ,Methods as below:
[0022]
[0023]
[0024] where t in is the time interval between two adjacent packets arriving at the node, t out is the time interval between two adjacent packets leaving the node, k, k>1, k∈N + Indicates the number of calculations, and α is a scaling factor whose value ranges from 0 to 1.
[0025] 2) Each node maintains a neighbor table to store the information of its neighbor nodes, mainly including neighbor node number, coordinate position, average data packet receiving rate, average data packet sending rate, current queue size of any neighbor node, neighbor node The prediction de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com