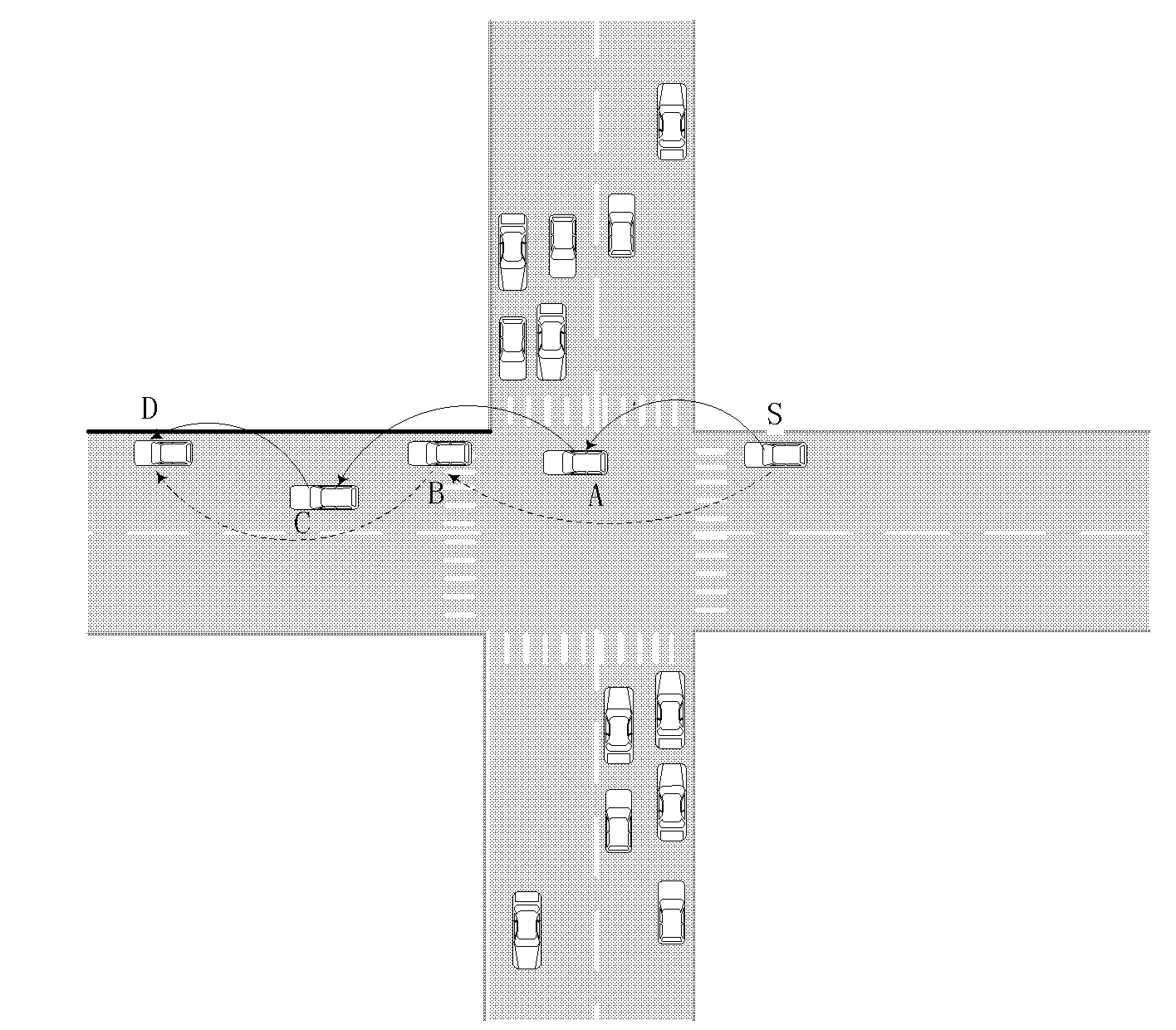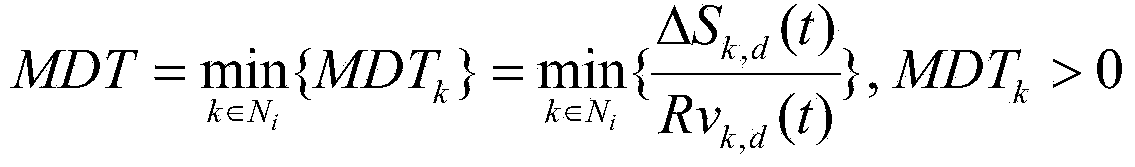Patents
Literature
49 results about "Geographic routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Geographic routing (also called georouting or position-based routing) is a routing principle that relies on geographic position information. It is mainly proposed for wireless networks and based on the idea that the source sends a message to the geographic location of the destination instead of using the network address. In the area of packet radio networks, the idea of using position information for routing was first proposed in the 1980s. and interconnection networks. Geographic routing requires that each node can determine its own location and that the source is aware of the location of the destination. With this information a message can be routed to the destination without knowledge of the network topology or a prior route discovery.
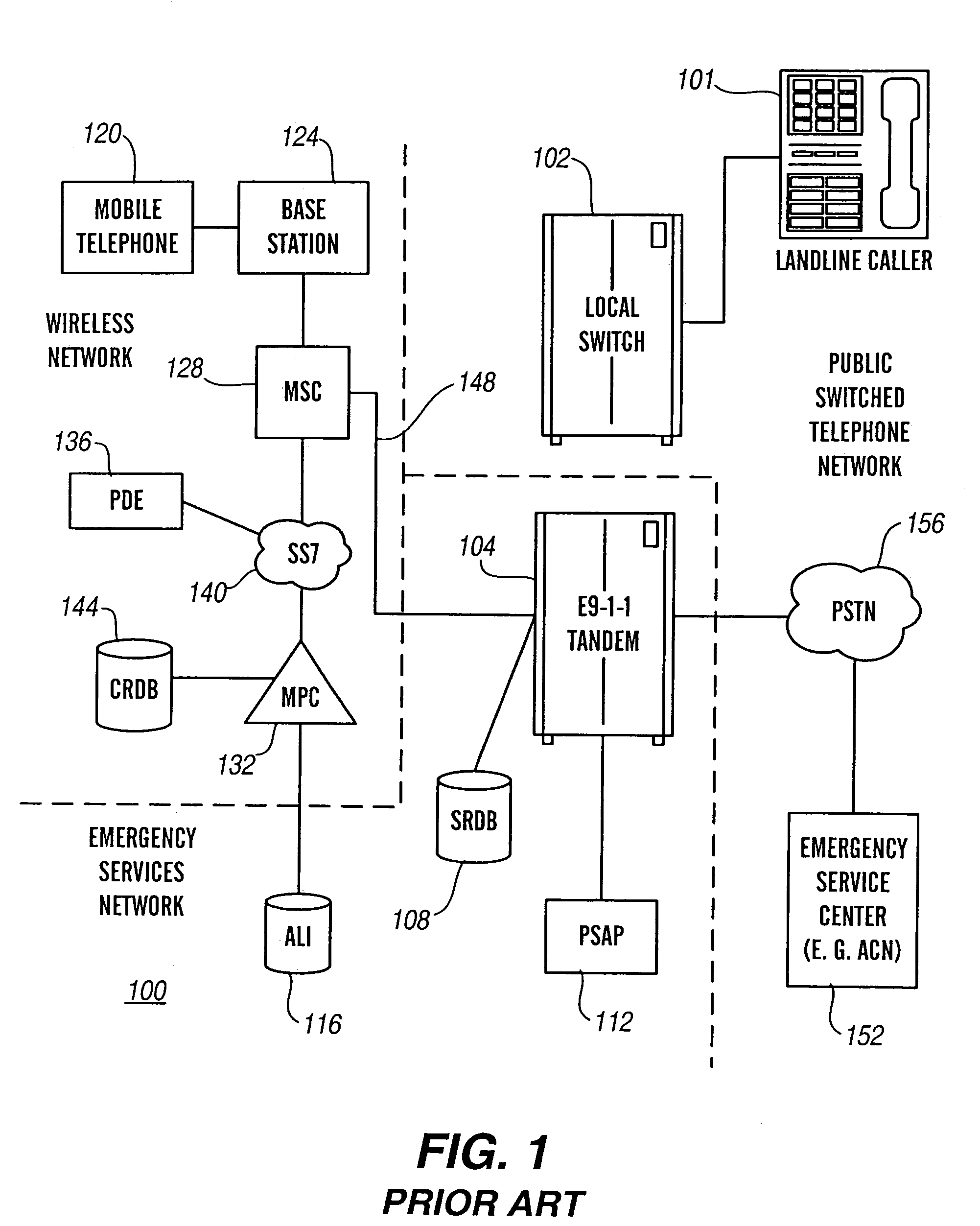
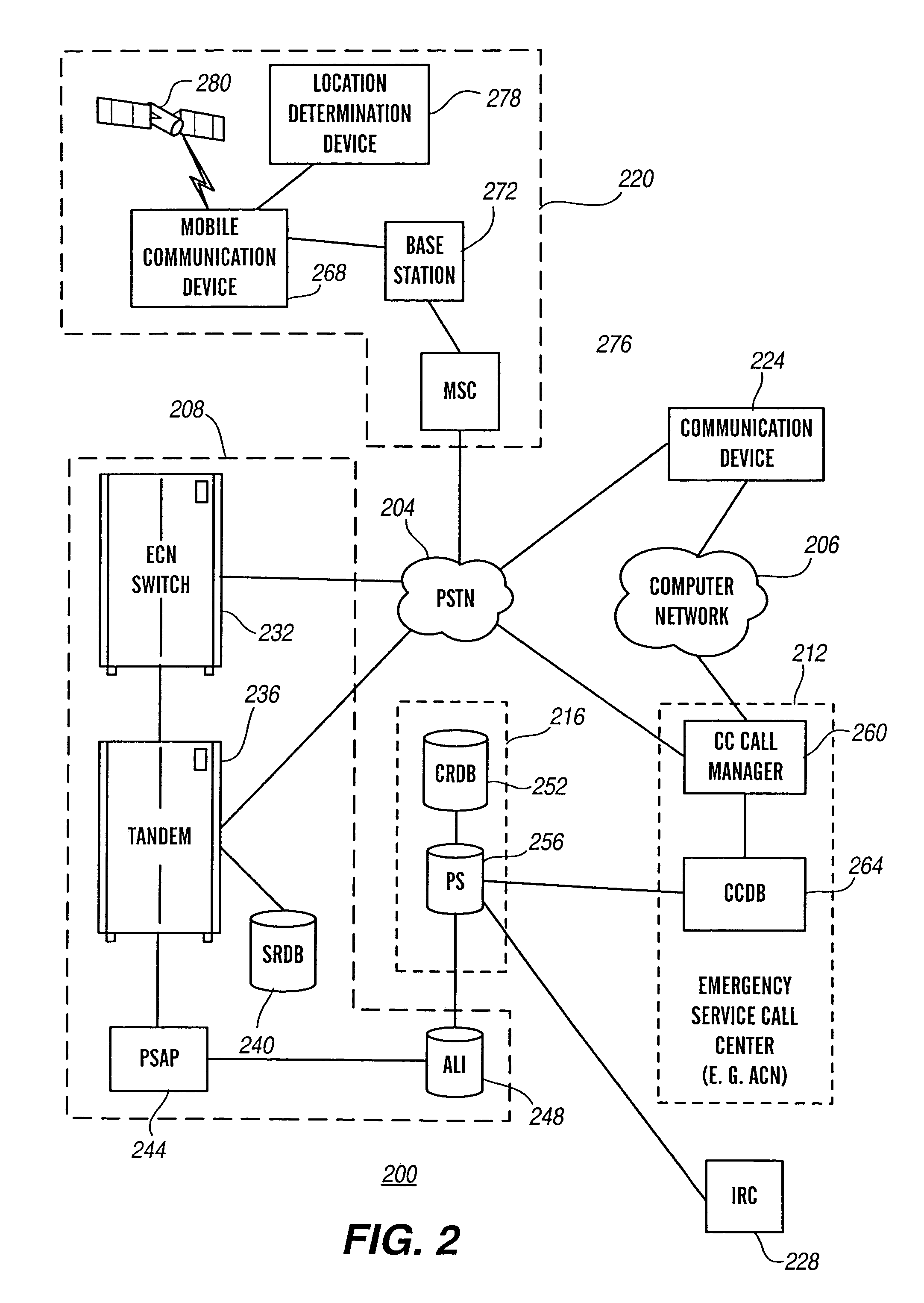
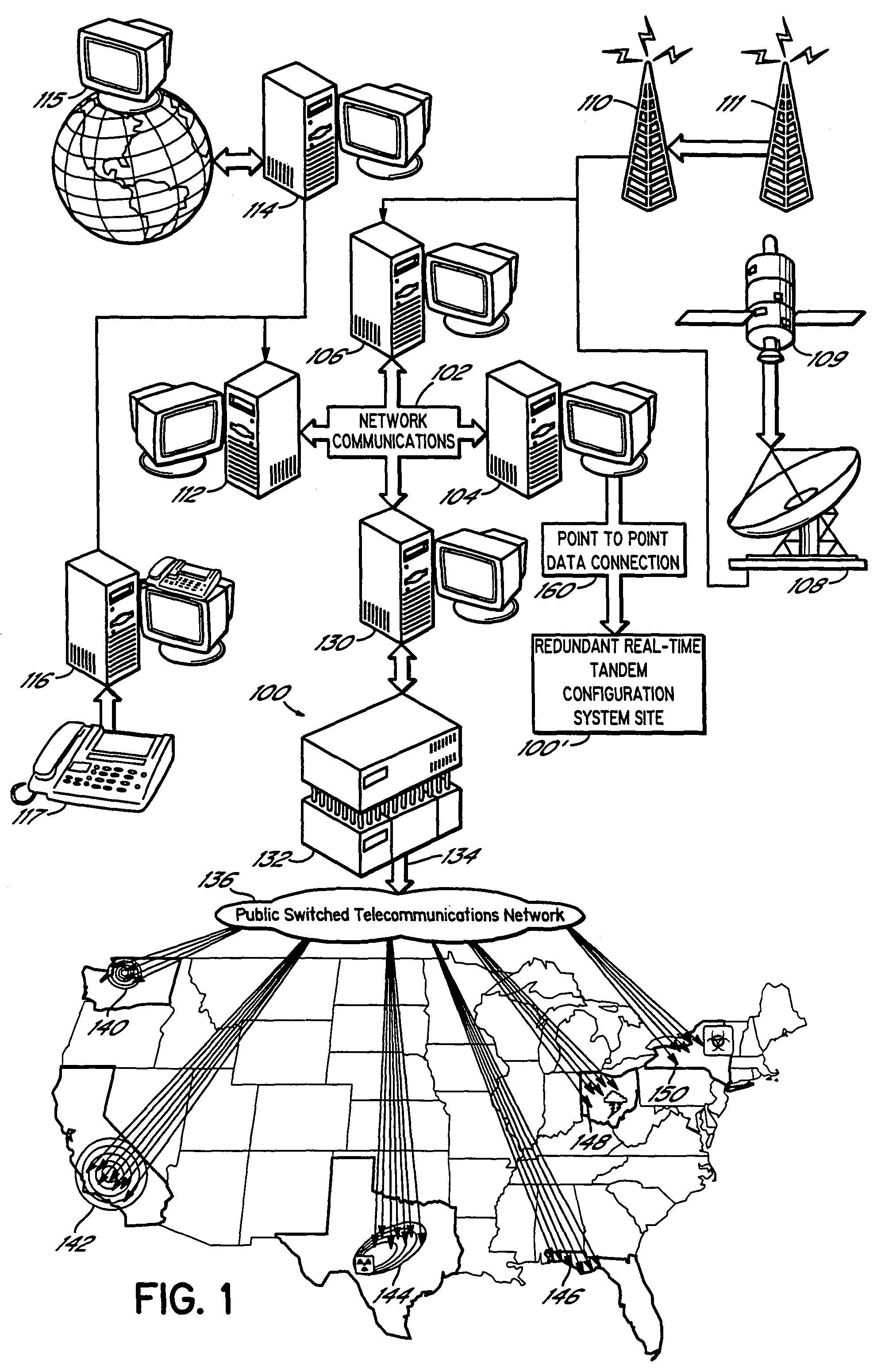
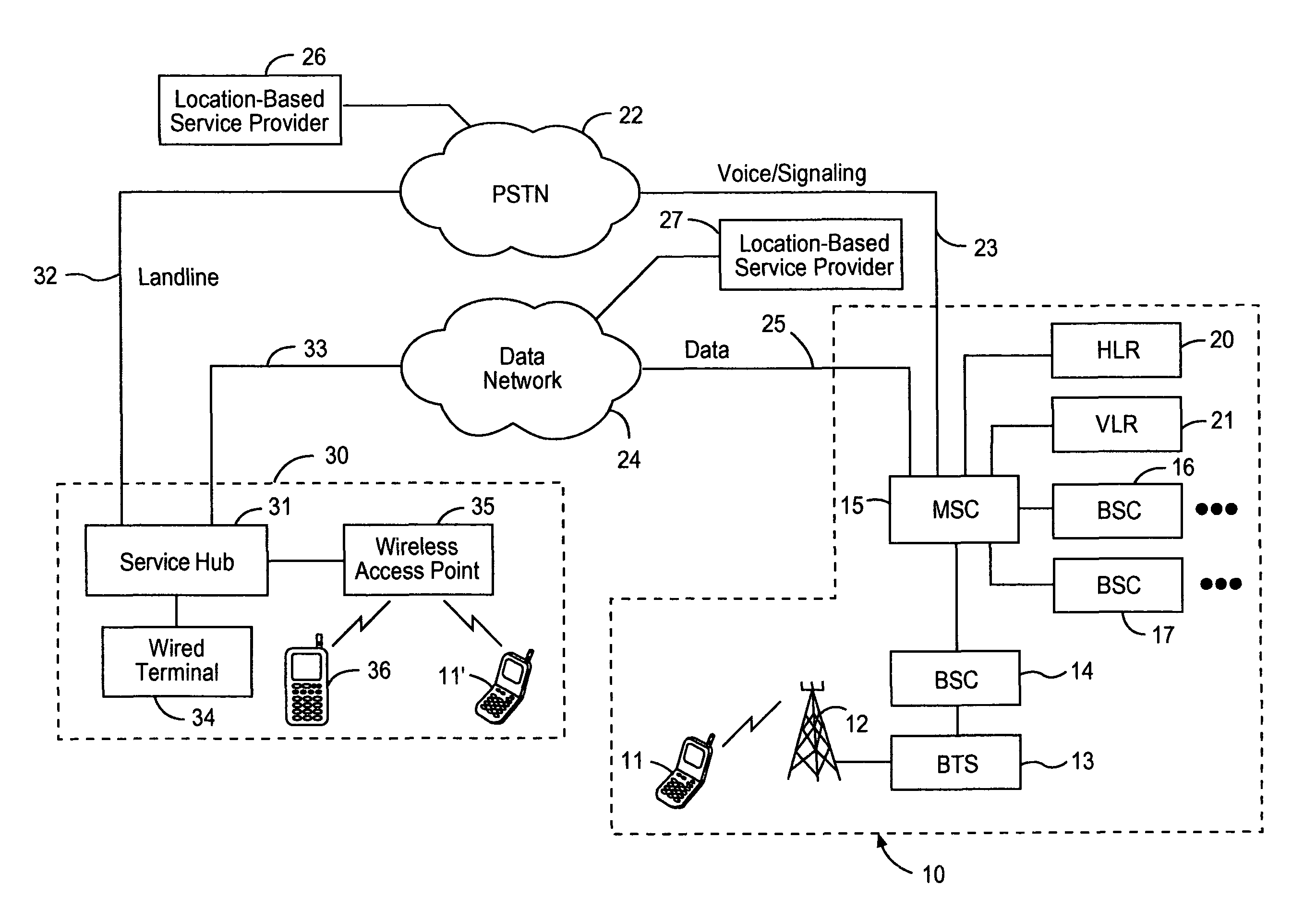
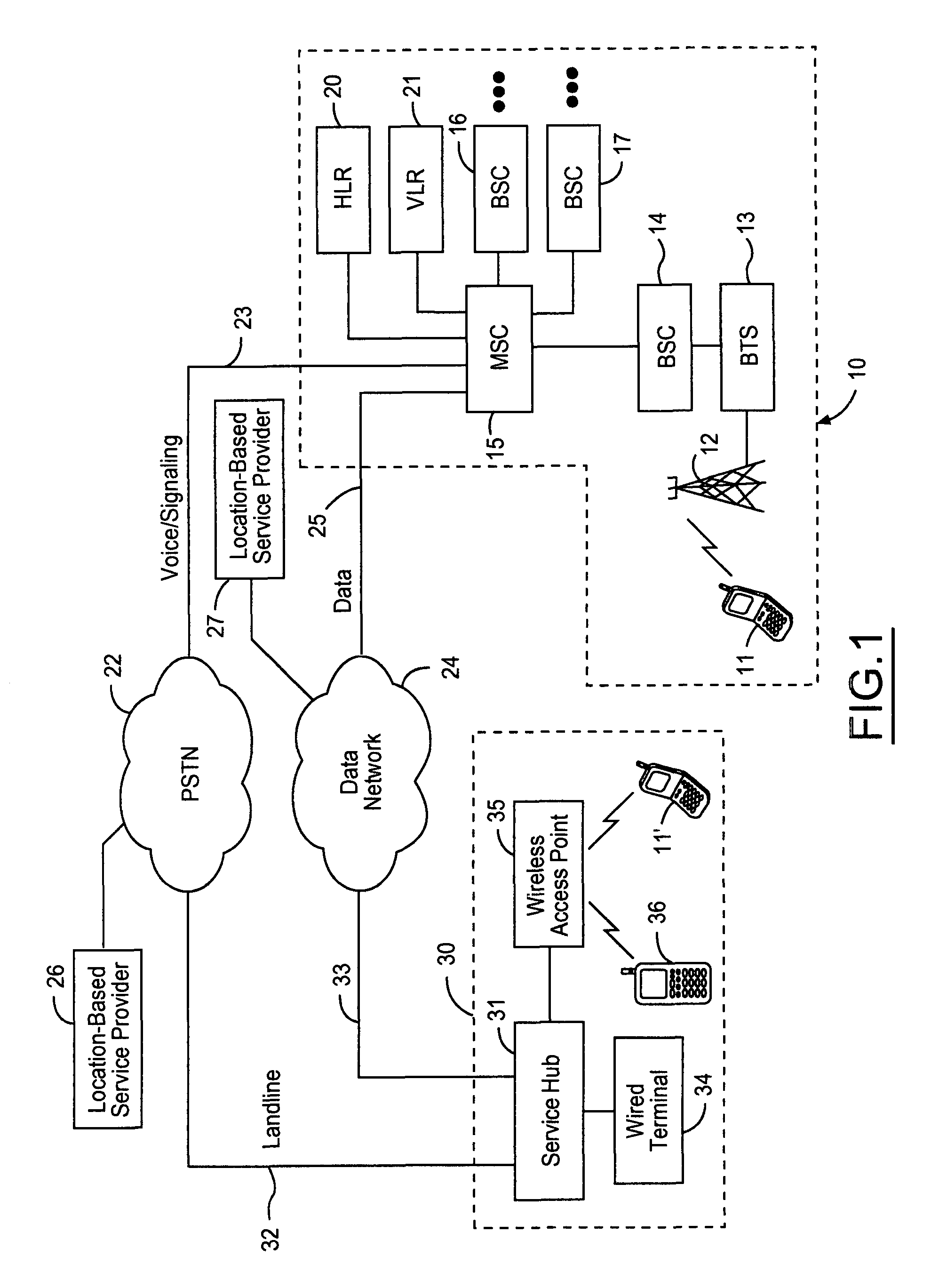
Geographic routing of emergency service call center emergency calls
InactiveUS7177397B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsEmergency connection handlingMonitoring callCall routing
The present invention is related to the delivery of requests for emergency service initially handled by an emergency service call center to a public safety answering point. The invention additionally allows for enhancement information to be provided to a public safety answering point operator visually in connection with calls routed to that public safety answering point. This information may include caller identification, and additional information, such as information regarding the location of the caller and the nature of the emergency. Furthermore, the routing of requests for emergency service to an appropriate public safety answering point can be accomplished for requests received over a wide geographic area. In particular, requests can be appropriately routed even though they may originate from locations encompassed by different E9-1-1 tandems. The present invention is particularly well suited for use in connection with automatic collision notification and personal alarm monitoring call centers serving areas encompassed by more than one E9-1-1 tandem.
Owner:INTRADO LIFE & SAFETY INC
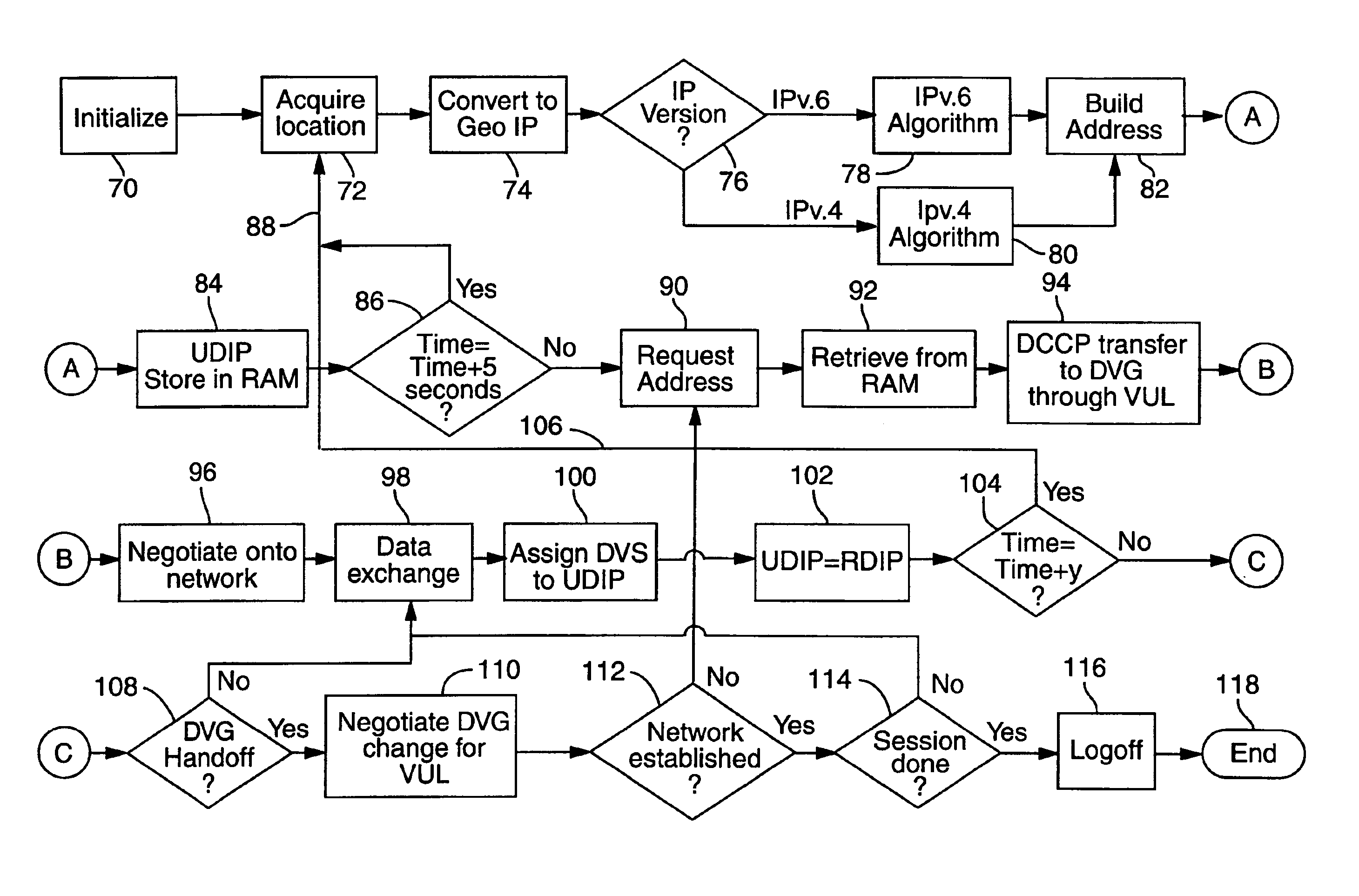
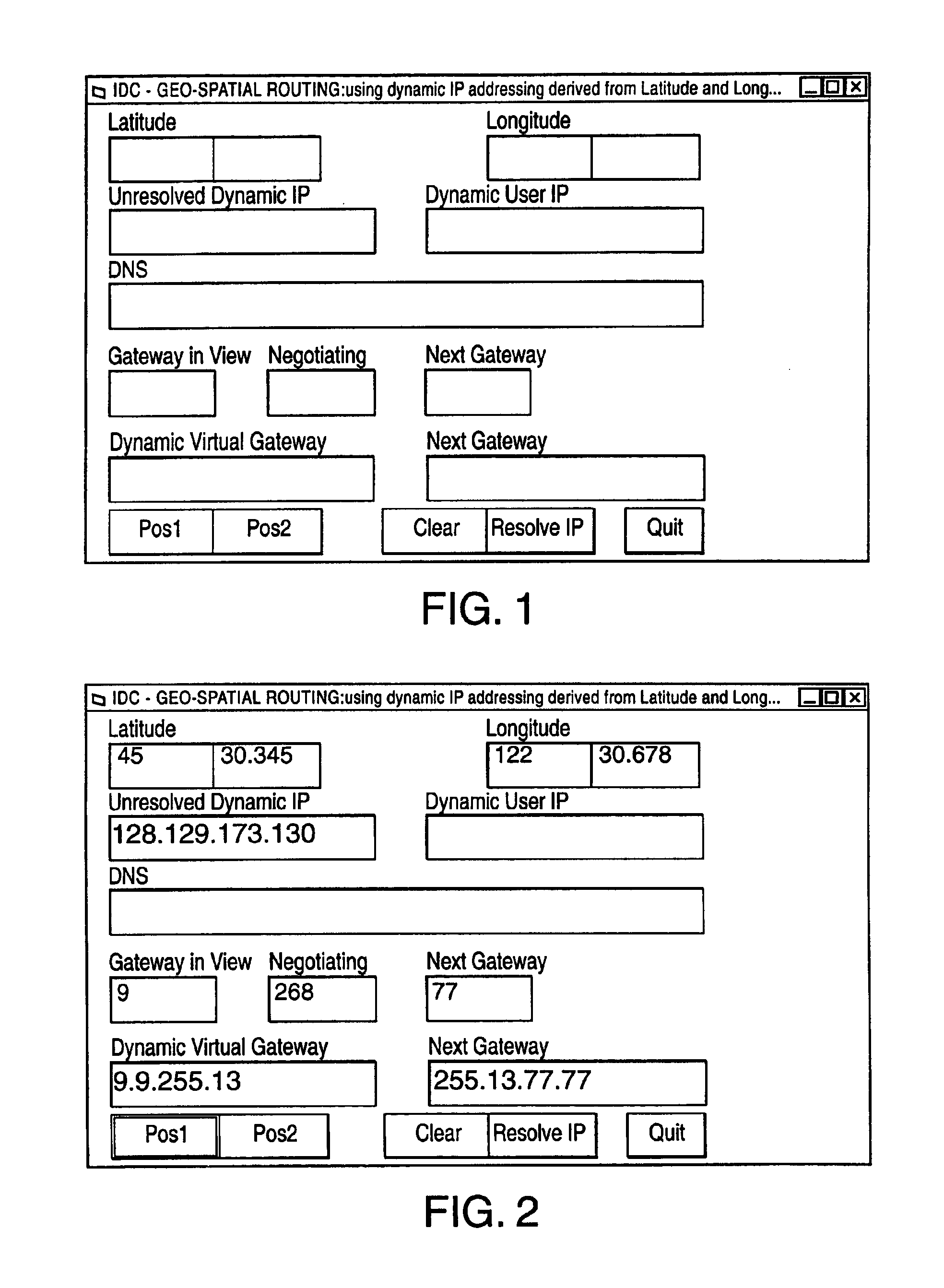
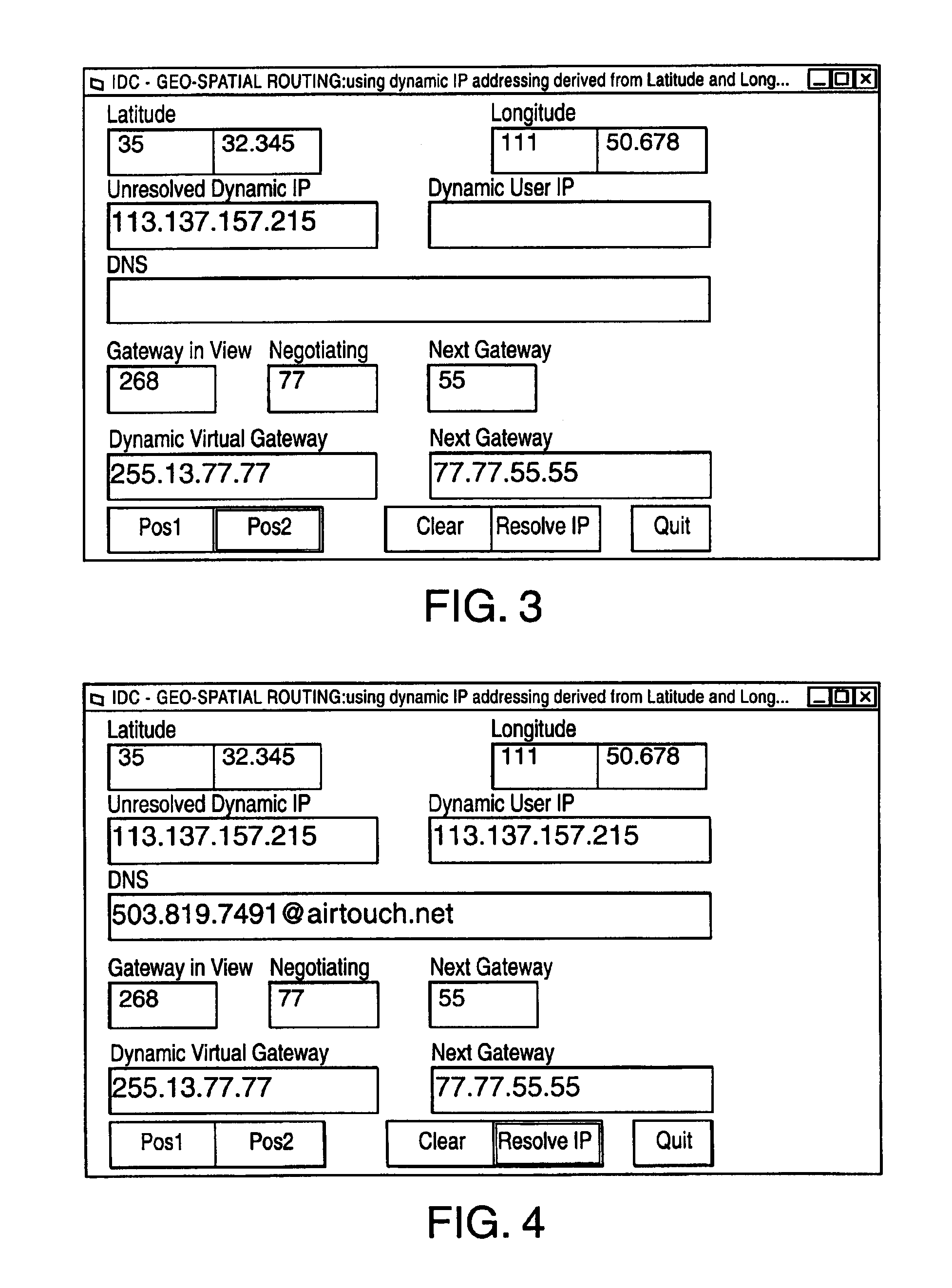
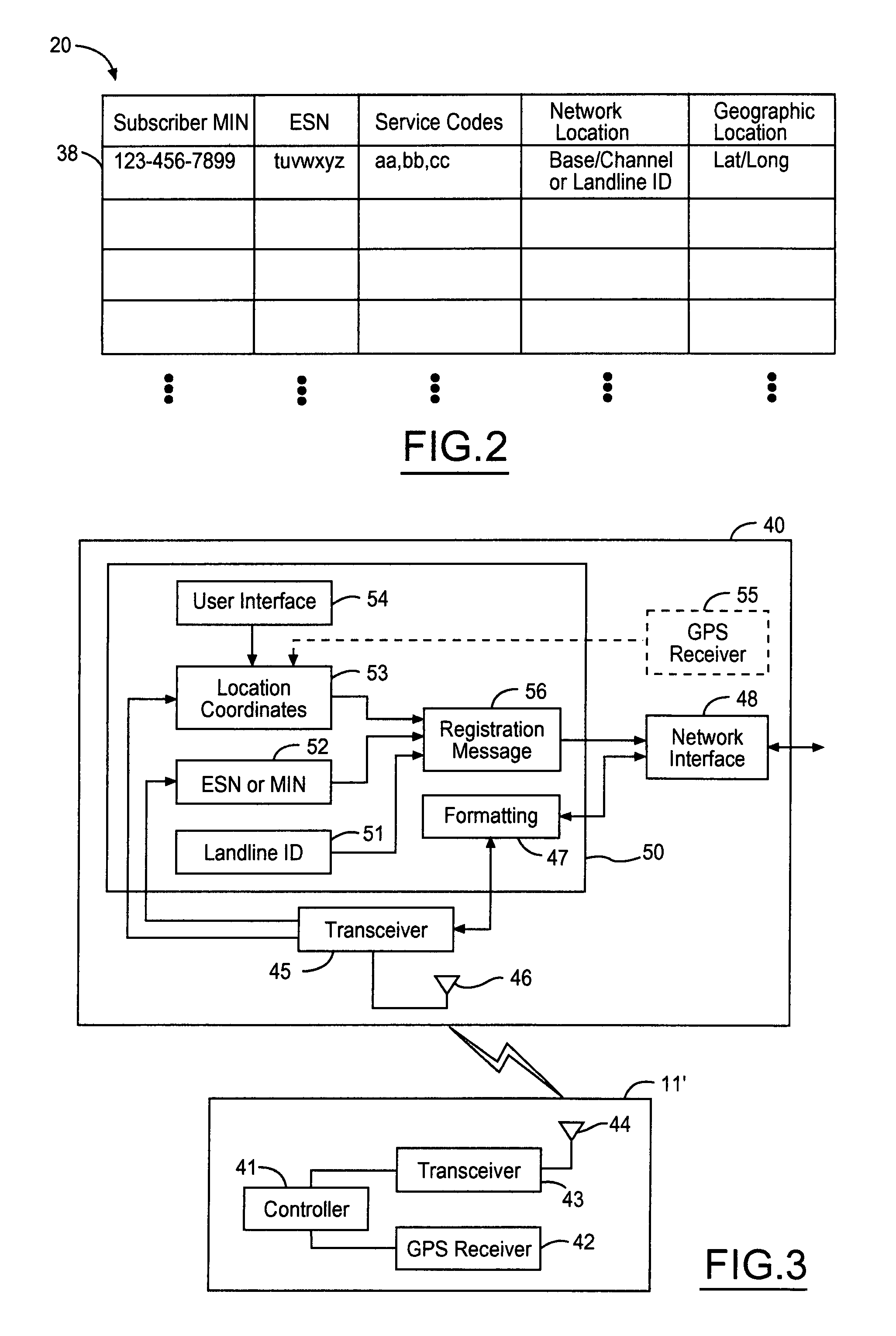
Geo-spacial internet protocol addressing
InactiveUS6920129B2Easy to useReadily availablePosition fixationTime-division multiplexLongitudeNetwork management
The invention provides for conversion of latitude and longitude to an addressing scheme that supports current TCP / IP (Ipv4) and future addressing (Ipv6 / Ipng) requirements. More specifically, it allows a decentralization of the unicast point to a device on the hosted network. Geographical Internet Protocol (geoIP) addressing will facilitate anycast routing schemes in which the nearest node has a statically assigned geoIP. Geo-routing and network management become a function of the geoIP address.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO +1
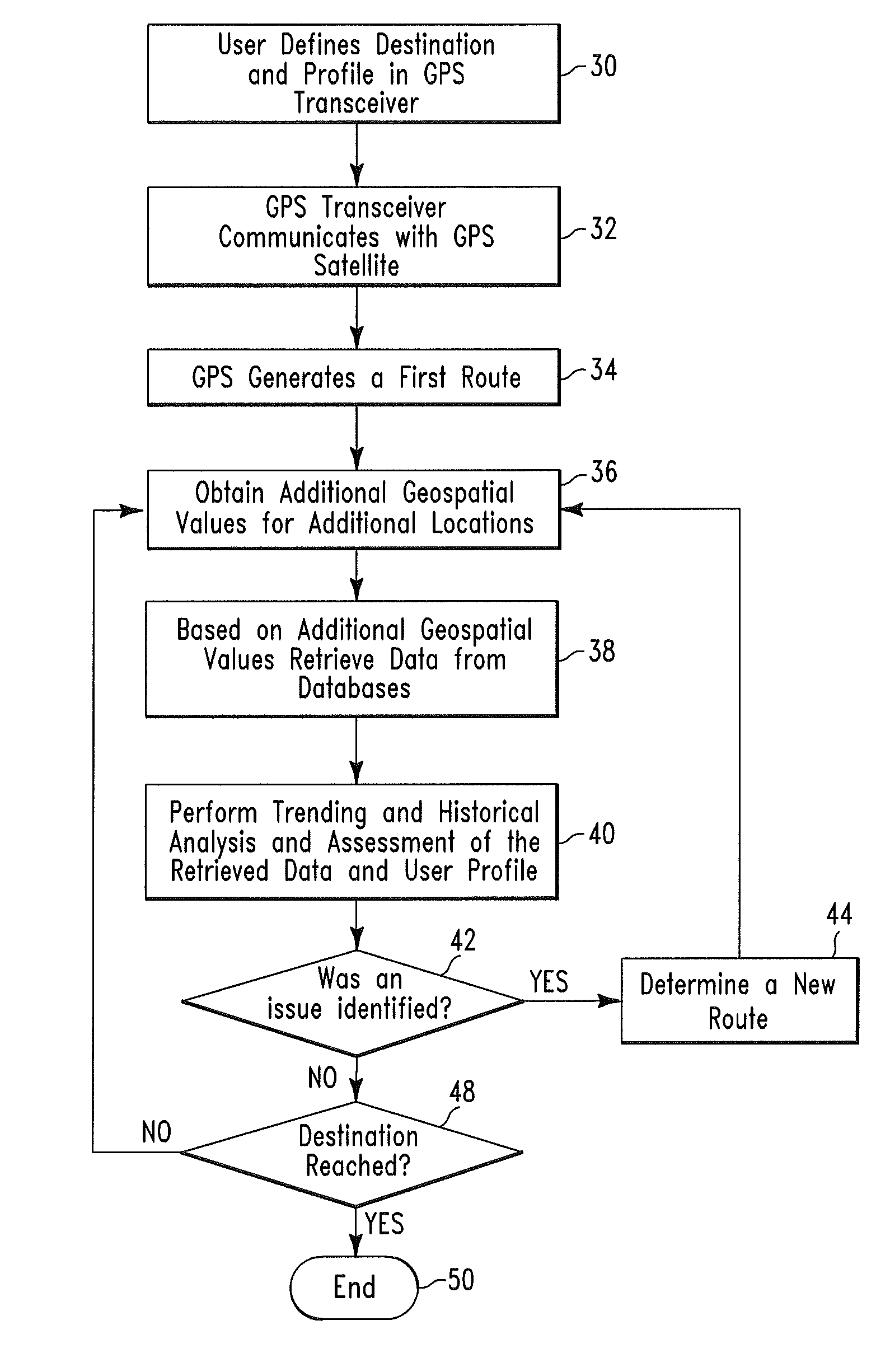
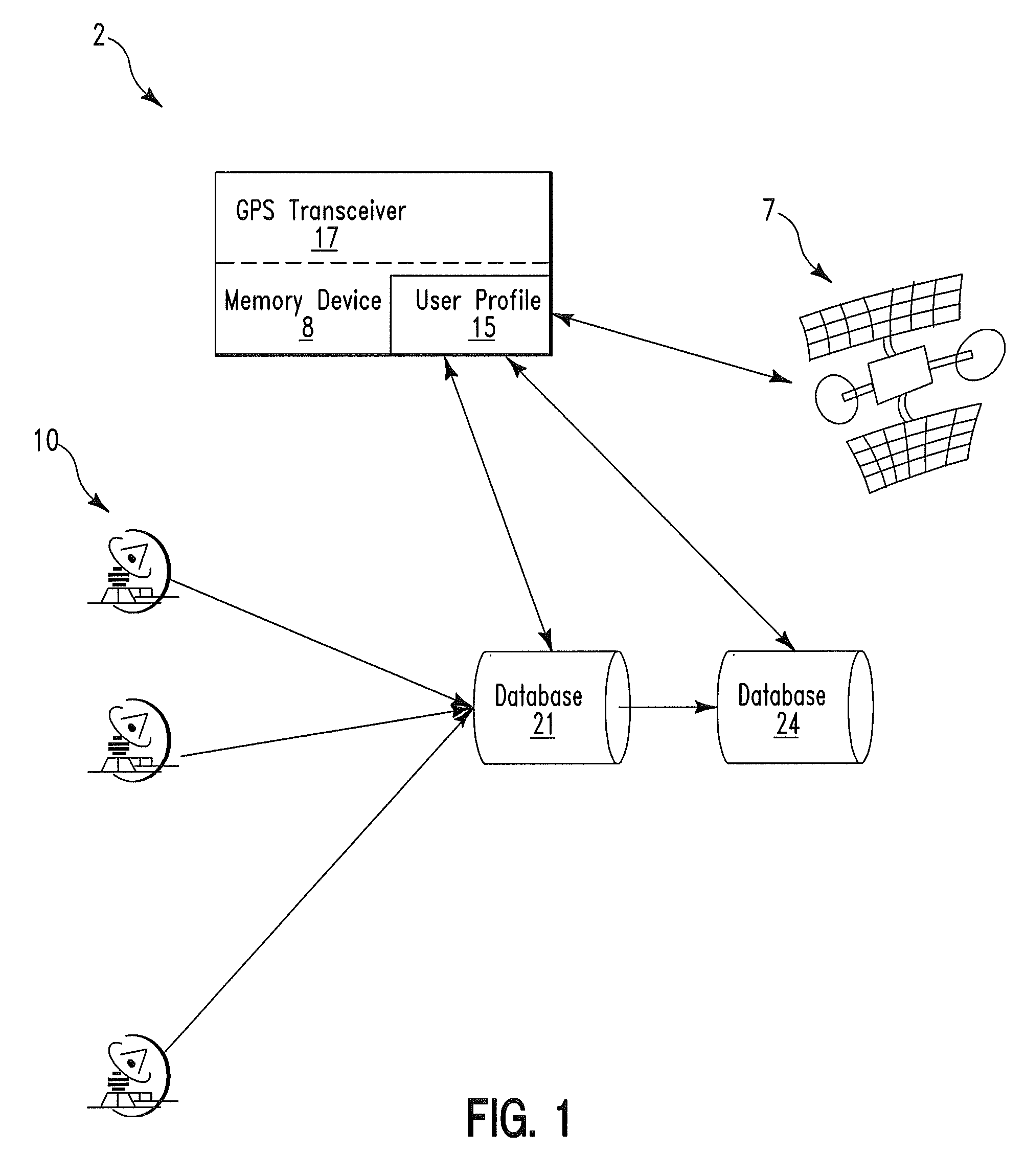
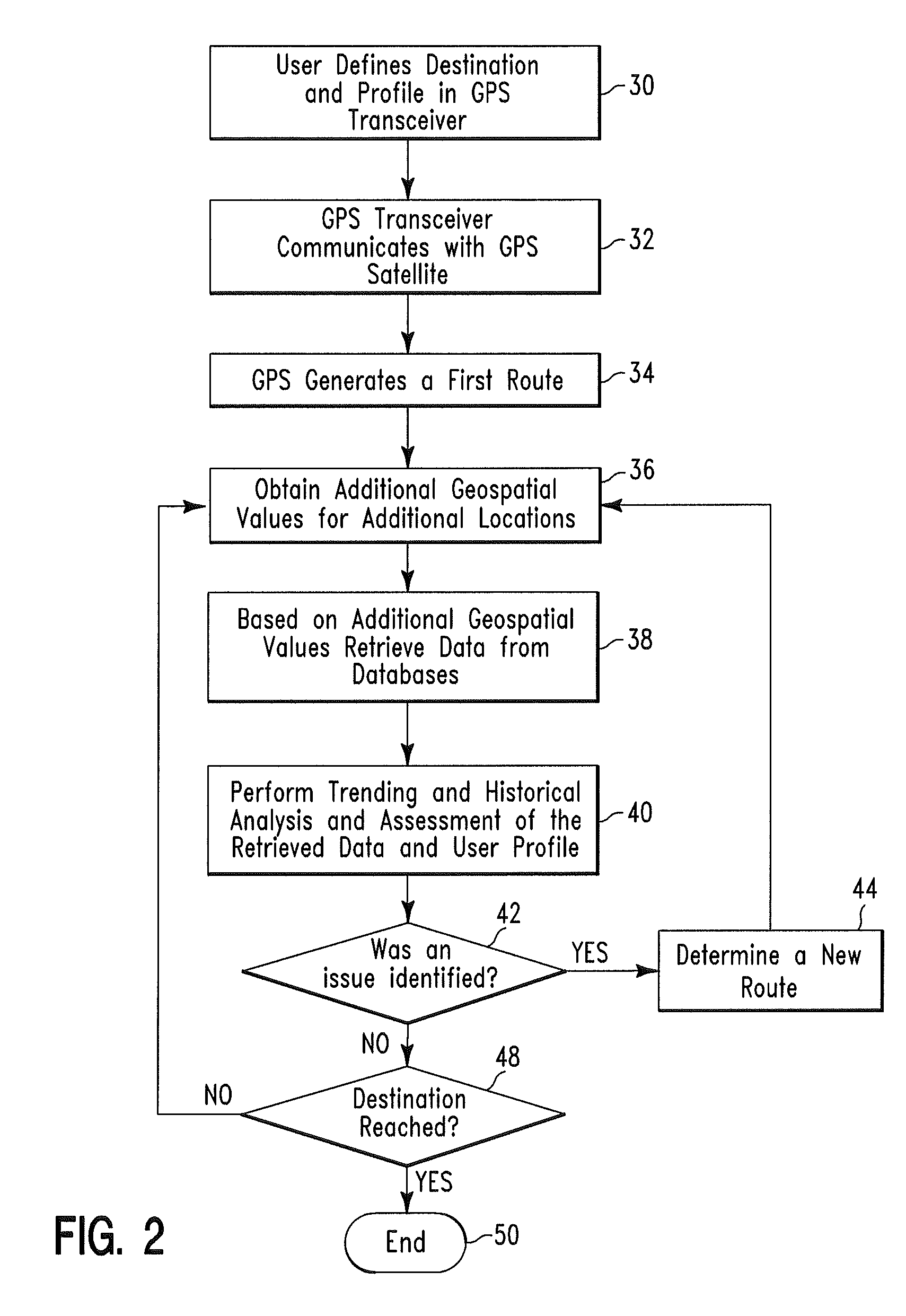
Routing method and system
InactiveUS7761225B2Analogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationTransceiverUser profile
A routing method and system. The method includes receiving by a global positioning satellite (GPS) transceiver, a user profile comprising user preference data and destination location data. The GPS transceiver retrieves first geospatial coordinate values for a current location of the user and a destination location. The GPS transceiver processes the user profile and the first geospatial coordinate values to identify a geographical route for traveling from the current location to the destination location. The GPS transceiver retrieves current traffic speed / traffic density data and historical traffic speed / traffic density data associated with second geospatial coordinate values for various locations located along the first geographical route. The GPS transceiver processes the current traffic speed / traffic density data and the historical traffic speed / traffic density data to determine if the first geographical route comprises an efficient geographical route for the user.
Owner:LINKEDIN
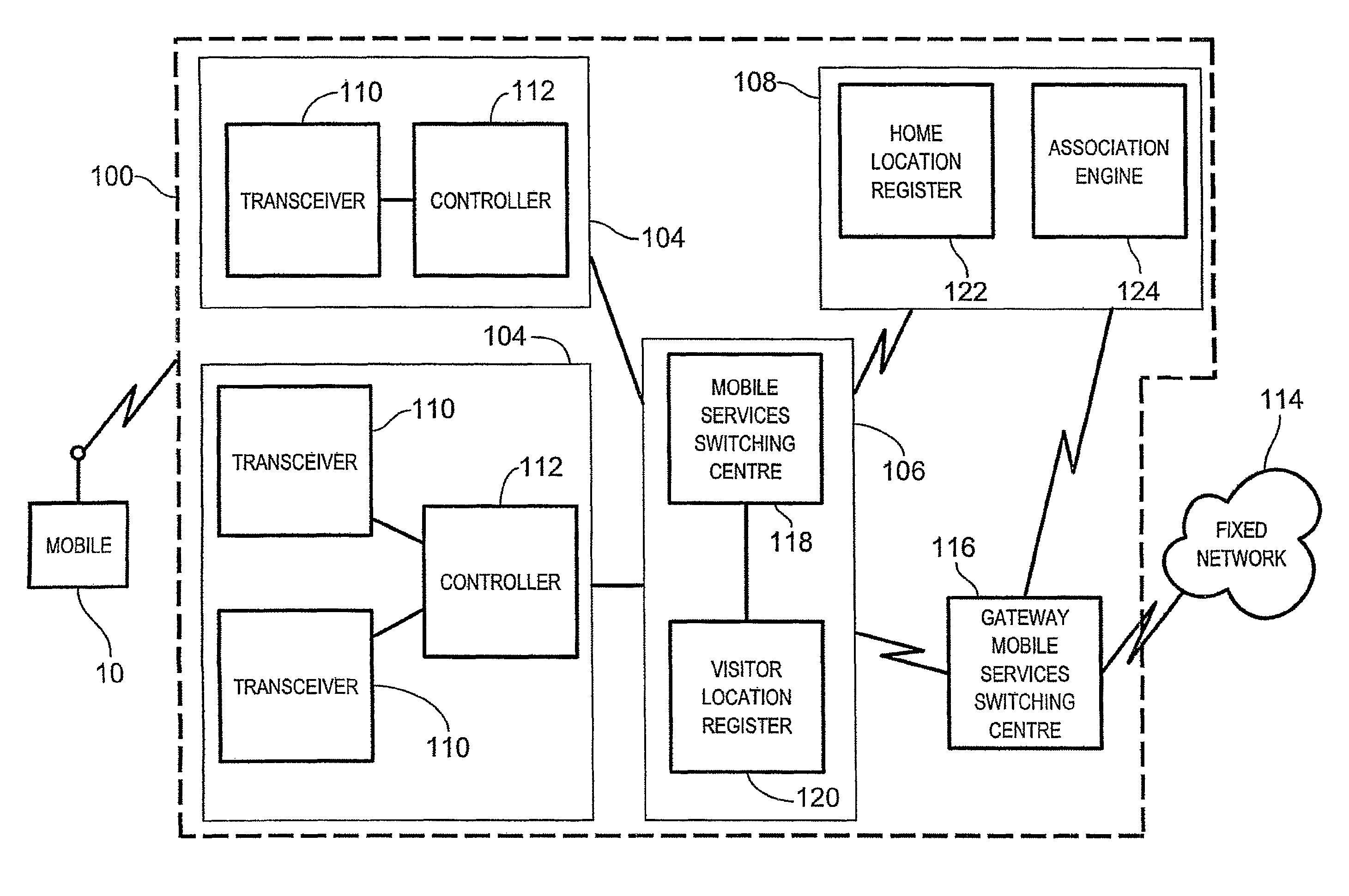
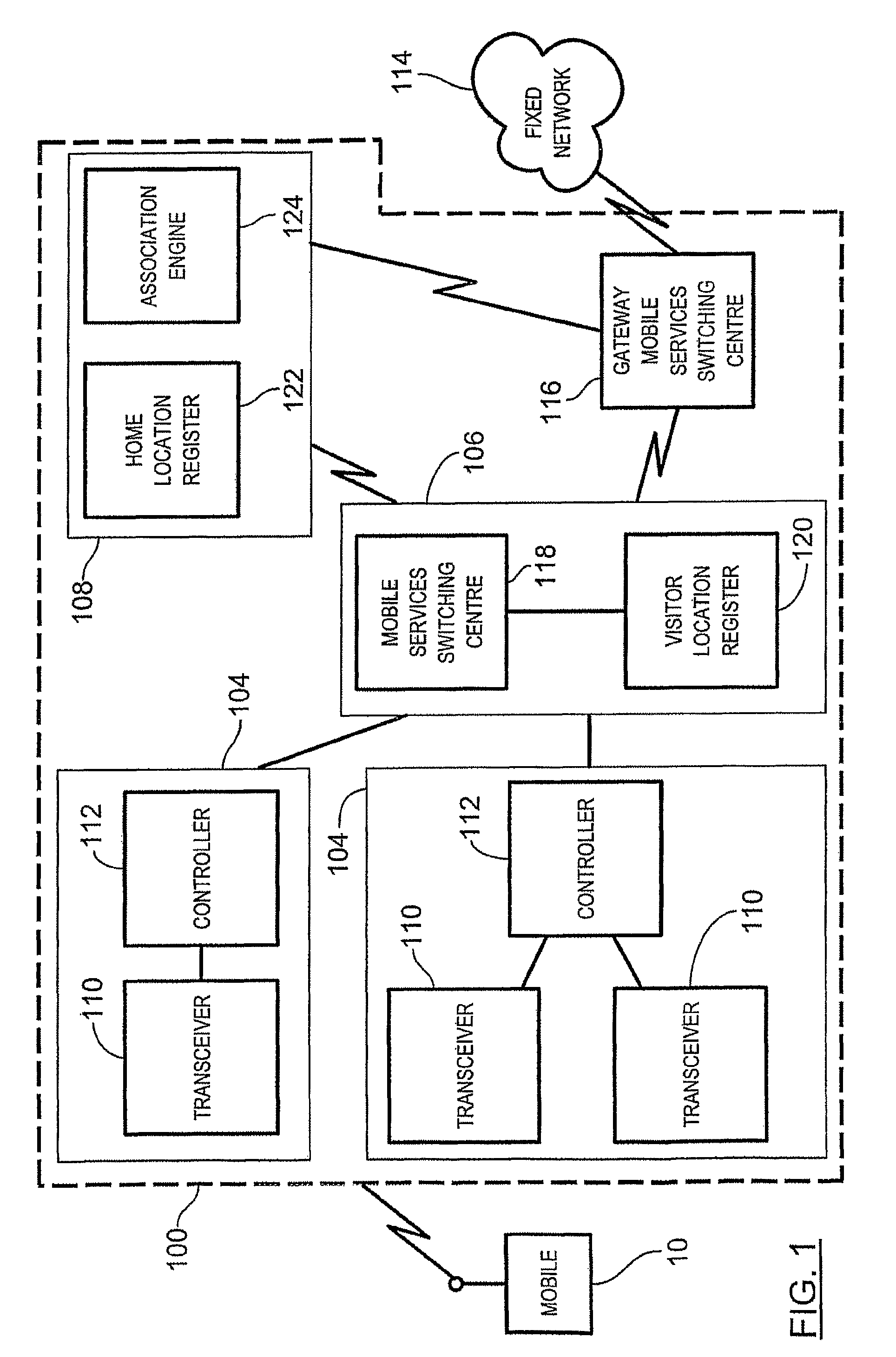
Dynamic identity association within a wireless network
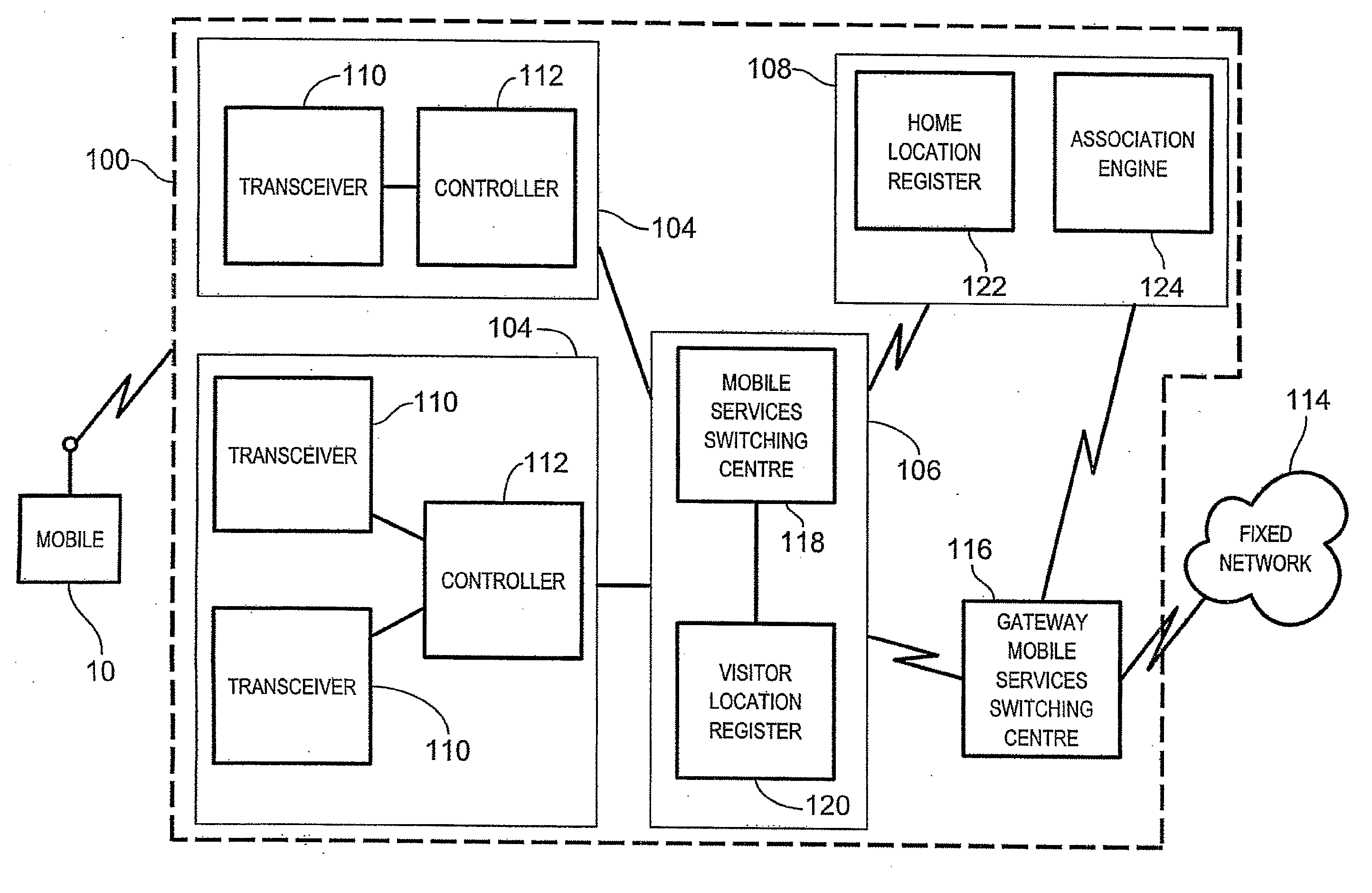
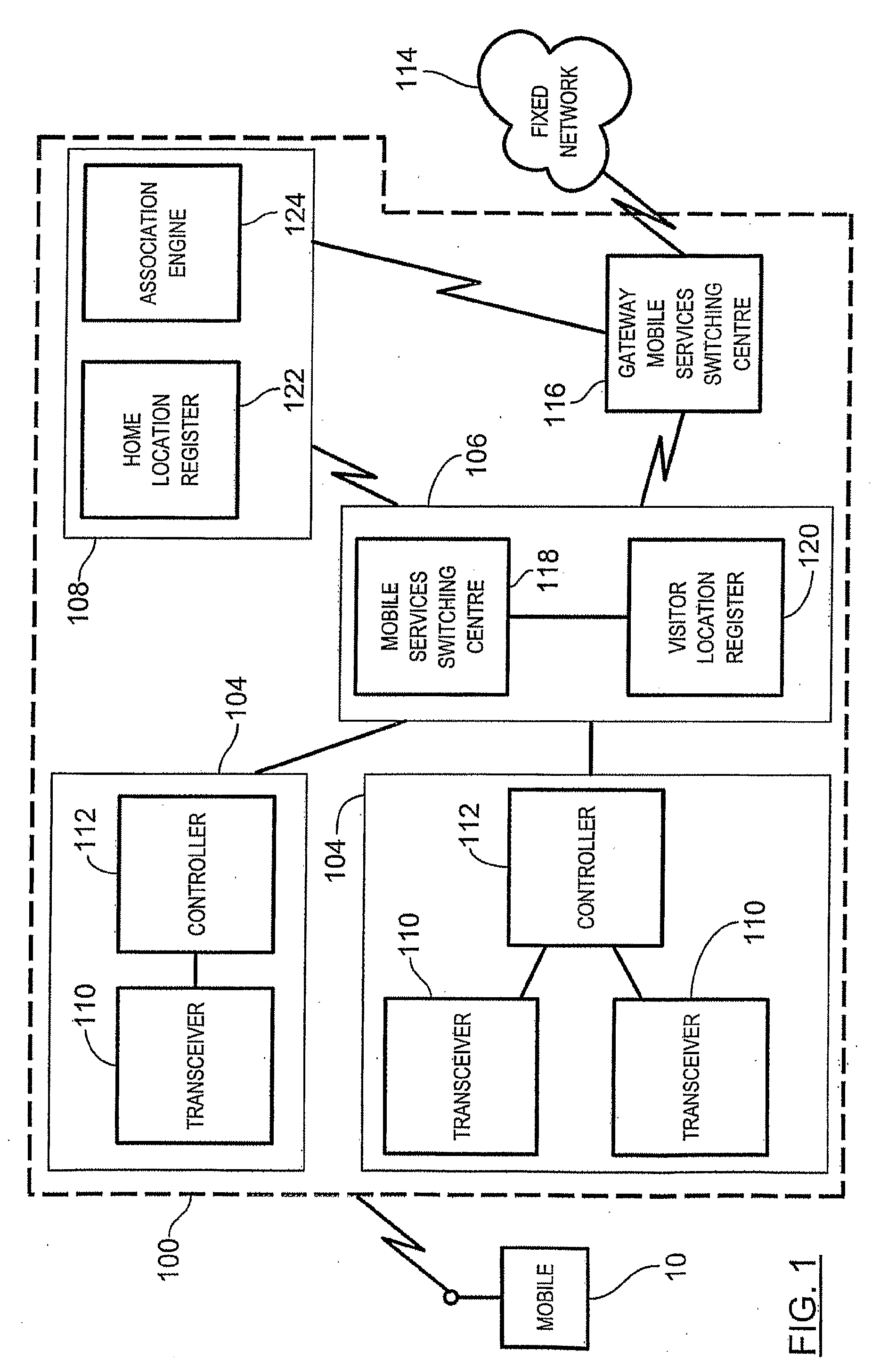
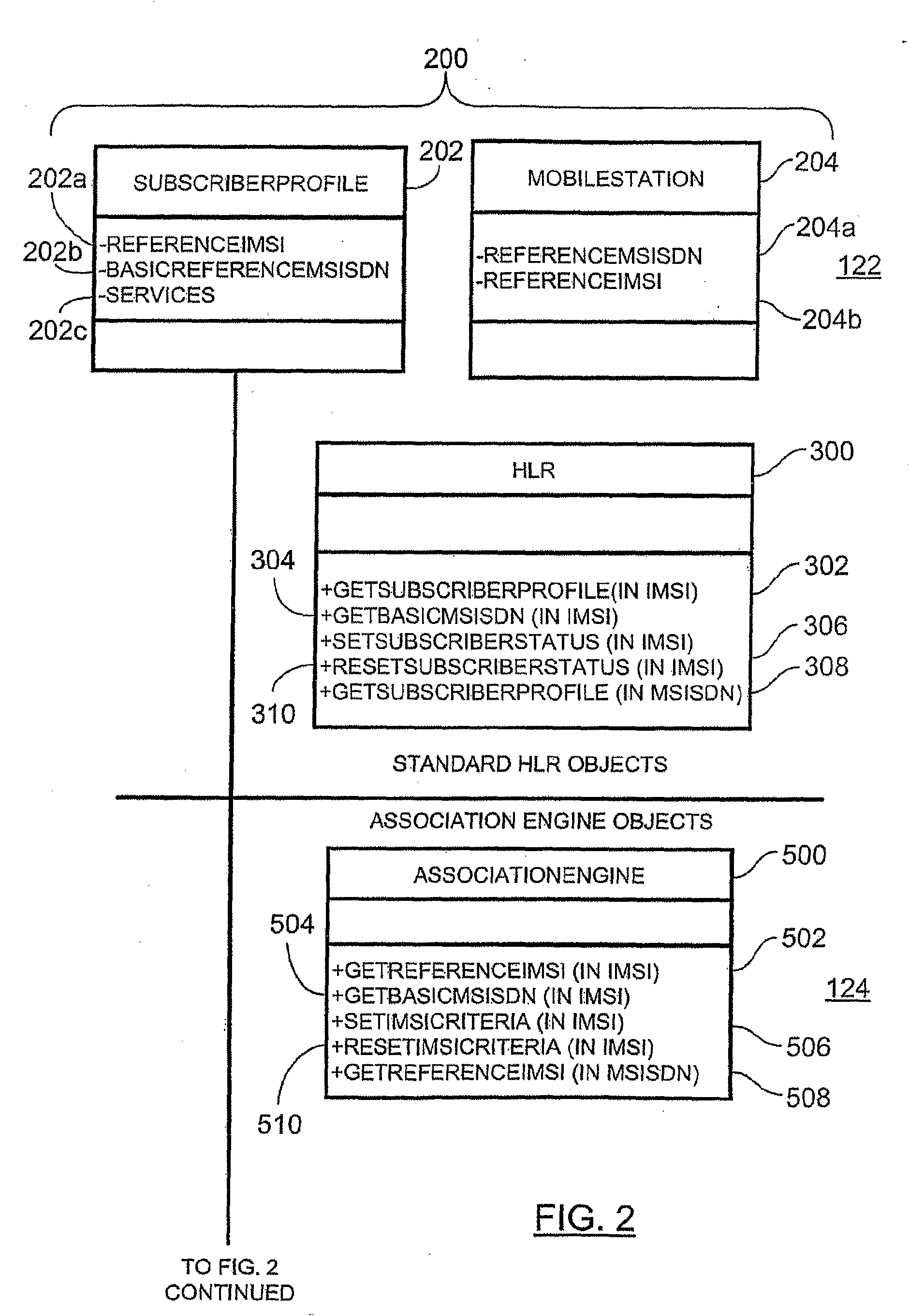
ActiveUS20090029684A1Special service for subscribersWireless commuication servicesGeographic regionsMobile station
A method of providing access to telecommunication services involves receiving a routing information request for terminating a communication with a mobile station located within a visited geographic region, the routing information request including a directory number local to the visited geographic region. A subscriber identity associated with the received directory number is then dynamically selecting from an evaluation of a decision tree, the decision tree associating a reference directory number with a plurality of reference subscriber identities. Each reference subscriber identity is associated with a telecommunications service user, each user being registered to receive telecommunication services within a respective home geographic region, the home geographic region being different from the visited geographic region. The mobile station receives access to the telecommunication services within the visited geographic region via the selected subscriber identity.
Owner:TEKELEC
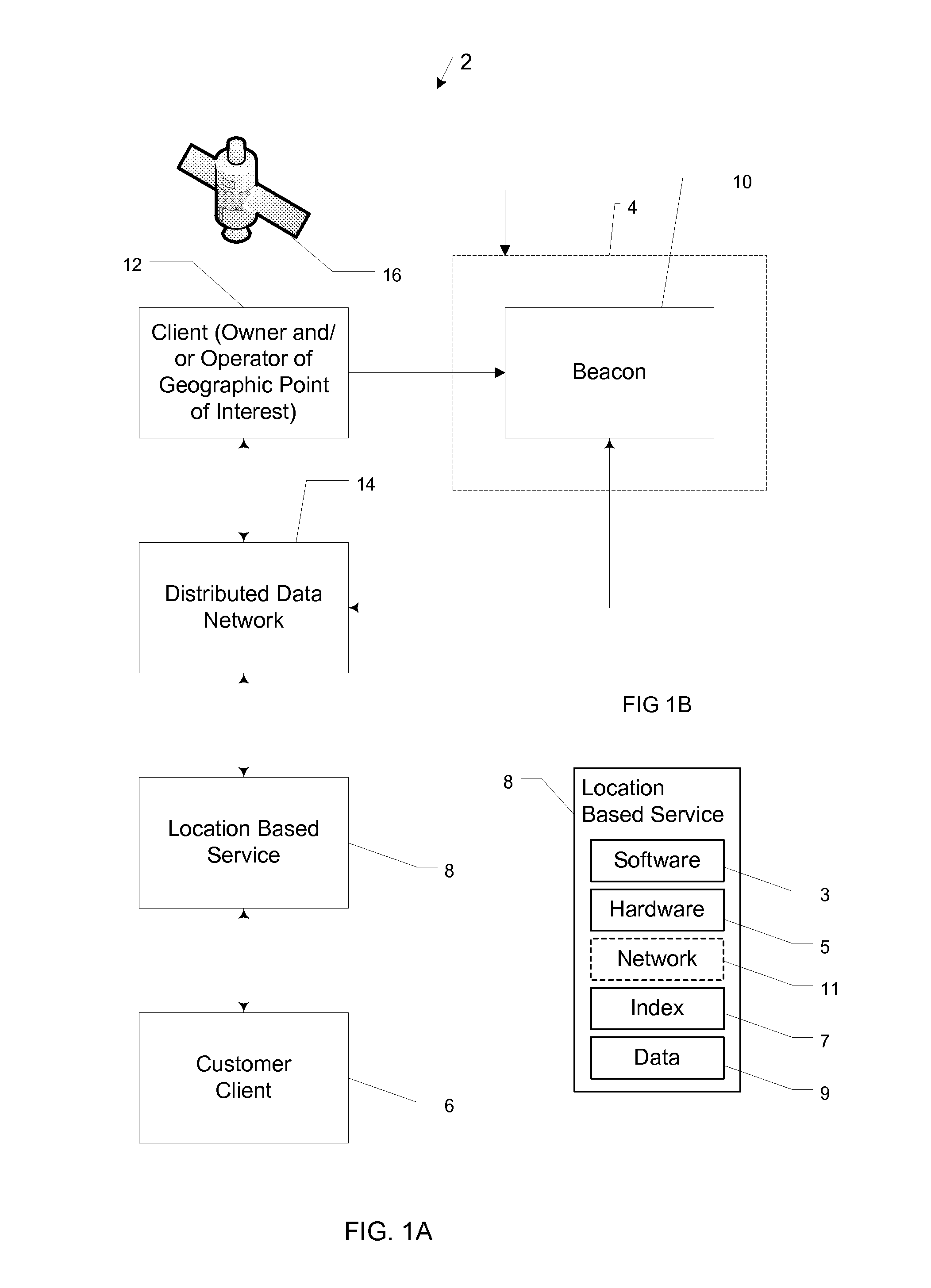
Device and system for providing current information for a geographic point of interest
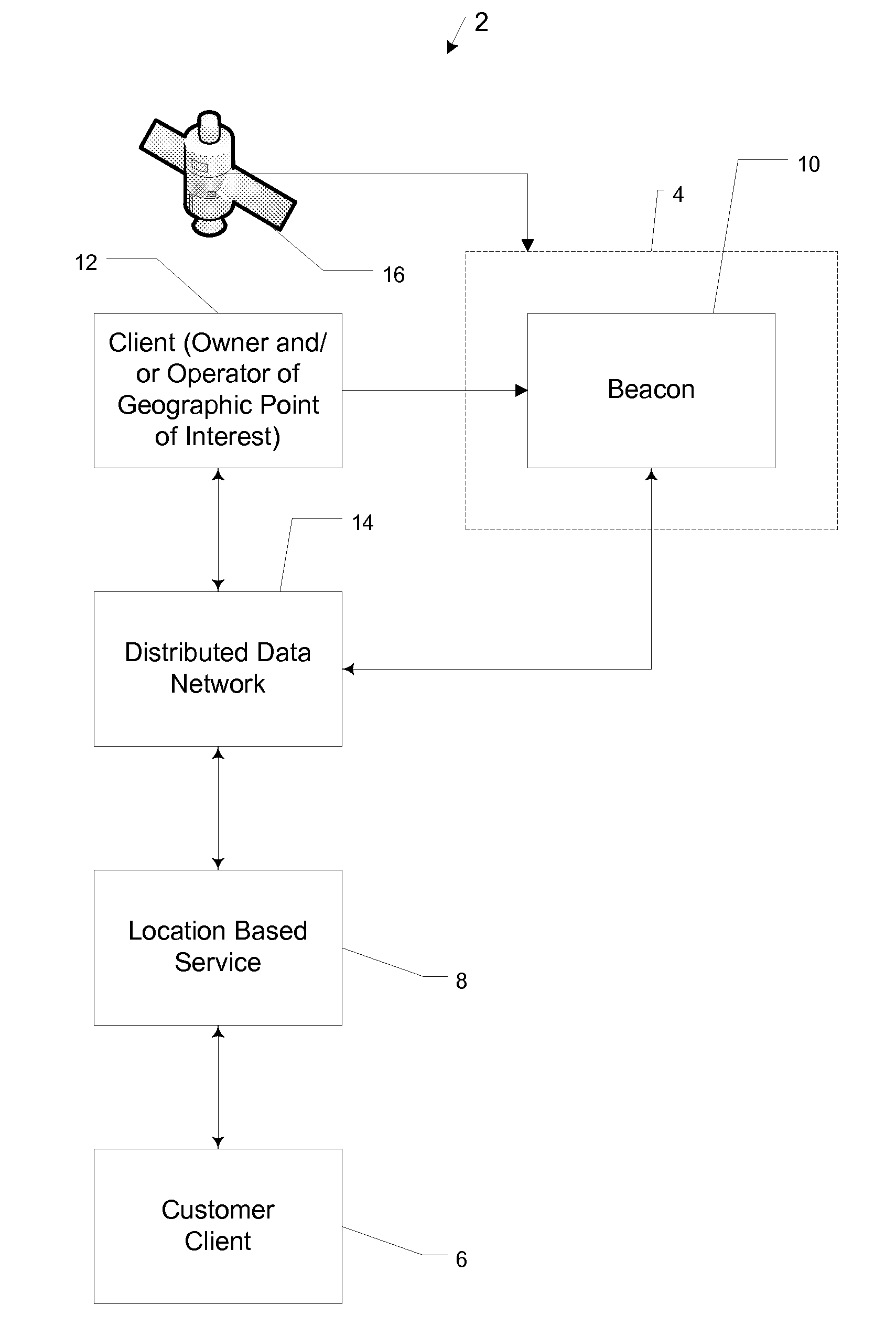
InactiveUS20120262277A1Digital data information retrievalElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingGeographic siteControl electronics
A computer-based system manages and communicates the identity, attributes, and current state of a geographic point of interest. The system includes a beacon device and a distributed data network. The beacon device includes a housing supporting control electronics, a display, and communication electronics. The beacon is placed at a visible location at the geographic point of interest and receives information concerning the geographical point of interest. The display visibly communicates the information while the communication electronics communicates the same information to the distributed data network. A user can query a location-based service and receive the same information from the distributed data network that is being communicated by the display, assuring communication of accurate and consistent information concerning the geographic point of interest.
Owner:RONIN LICENSING
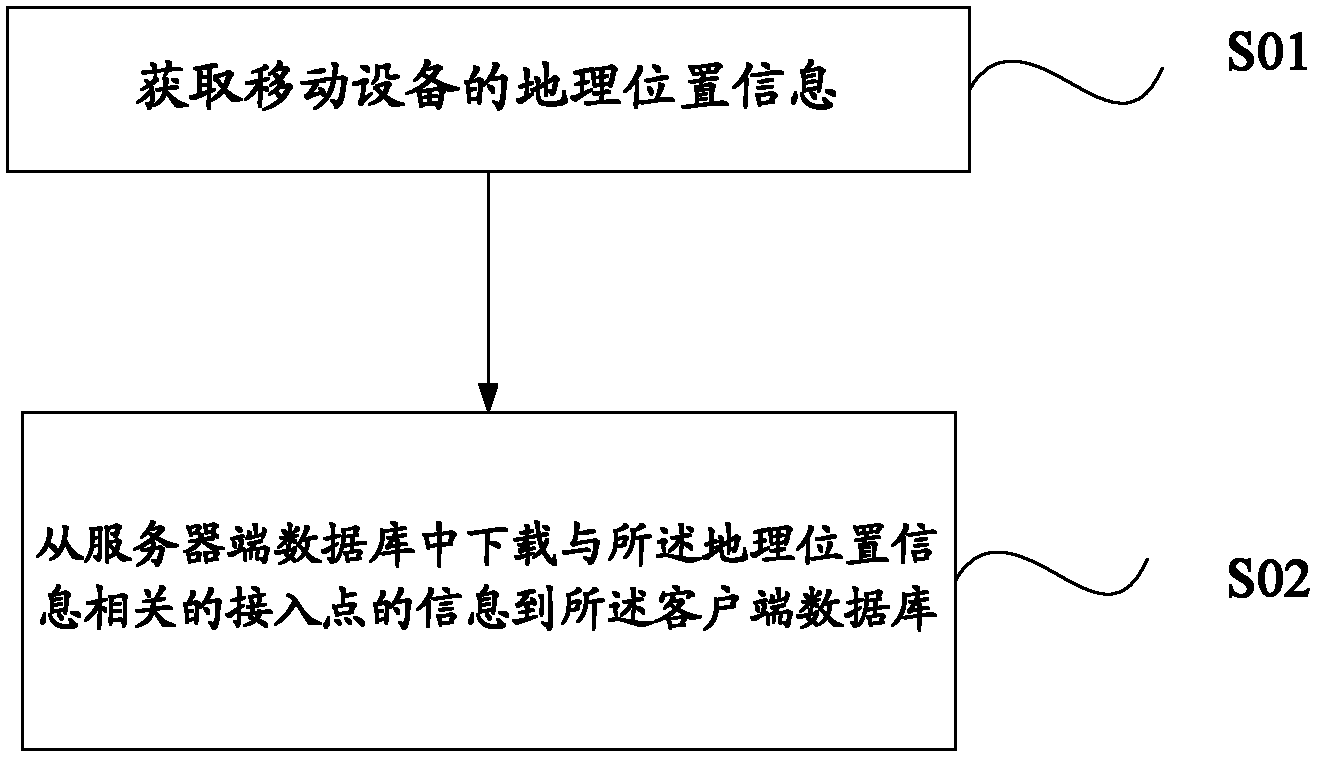
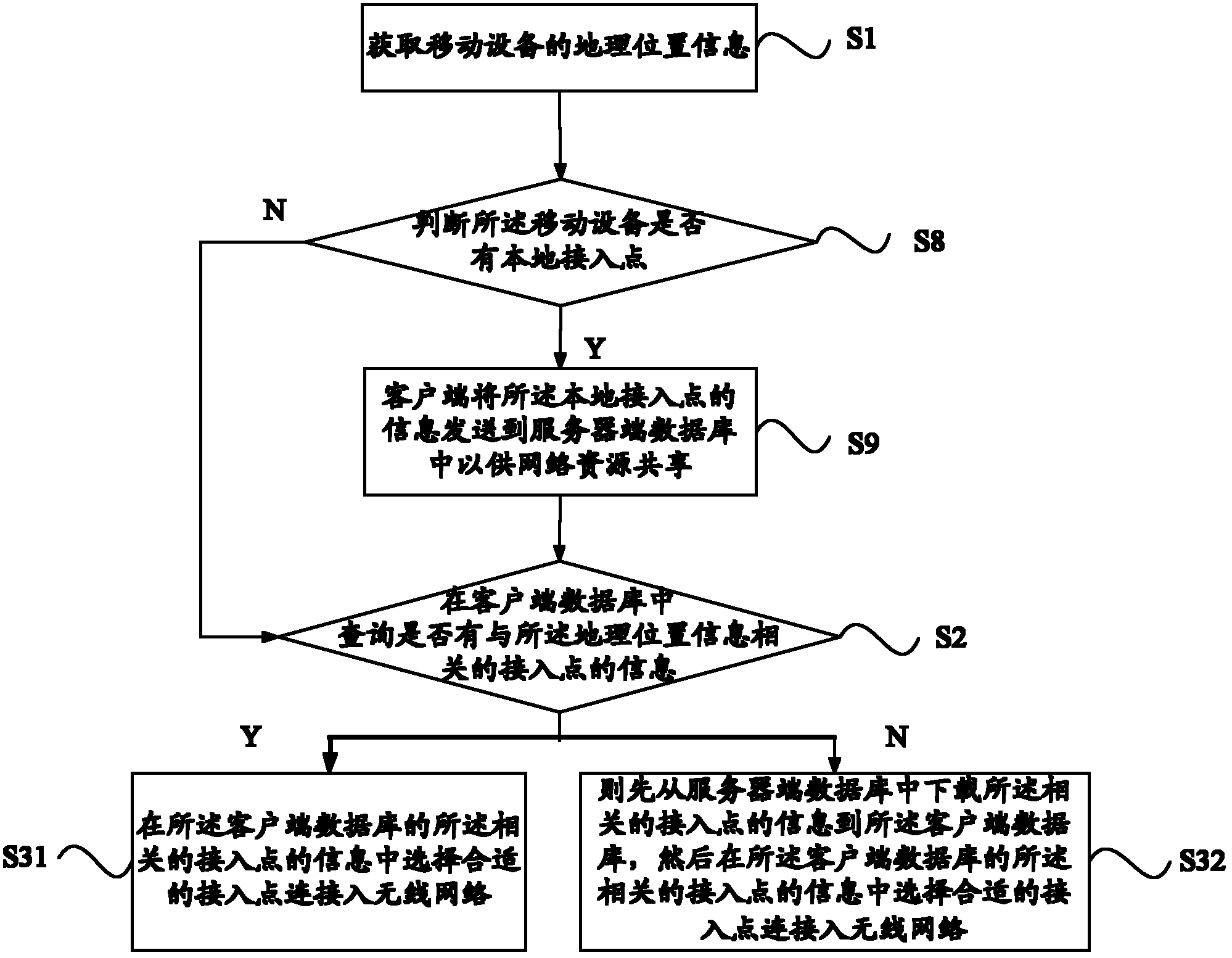
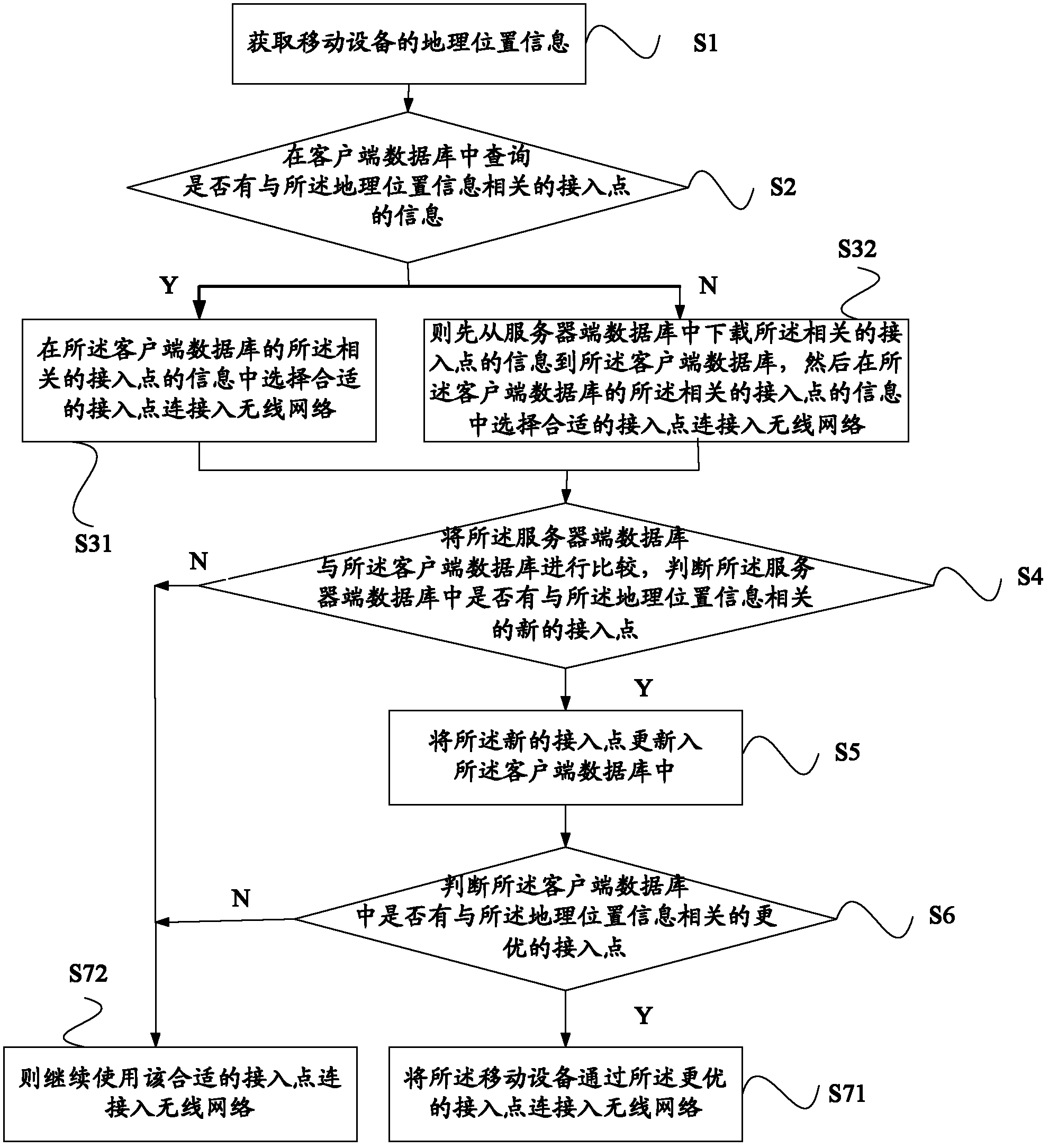
Method and system for obtaining wireless access point
InactiveCN102291799AAvoid occupyingEffectively foundAssess restrictionGeographic siteTelecommunications
The present invention relates to a method and system for acquiring a wireless access point, the method comprising: acquiring geographic location information of a mobile device; downloading information of wireless access points related to the geographic location information from a server-side database to the The client database described above. , the present invention obtains the geographic location information of the mobile device, and downloads the information of the wireless access point related to the geographic location information from the server-side database to the client database, so as to facilitate users who have not obtained wireless access before When you click on the permissions, you can obtain the permissions of these wireless access points through the wireless access point permissions shared by others, and use these contributed permissions to surf the Internet.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHANGMEN TECH
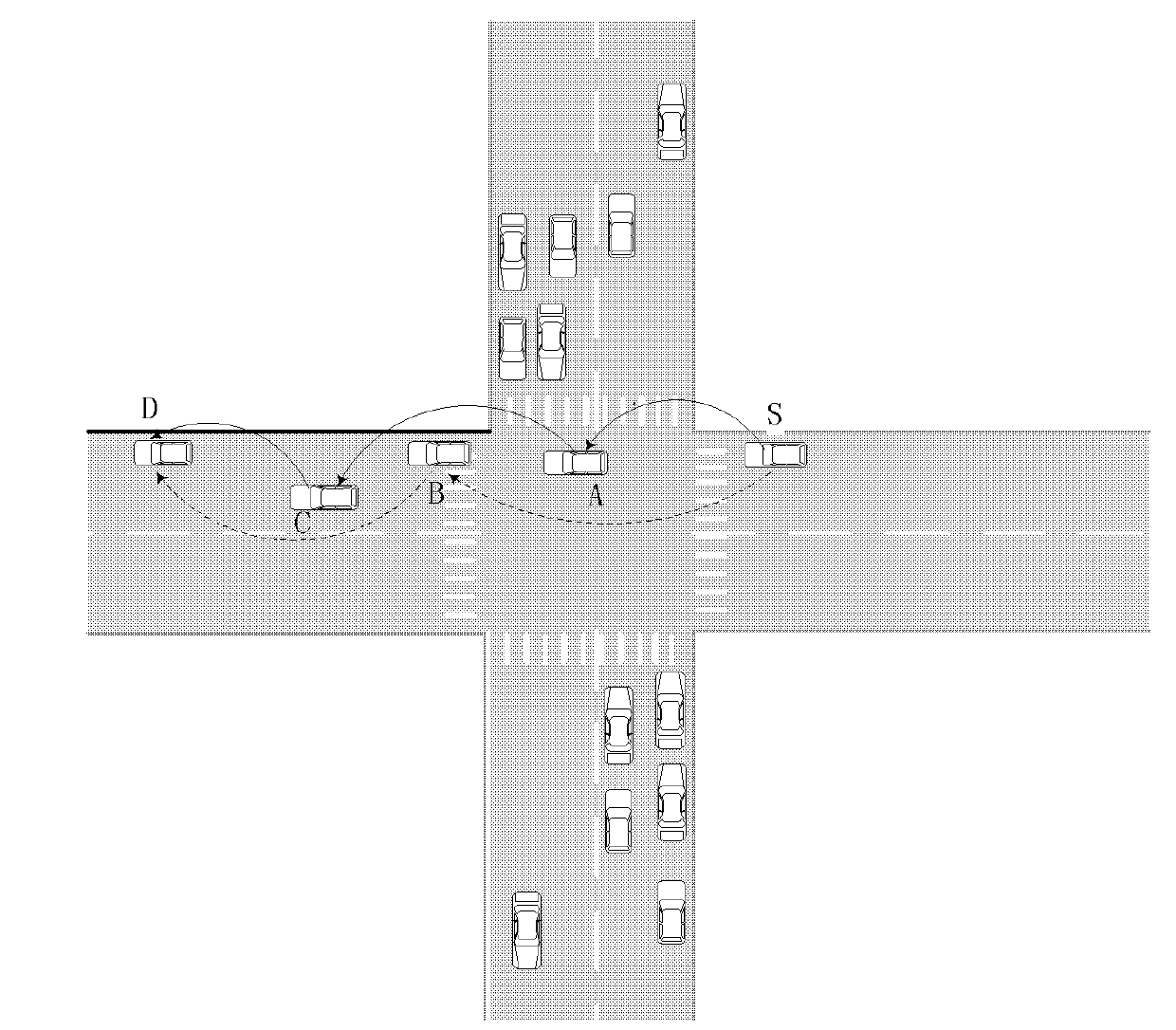
Prediction-based routing method at intersection in vehicle self-organizing network
InactiveCN102137462AShort transmission distanceGuaranteed normal transmissionAssess restrictionTransmissionIn vehicleTransmission time delay
The invention discloses a prediction-based routing method at an intersection in a vehicle self-organizing network, and mainly solves the problem that when a packet is routed at the intersection, a link is unstable in the prior art. The scheme for implementing the method is that: when the packet arrives at a previous hop node of the intersection, the node predicts the next intersection to which the packet is transmitted; a weight of each adjacent intersection is calculated according to the density of adjacent road sections and a distance from the next intersection to a destination, and the intersection with the largest weight is selected as the next temporary destination for transmitting the packet; and when the packet is forwarded in a greedy mode in the road section, if the selected nodeis positioned in the boundary of the transmission range and is opposite to a driving direction of the transmitting node, a node secondarily nearest to the destination is selected, otherwise the packet is directly forwarded to the selected node. Compared with the geographic routing in city scenarios (GPCR) protocol and the greedy perimeter stateless routing for wireless networks in urban vehicularscenarios (GpsrJ+ protocol), the method has the advantages that: the transmission rate of the packet is increased, the transmission time delay of the packet is reduced, and the method can be applicable to the vehicle self-organizing network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
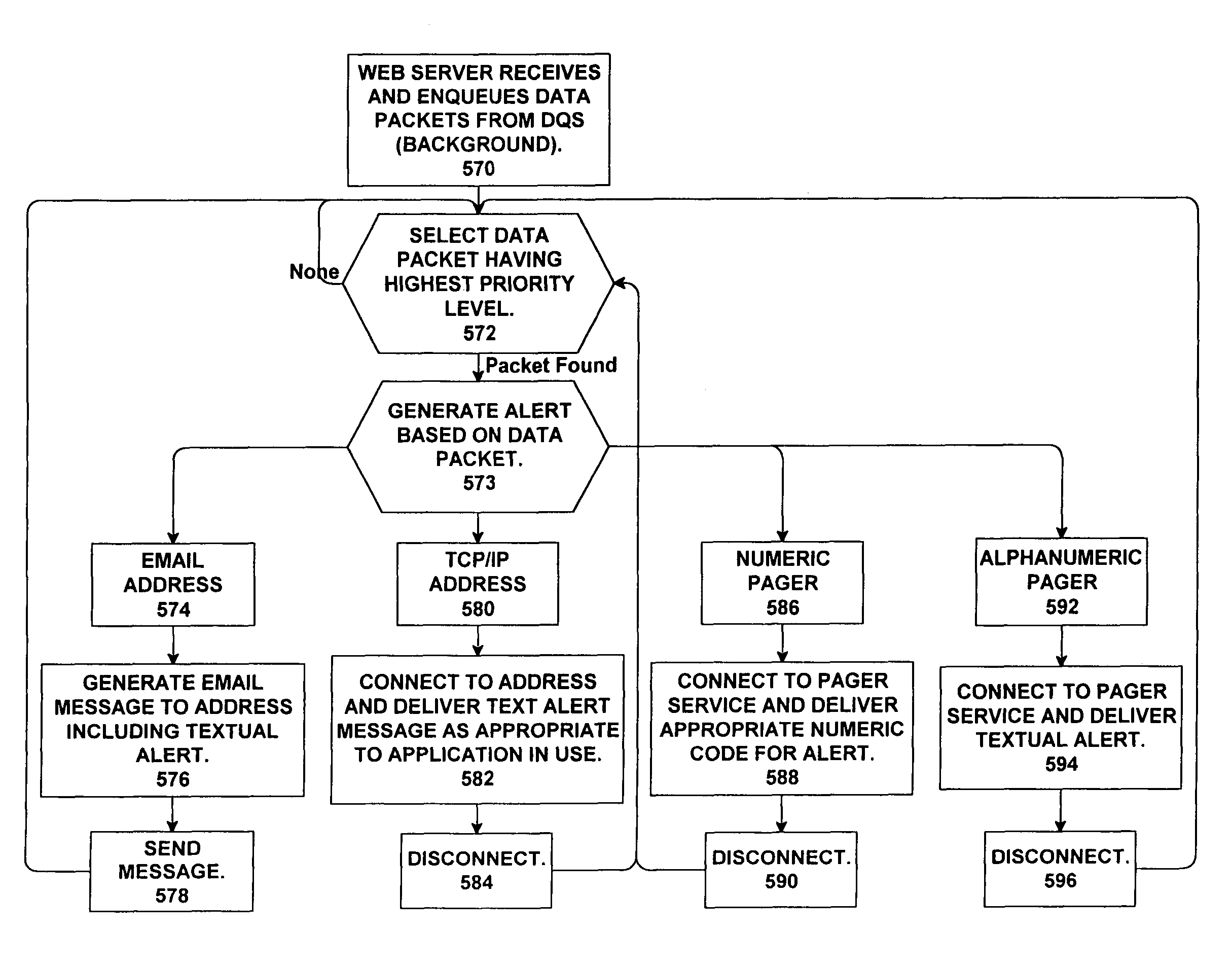
Alert notification system
A system for providing alert notifications to multiple persons or to a plurality of related geographic locations. The system stores a database of information including a plurality of communications identifiers and additional information for subscribers having those identifiers, including geographic locations and / or school / organization membership information. The system responds to commands identifying alerts to be delivered to affected geographic areas or schools / organizations, by retrieving communications identifiers in the threatened geographic location or associated with the named school / organization, establishing a communications connection using each retrieved communication identifier, and delivering the alert. Alerts may be initiated by authorized personnel via telephone or Internet interaction with the system, or may be generated automatically from data feeds such as the EMWIN system of the National Weather Service. Alerts may be delivered via telephone, pager (voice or text), e-mail, Internet, or other media.
Owner:ZIMMERS STEVEN L +1
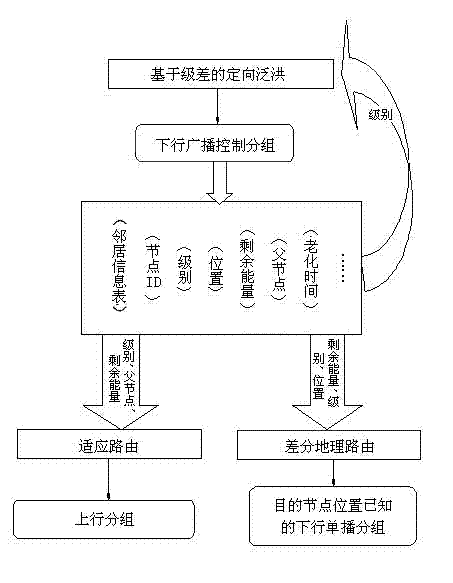
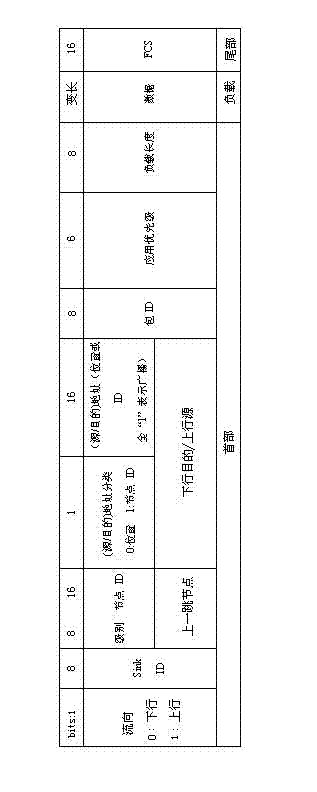
Method for adaptively routing underwater sensor network on basis of difference
InactiveCN102868974ACutting costsLower latencyPower managementEnergy efficient ICTPathPingEngineering
The invention generally relates to the technical field of network communication, and particularly relates to a method for routing an underwater sensor network. The method for routing comprises the following constituent parts: (1) node grade definition; (2) node grade information acquiring and updating processes; (3) neighbor node information recording; (4) directional flooding mechanism based on grade difference; (5) adaptive routing step based on the grade difference, node density and residual energy; and (6) differential geographical routing step based on the grade difference and distance. The method has the following advantages that the best next hop adaptive routing is determined on the basis of the neighbor table information to reduce redundant paths, so that the energy efficiency is improved to a great extent; and the adaptive routing adopts immediate routing, so that the inhibition time of the conventional underwater UWSN (underwater wireless sensor network) routing to a received package is avoided, and the time delay from terminal to terminal is reduced. A great deal of simulation experiments prove that through an underwater sensor network adaptive routing protocol based on the difference, the energy consumption can be reduced to a great extent, the time delay from terminal to terminal is reduced, the node utilization equity is improved, and the whole network life time is prolonged.
Owner:QINGHAI NORMAL UNIV +1
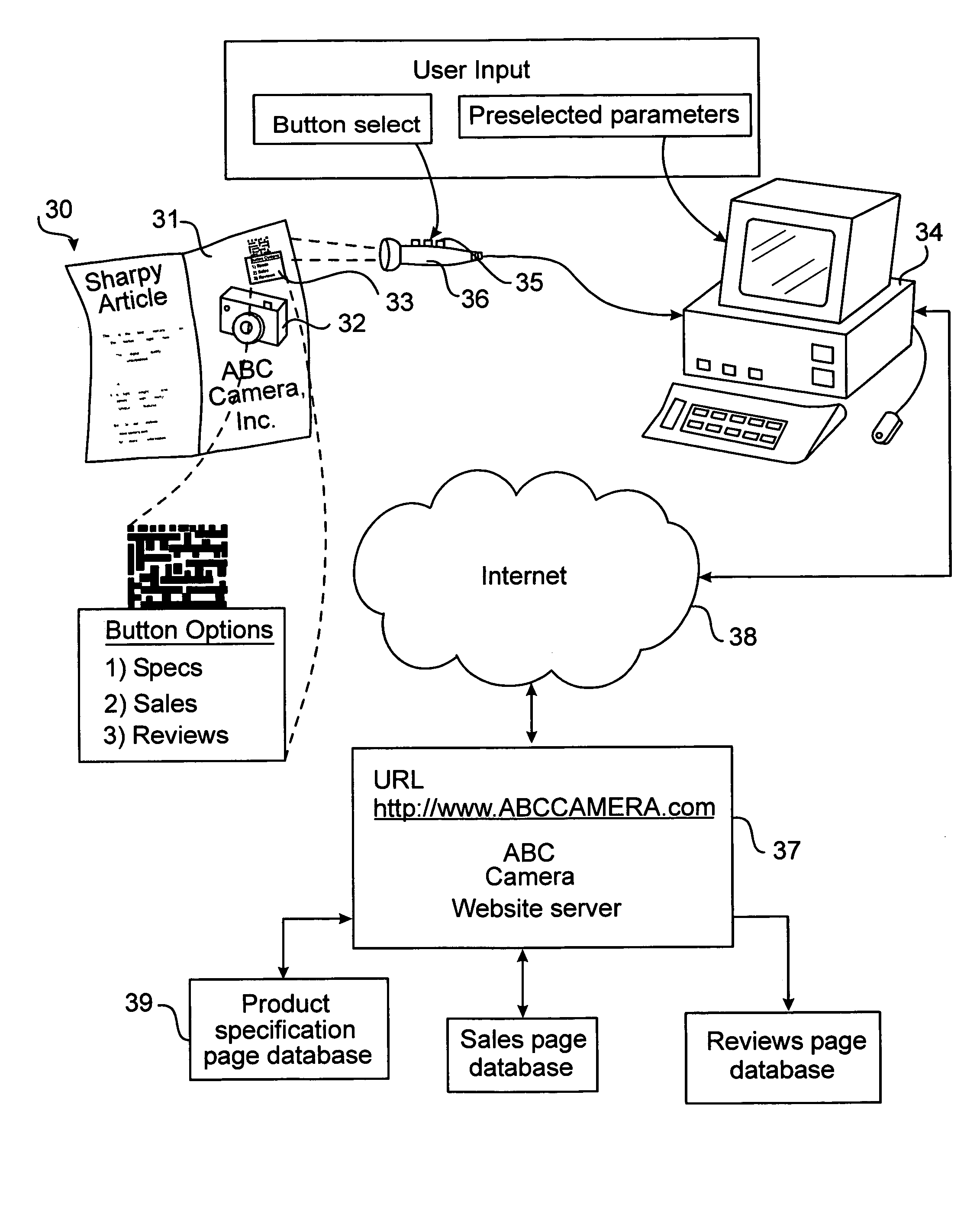
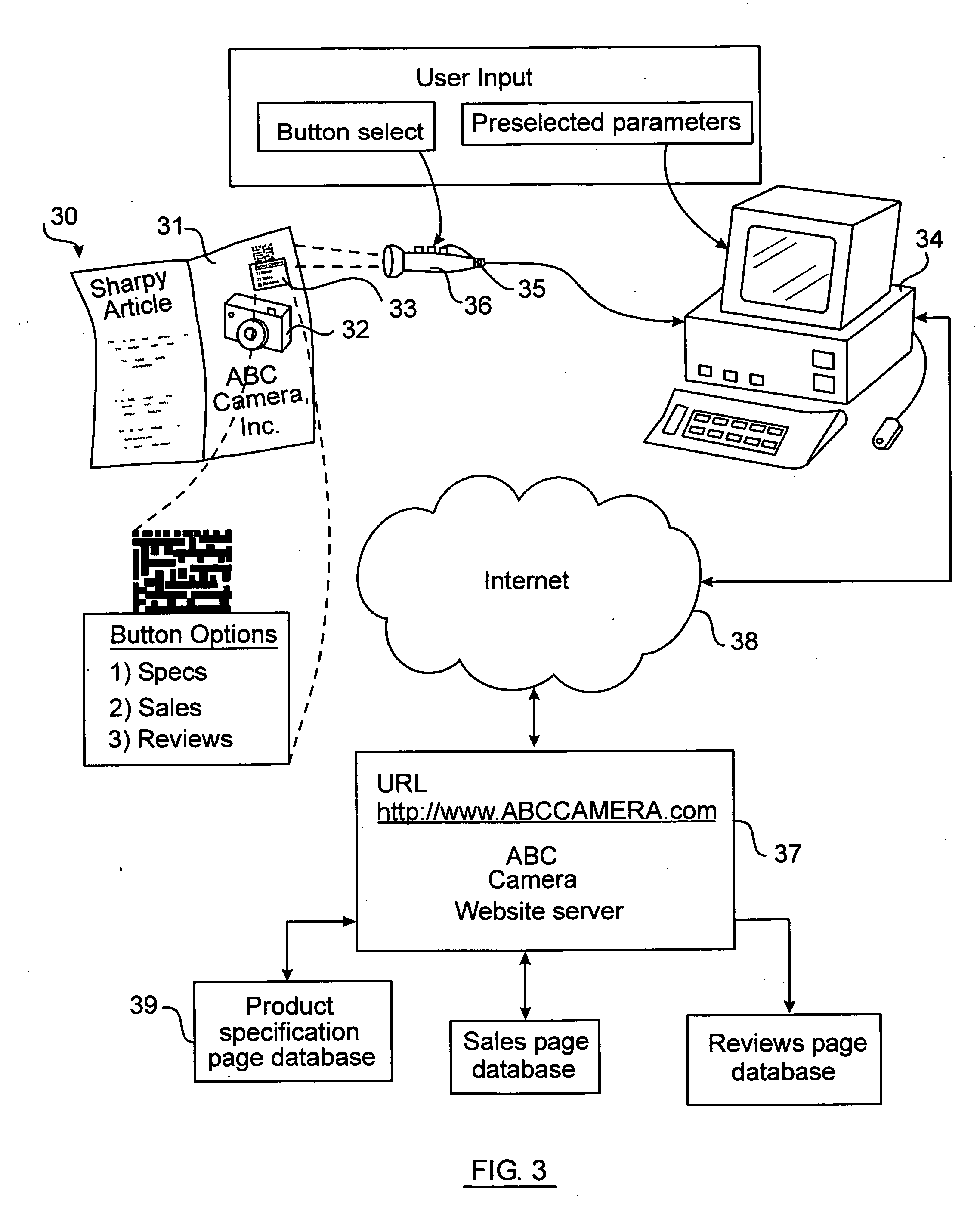
Interactive printed page optical code data access system and method
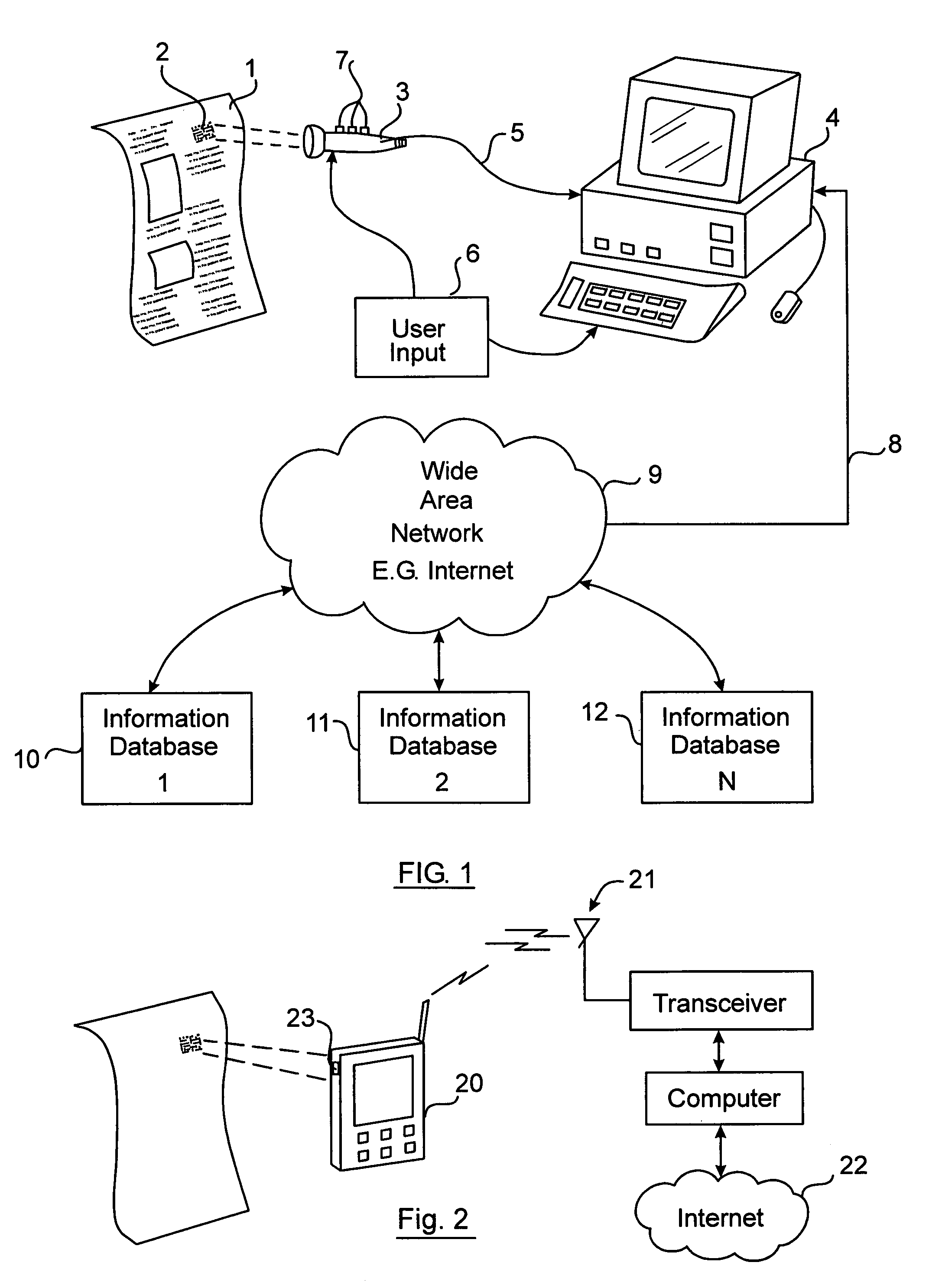
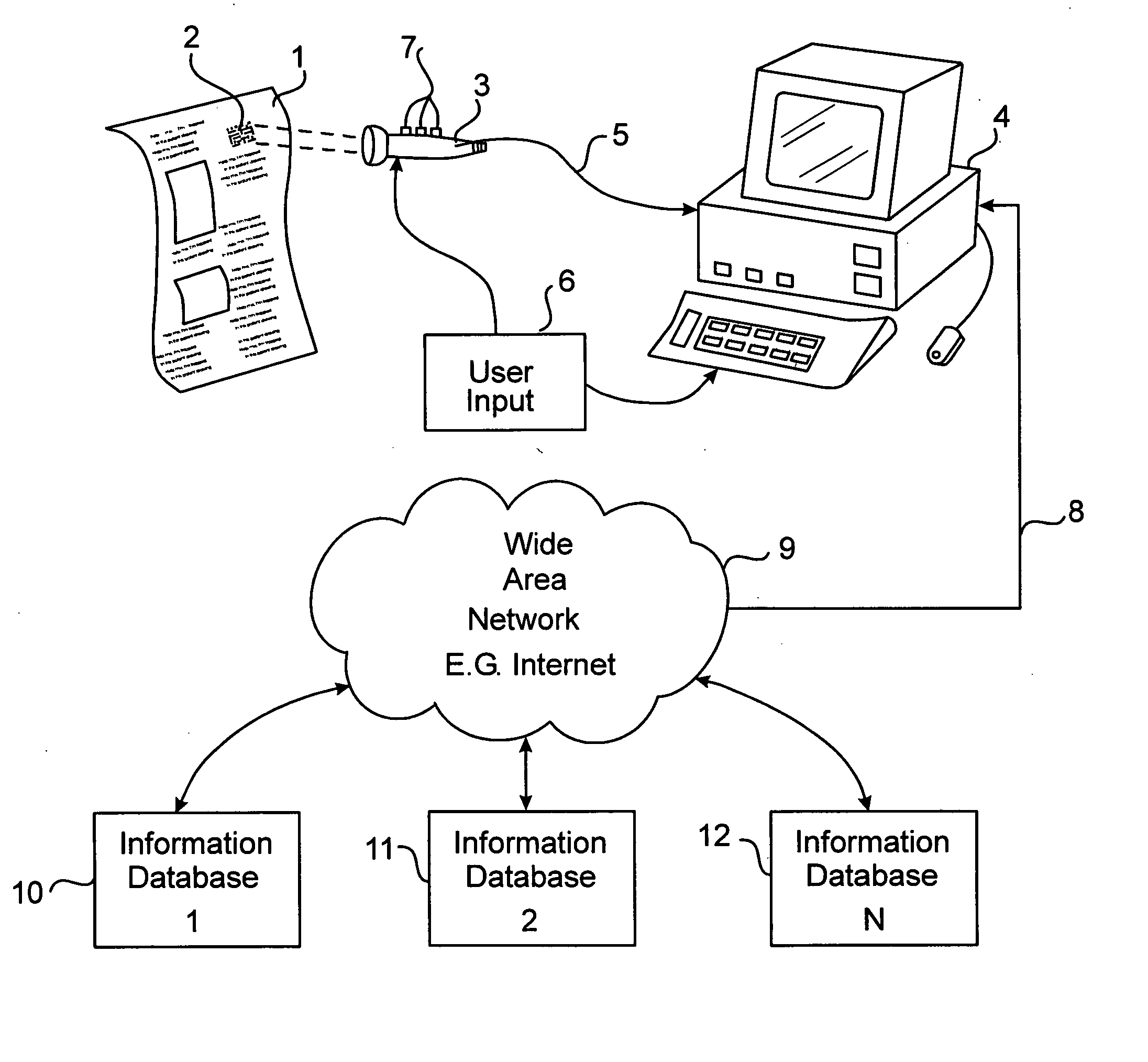
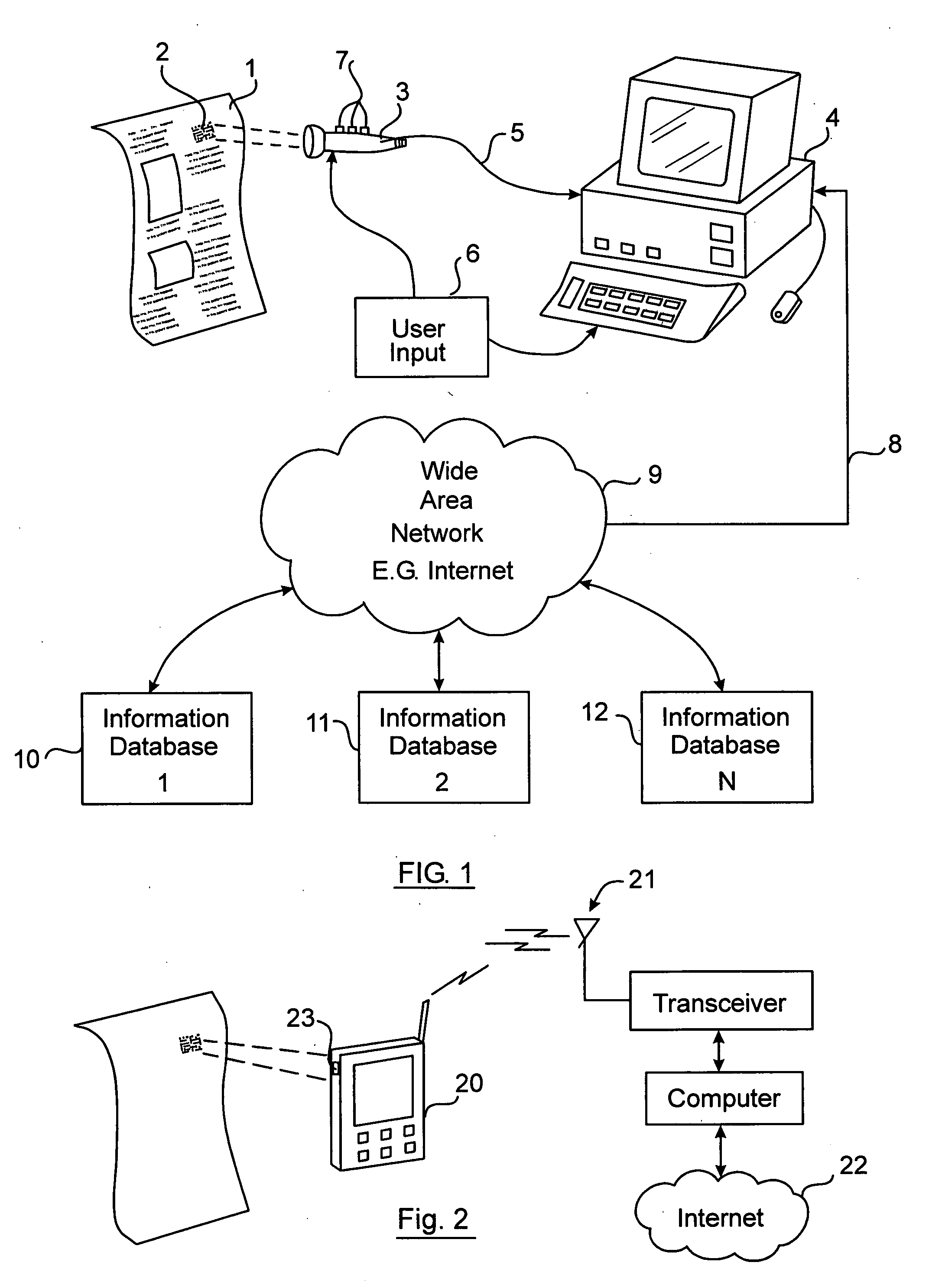
InactiveUS7505928B2Efficiently and interactivelyWide degree of flexibilityCommerceUser inputGeolocation
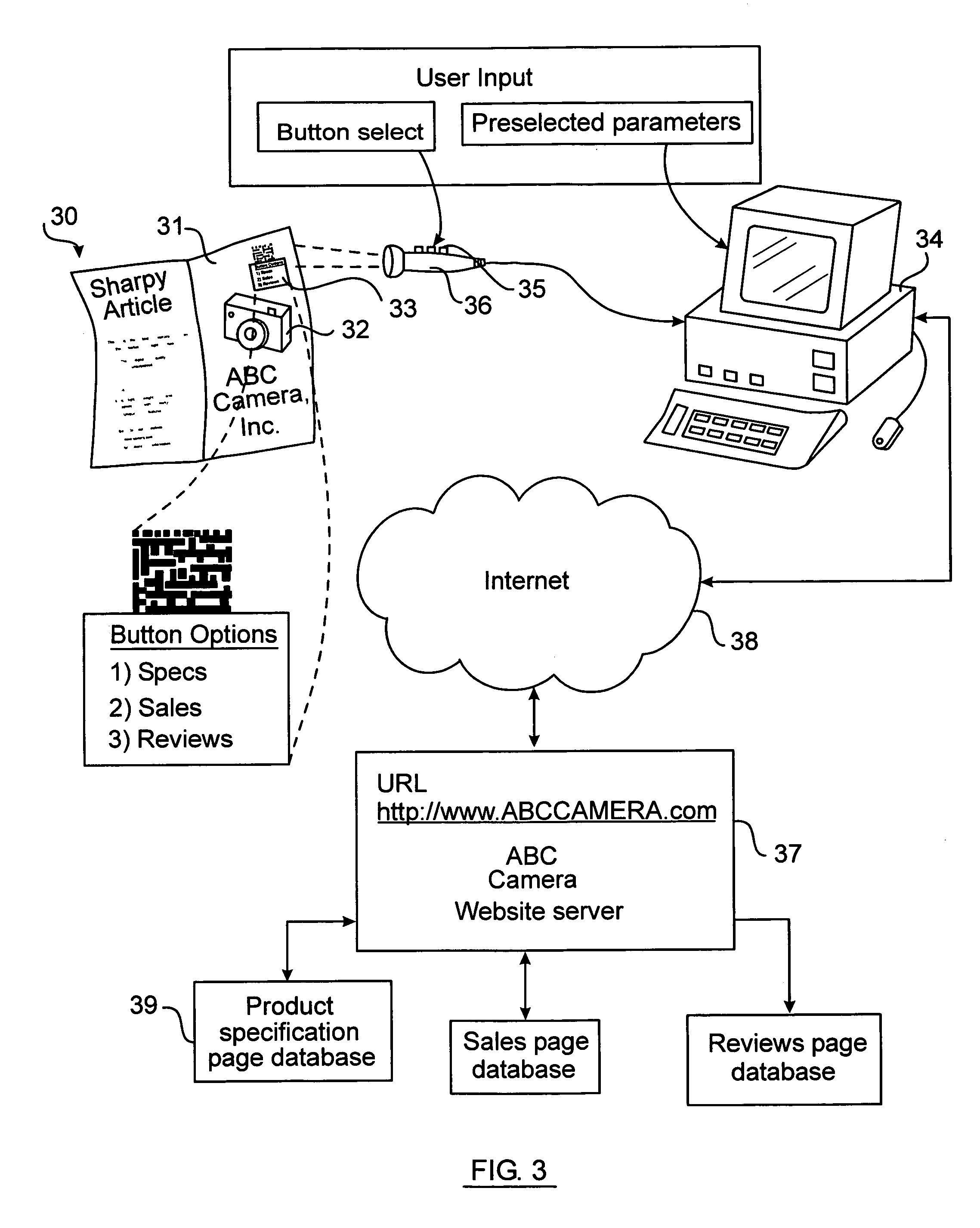
An interactive wide area computer network system and method for accessing and transmitting data using a printed page optical code. The code includes a system configuration mode identifier which configures the system to perform specified functions and allow the user certain interactive options. Based on the configuration mode and the user's selected option, the system generates and executes the necessary queries, commands, and responses to be routed upon the network. In an embodiment, a two dimensional optical code (“2DOC” or “barcode”) is printed on a magazine page advertisement containing information such as internet web addresses, product identity, advertisement identity, location, page number, magazine issue number, and geographic routing numbers. The system extracts this information using an optical code reader and combines it with user input parameters to generate network commands which access web pages, and / or transmit and receive relevant data via a user's computer connected to the internet and running an internet browser. The user may select an option wherein the system performs unique tasks depending on the advertisement.
Owner:LEBASCHI ALI
Interactive printed page optical code data access system and method
InactiveUS20060106623A1Efficiently and interactively accessWide degree of flexibilityCommerceUser inputThe Internet
An interactive wide area computer network system and method for accessing and transmitting data using a printed page optical code. The code includes a system configuration mode identifier which configures the system to perform specified functions and allow the user certain interactive options. Based of the configuration mode and the user's selected option, the system generates and executes the necessary queries, commands, and responses to be routed upon the network. In an embodiment, a two dimensional optical code (“2DOC” or “barcode”) is printed on a magazine page advertisement containing information such as internet web addresses, product identity, advertisement identity, location, page number, magazine issue number, and geographic routing numbers. The system extracts this information using an optical code reader and combines it with user input parameters to generate network commands which access webpages, and / or transmit and receive relevant data via a users computer connected to the internet and running an internet browser. The user may select an option wherein the system performs unique tasks depending on the advertisement.
Owner:LEBASCHI ALI
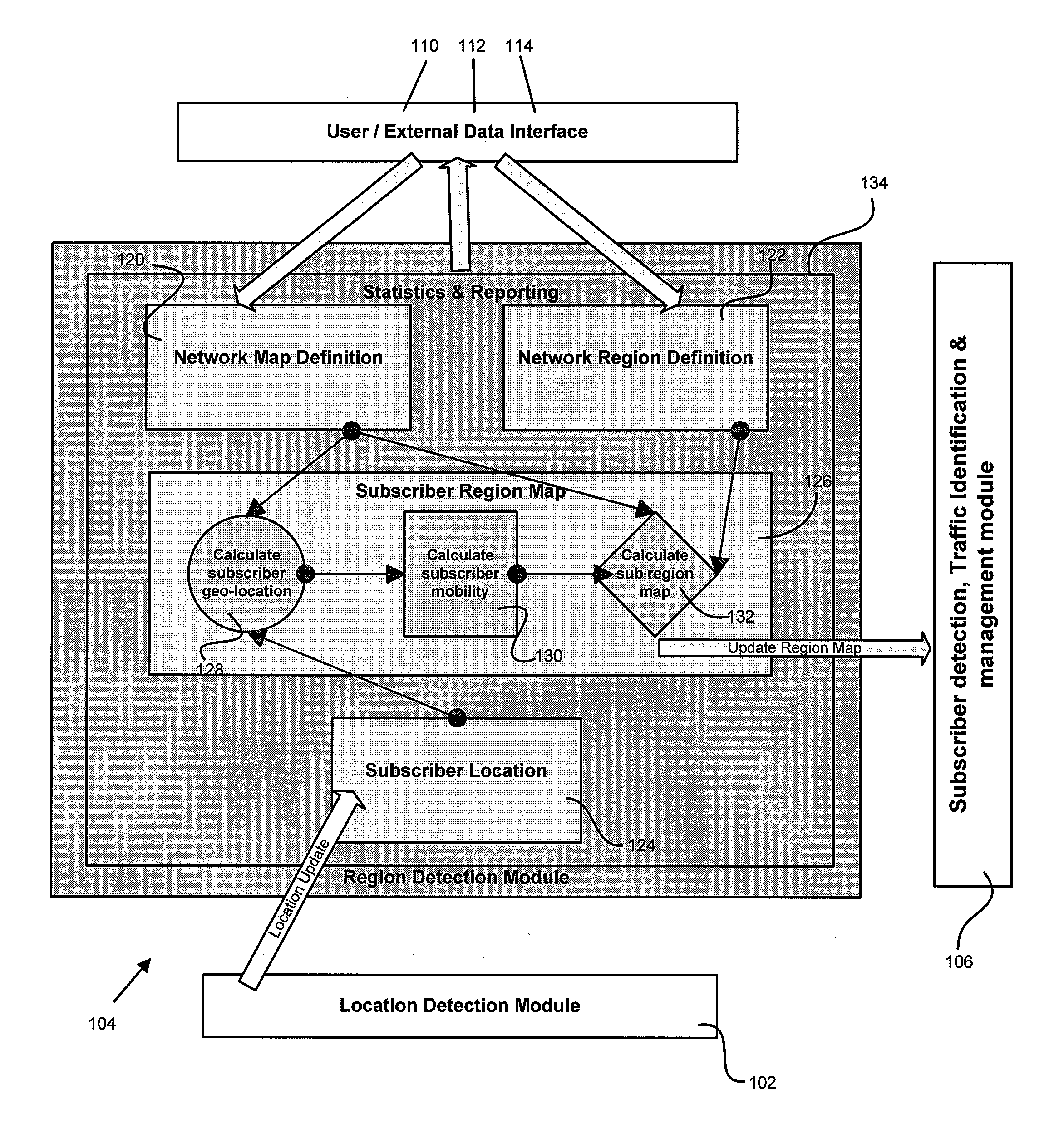
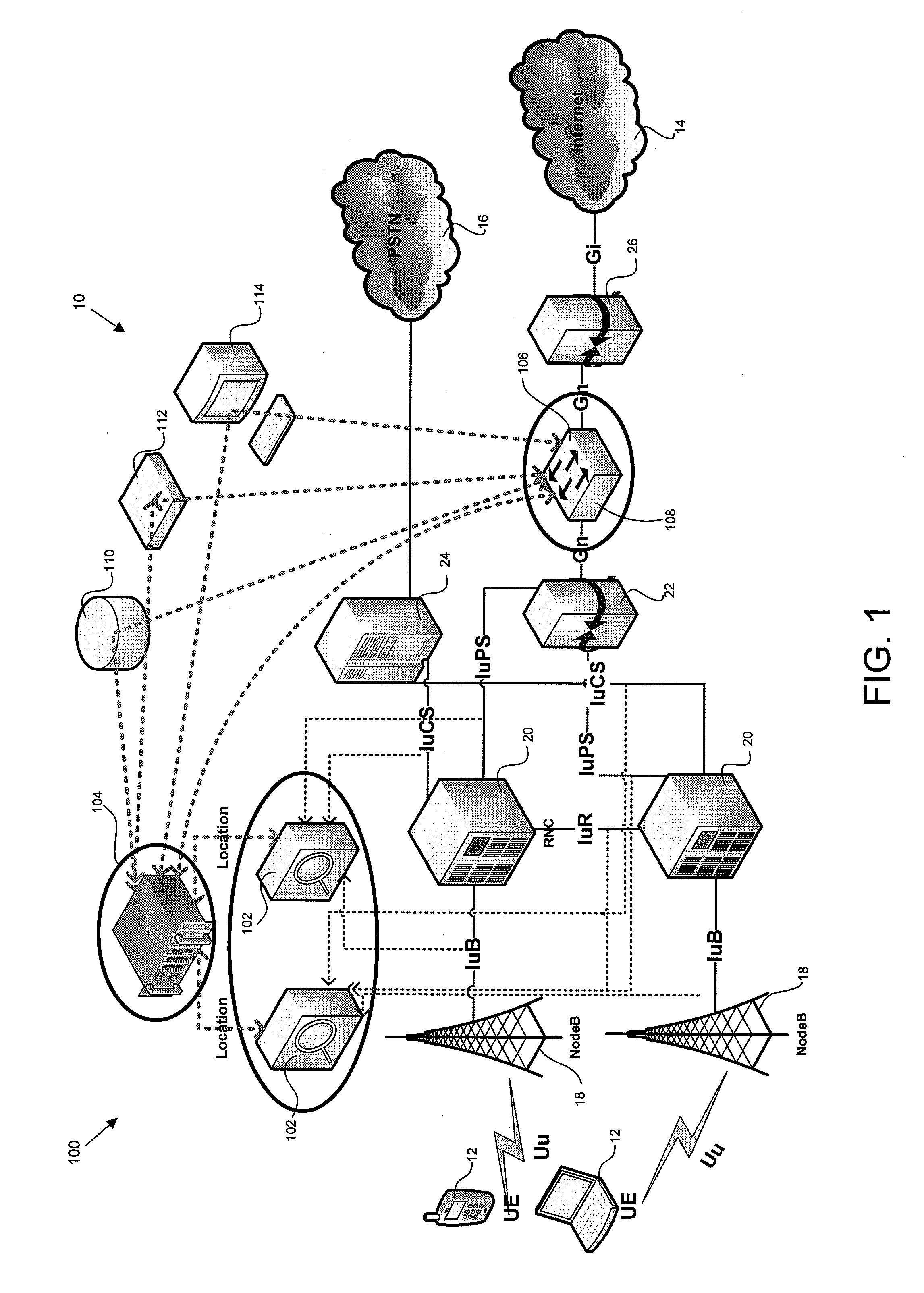
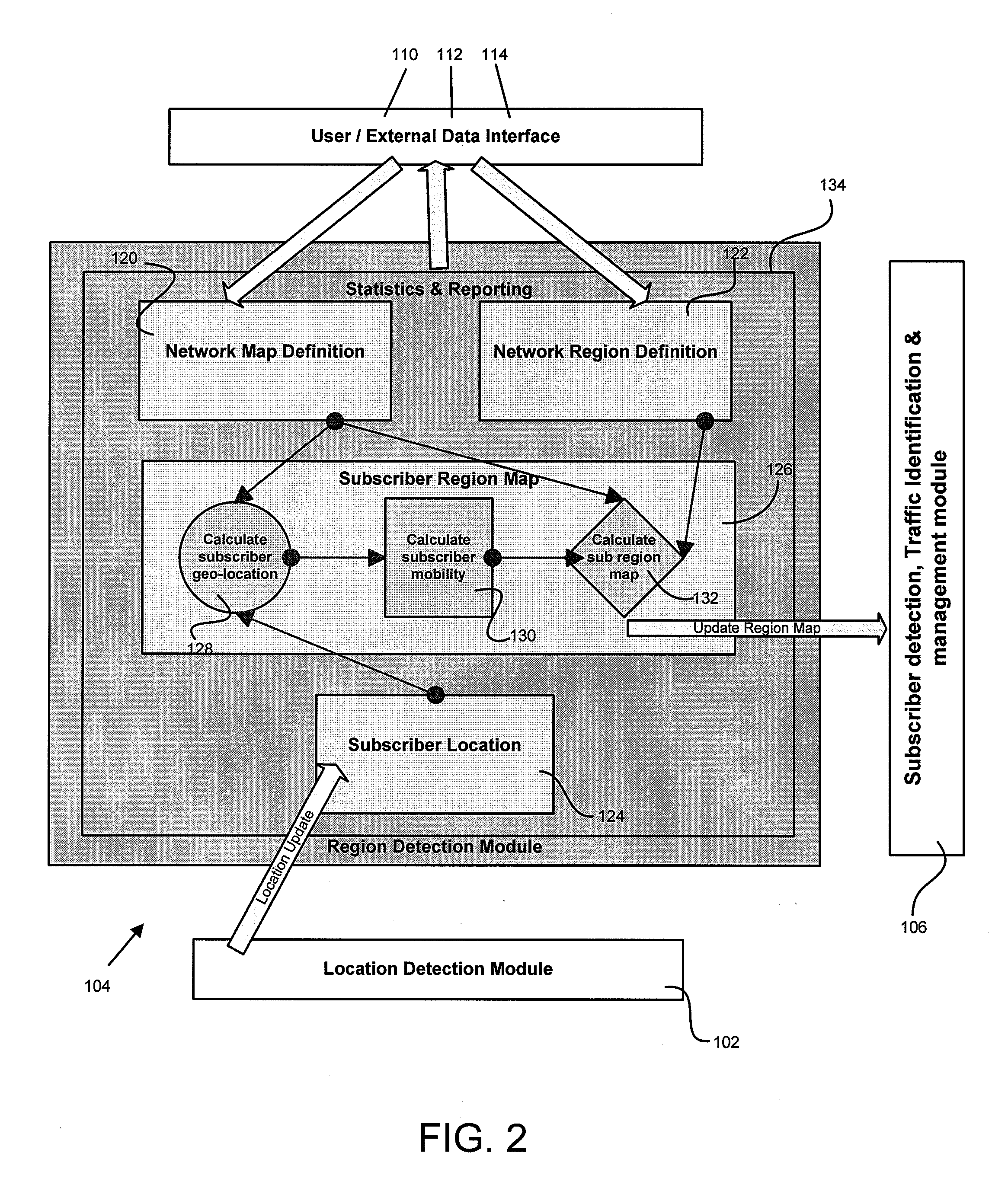
Methods and systems for network services related to geographic location
ActiveUS20130210464A1Network traffic/resource managementLocation information based serviceTraffic capacityLocation detection
A method for applying network services related to geographic location including receiving regions within a map and receiving geo-service definitions for the regions. The method includes determining a subscriber's region and determining information related to the subscriber's traffic flow. The method then applies geo-service definitions based on the subscriber's region and the information related to the traffic flow. A system for applying network services related to geographic location having a location detection module for detecting a subscriber's location and a region detection module for determining the subscriber's region within a map based on the subscriber's location. The system further including a geo-service definition and enablement module for defining geo-service definitions and actions; and a subscriber detection and traffic management module adapted to receive the subscriber's region and apply geo-service definitions to the subscriber traffic flow based in part on the region of the subscriber.
Owner:SANDVINE CORP
Distance-based energy balance dynamic geographic routing method in underwater sensor network
InactiveCN109246786AMake up for deficienciesReduce sending dataNetwork topologiesTopology informationUnderwater sensor networks
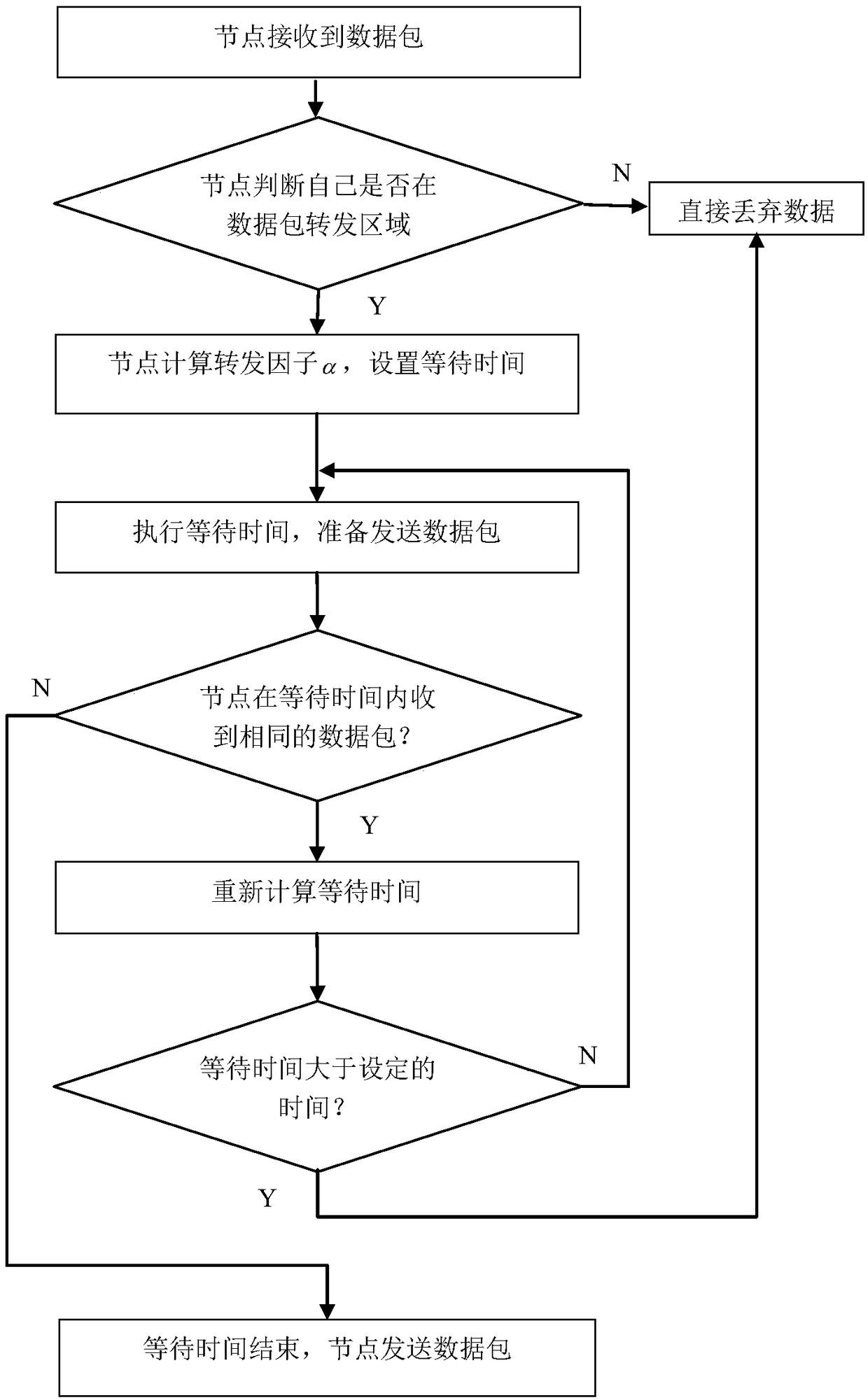
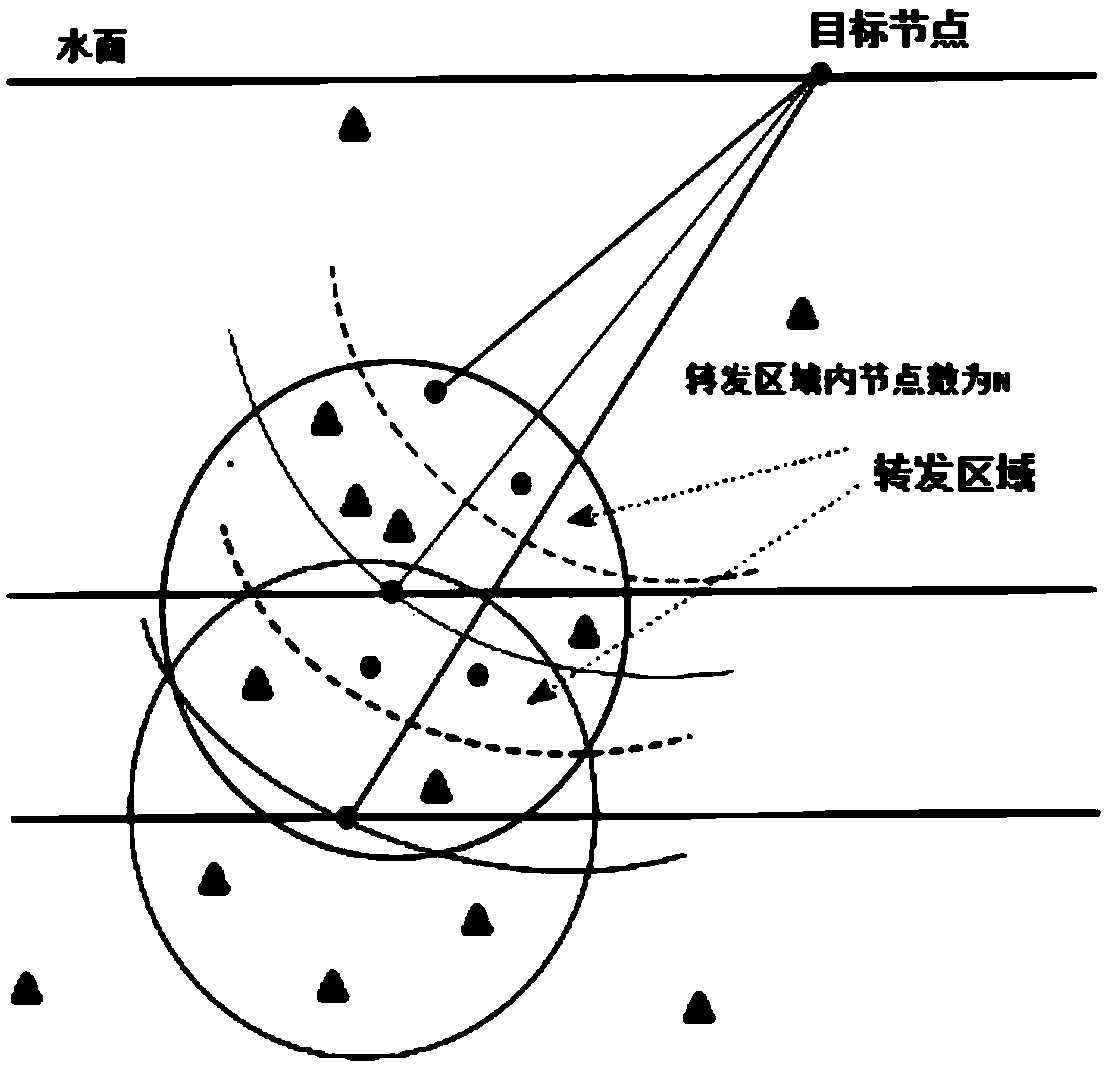
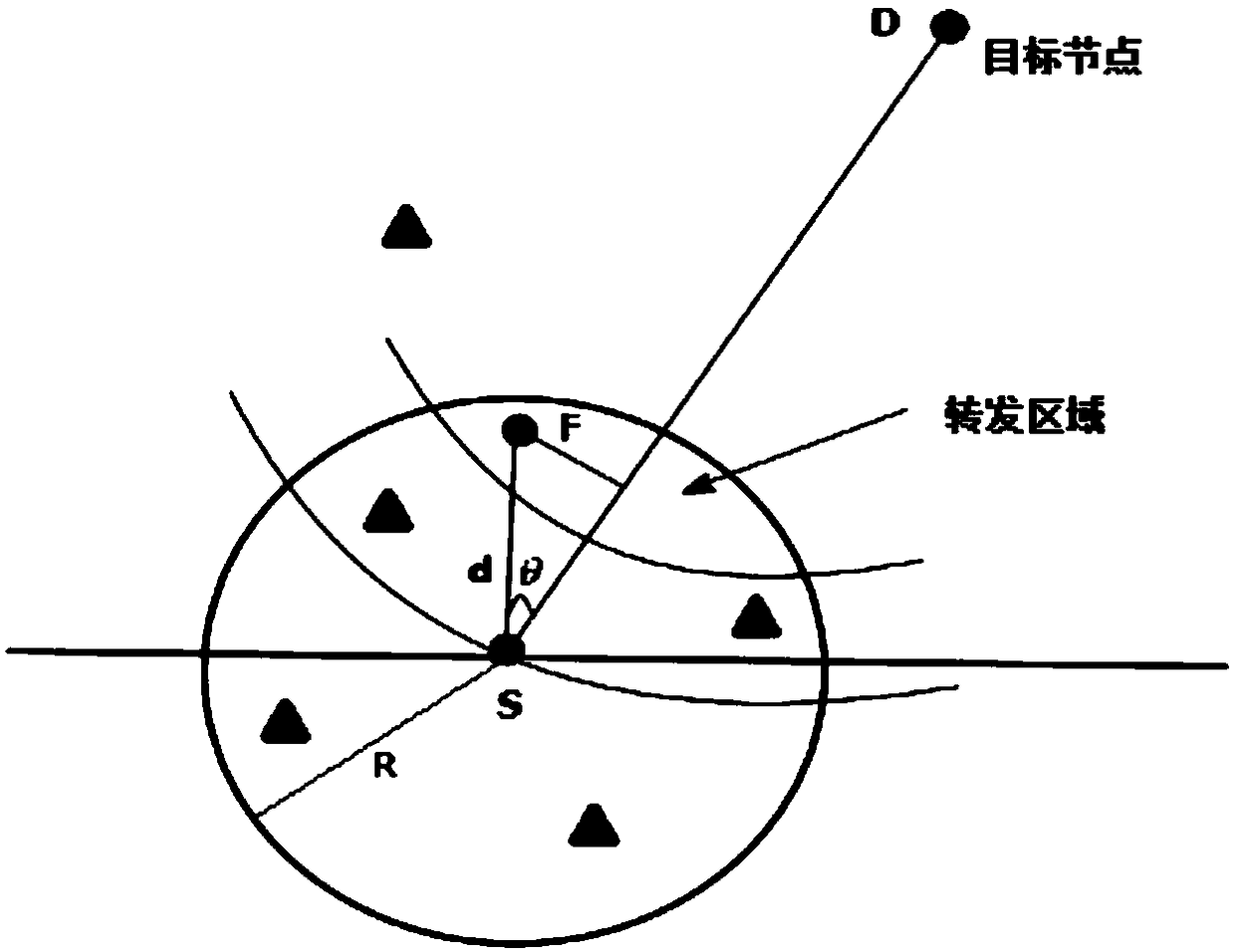
The invention discloses a distance-based energy balance dynamic geographic routing method in an underwater sensor network, and the method comprises the steps: establishing and maintaining a neighbor node table; selecting neighbor nodes that forward a data packet according to the neighbor node table to form a data packet forwarding area; calculating a forwarding factor; and setting the time for theadjacent sensor nodes in waiting for the forwarding of the data packet according to the forwarding factor. The method performs routing selection through the coordinate position information of the nodes, effectively compensates for some defects of a topology information routing method, dynamically adjusts the size of the forwarding area, reduces excessive redundant nodes for sending data, and enables a routing protocol to have dynamic adaptability. The greater the remaining energy of a node is, the easier it is to forward data, and vice versa. Finally, energy balance can be achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
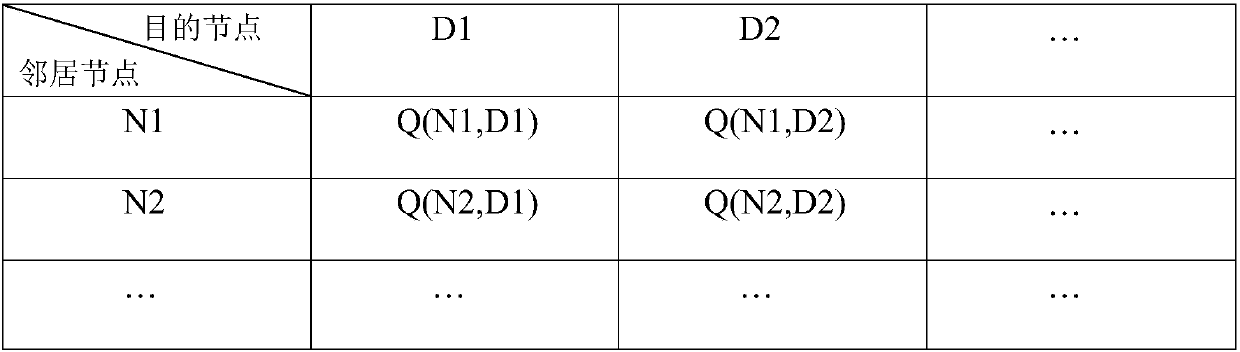
Unmanned aerial vehicle cluster intelligent geographical routing method of Q-learning
InactiveCN108040353ASolve the problem of unreliable pathsImprove robustnessWireless communicationUncrewed vehicleComputer science
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle cluster intelligent geographical routing method of Q-learning. The method comprises the following steps: distributing an autonomous learning task to each network by adopting the advantage of continuously exchanging information with surrounding environment to obtain an optimal solution of a Q-learning algorithm, and computing an award function in the Q-learning algorithm by using effective packet forwarding rate when the influences on the packet transmission performance by the link quality state and the transmission distance are considered at the same time. Each node performs the dynamic adjusting by periodically exchanging information with a neighbor node so as to search the optimal routing path, the problem that the path is unreliable dueto the topology change in a UAV cluster network is effectively solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
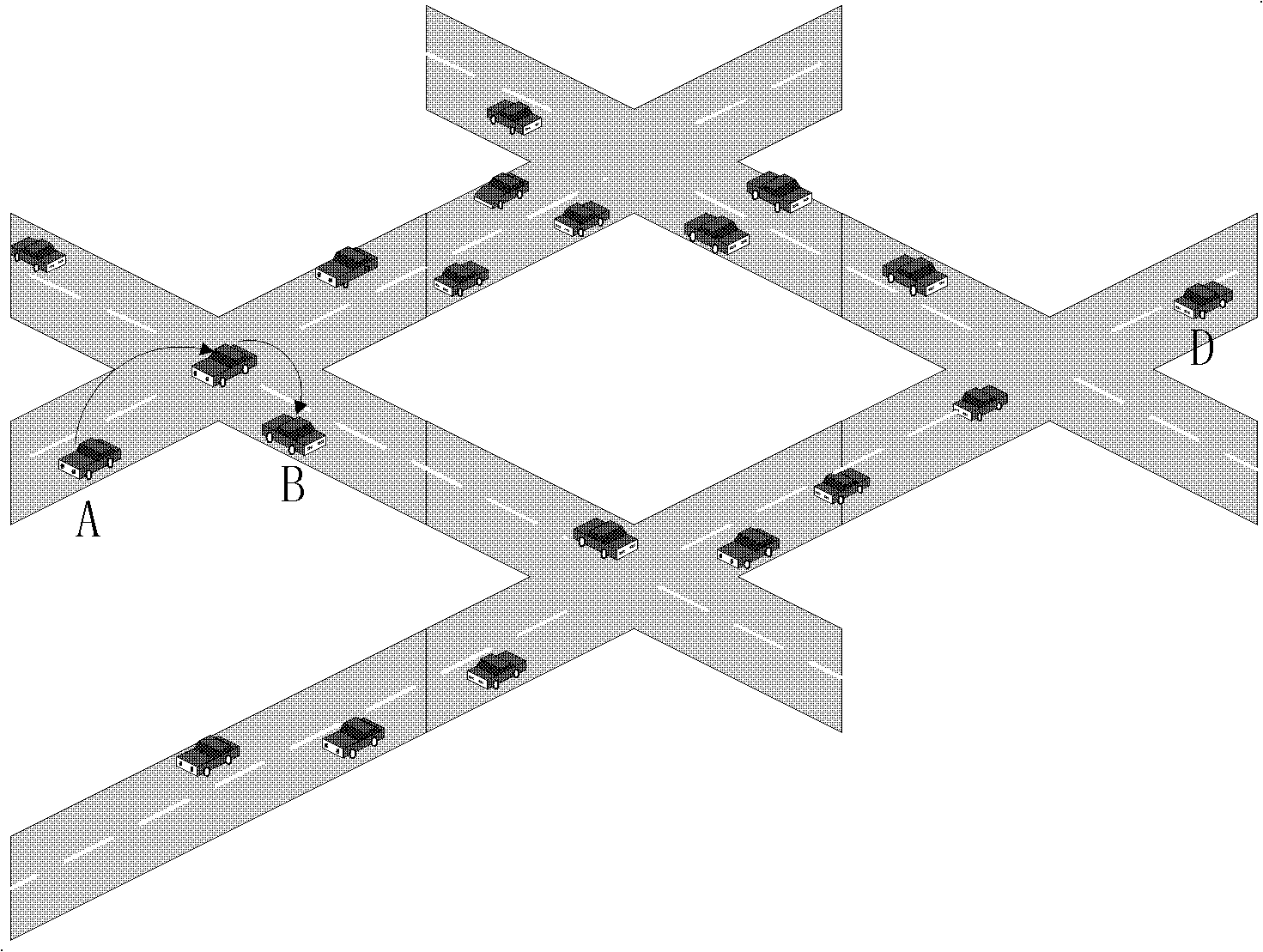
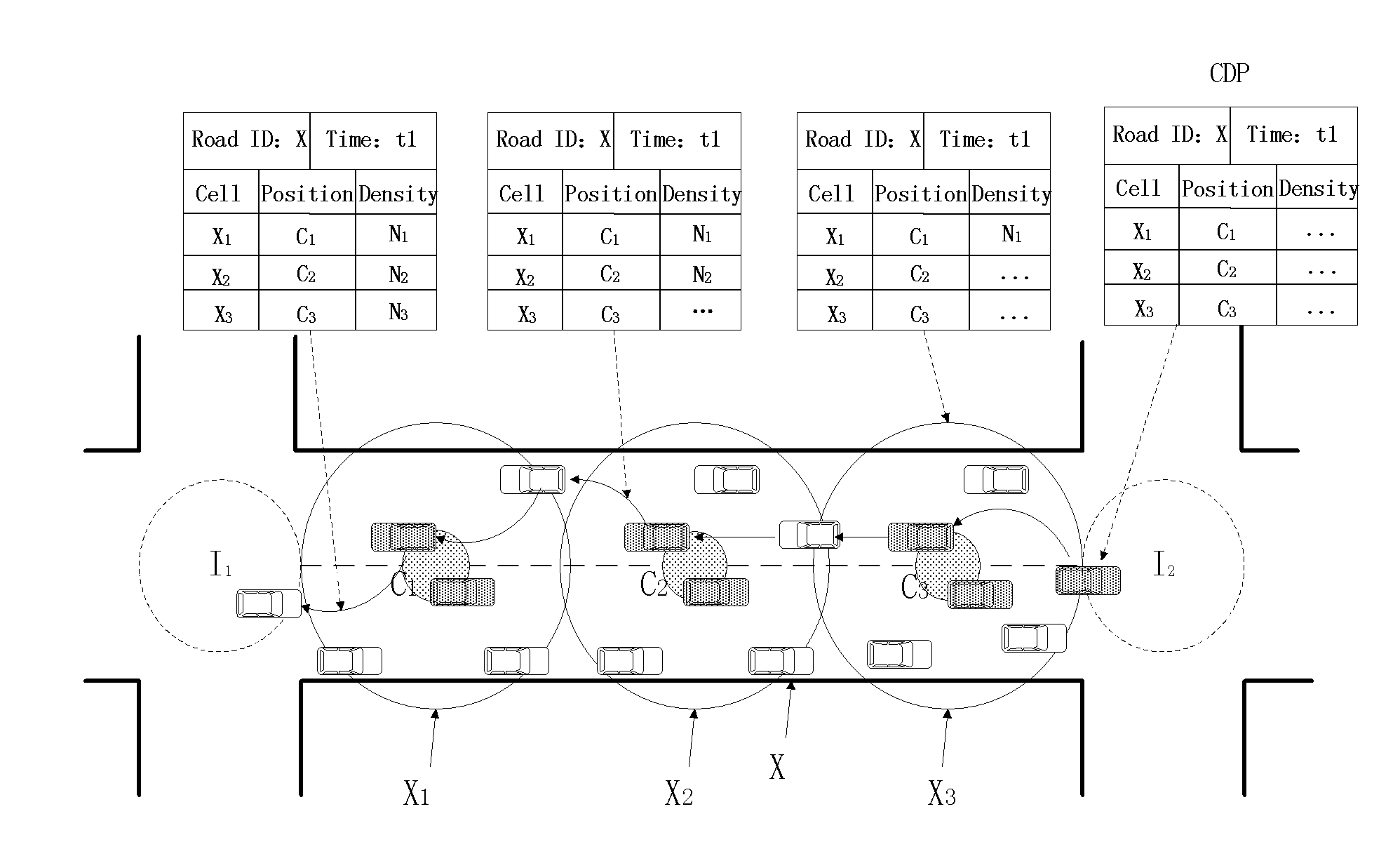
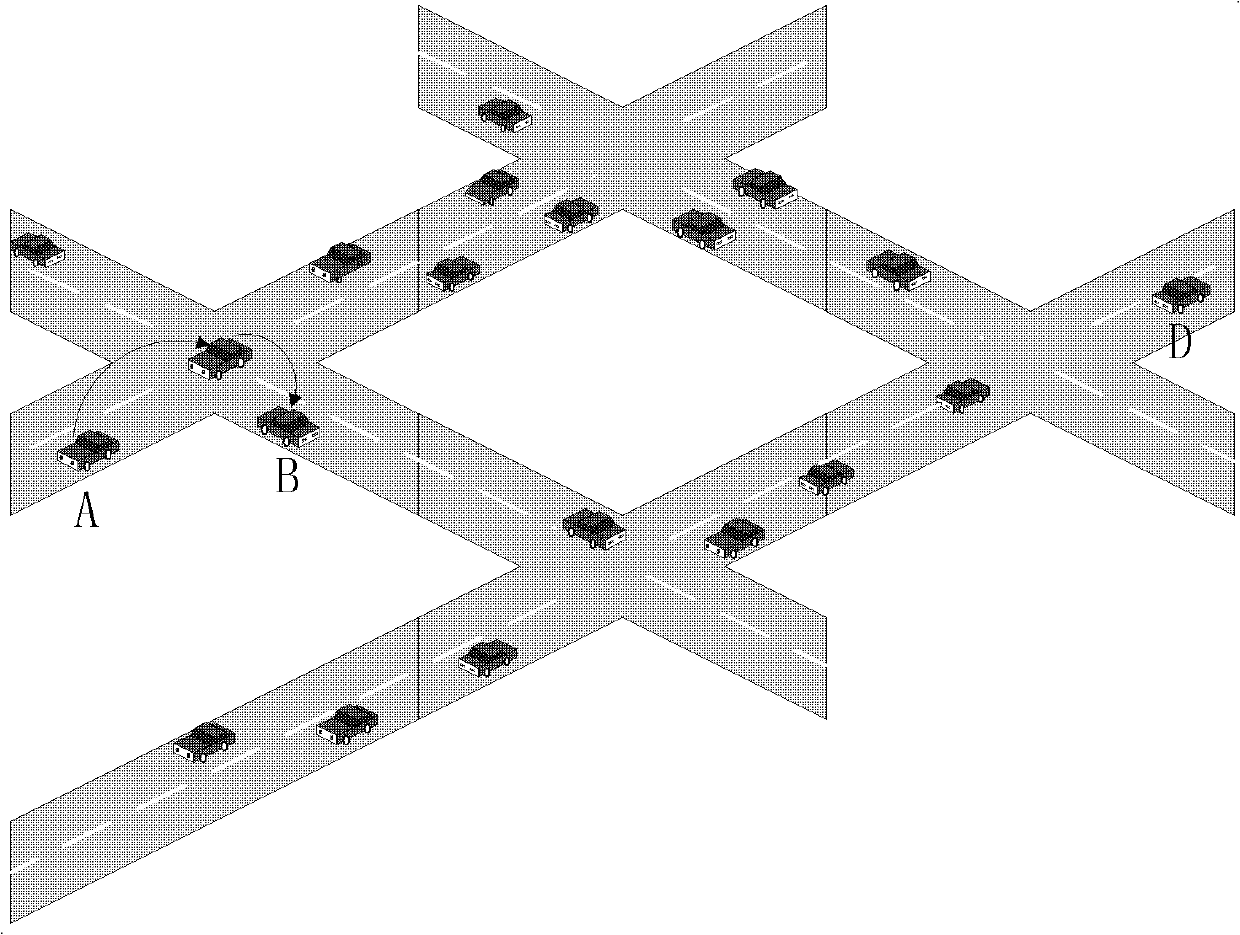
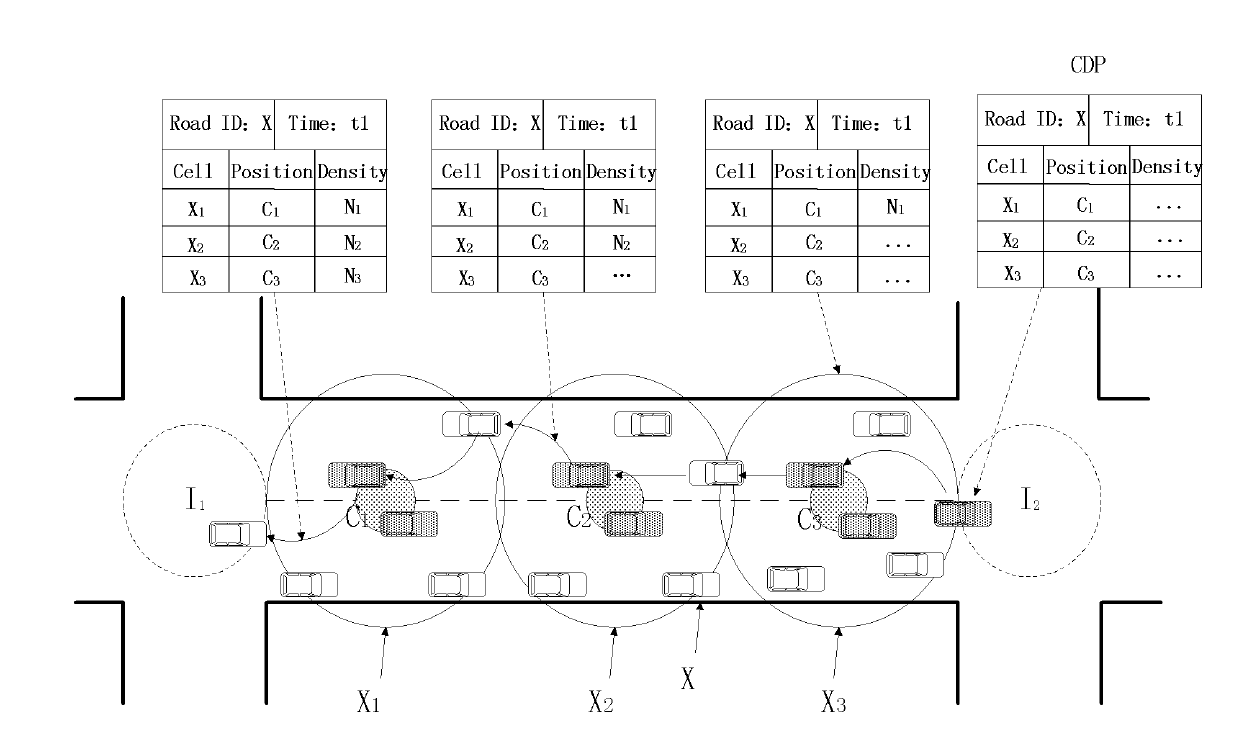
Connection and distance balancing VANET (Vehicular Ad Hoc Network) geographical routing protocol
The invention discloses a connection and distance balancing VANET geographical routing protocol. According to road characteristics, for the first time, the optimal next hop is selected by calculating a CDP (Product of Connection and Distance), and a disconnected route is timely recovered in a local recovery method. The routing protocol divides the routing process into two stages including that 1) in a route establishing stage, a vehicle determines whether the position thereof belongs to an intersection or road area, wherein if a node is placed in the road area, a neighbor node with the maximal CDP value is selected as the next hop for the node; if the node is in the intersection area, a next road is first selected for the node, the CDP of a neighbor node in the road is calculated, and the optimal next hop is selected; and according to the CDP values, the optimal next hops are successively selected, and a high-efficiency route is finally established; and 2) in a route recovery stage, a local recovery strategy is employed for the nodes, and a carrying-forwarding strategy is employed when local recovery failure or routing void occurs.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
AANET combined routing algorithm based on geographical location information
InactiveCN104202724AEasy accessEfficient use ofLocation information based serviceAviationGeolocation
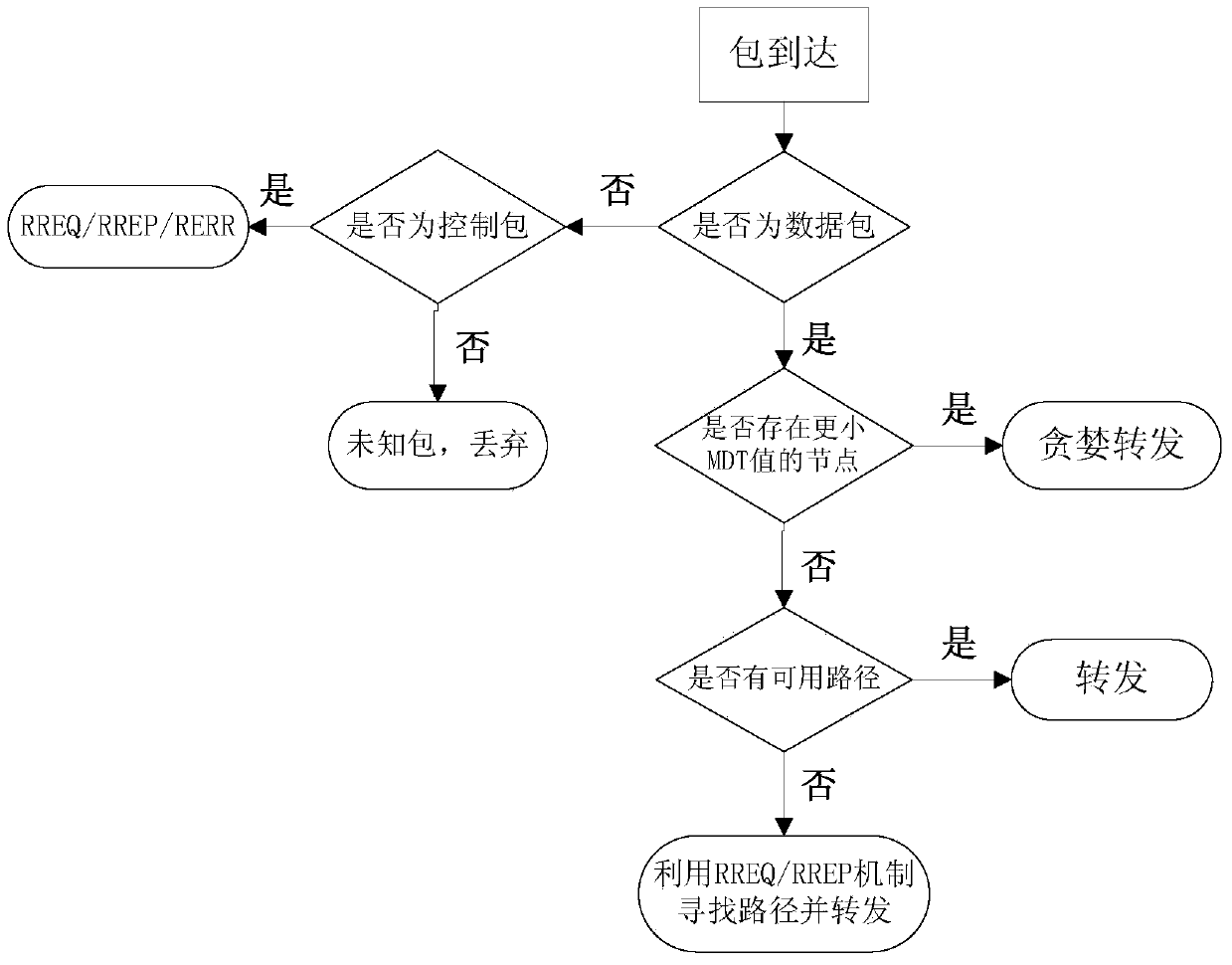
The invention discloses an AANET combined routing algorithm based on geographical location information. Greedy forwarding strategies and reactive routing in geographic routing are combined. Aiming at the high dynamic and low node density characteristics of an aviation ad-hoc network, the greedy forwarding strategies in the geographic routing is modified first, and new routing metric considers both the geographical locations of nodes and relative speed among nodes and eliminates unstable next-hop forwarding nodes. The algorithm combines good characteristics of traditional reactive routing, uses an RREQ / RREP mechanism to replace the periphery forwarding mechanism in the geographic routing, and routing void can be processed effectively. Compared with other methods, the algorithm combines the advantages of two algorithms and is more adaptive to the network environments of the aviation ad-hoc network.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Wireline terminal accessing mobile telephone services
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
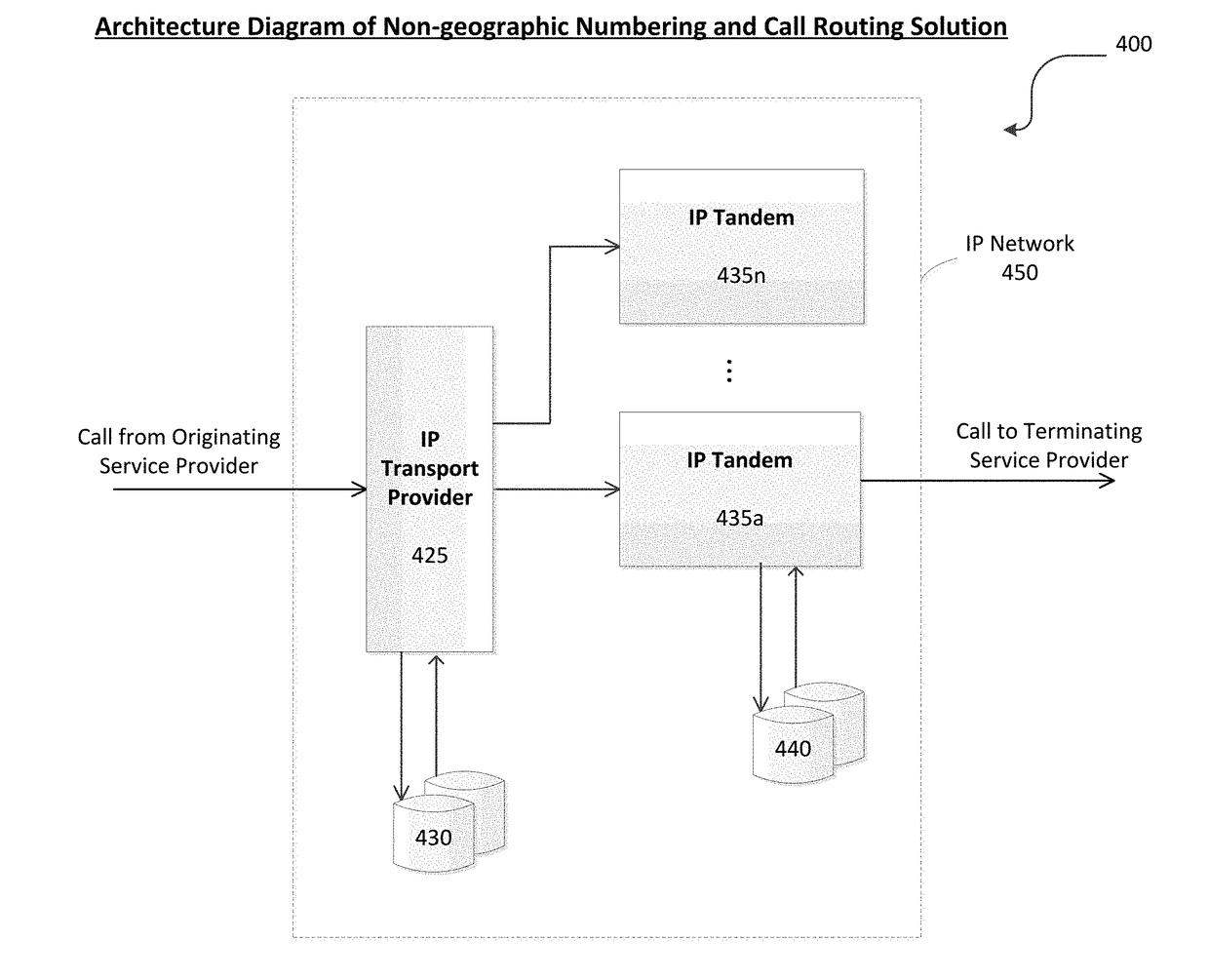
Non-geographic numbering and call routing
InactiveUS20180227429A1Interconnection arrangementsSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsGeographic siteTelecommunications network
Systems and methods for non-geographic numbering, addressing, managing, and routing calls through a telecommunications network. Particularly, this invention relates to the concept of a parallel IP-based telecommunications network which can manage and route calls to a non-geographic telephone number. The invention further relates to nationwide number portability (NNP), that is, porting telephone numbers across different geographies and routing calls to the ported telephone numbers via a new architecture that includes an IP transport provider, IP tandems and an administrative agency that administers non-geographic routing numbers and non-geographic telephone numbers. According to disclosed embodiments, the system and method allow a service provider to route calls to a telephone number which is not dependent on a geographic area code. The system and method further allow a service provider to port a geographic telephone number to a non-geographic telephone number, while keeping and / or changing the service provider associated with the telephone number.
Owner:NEUSTAR
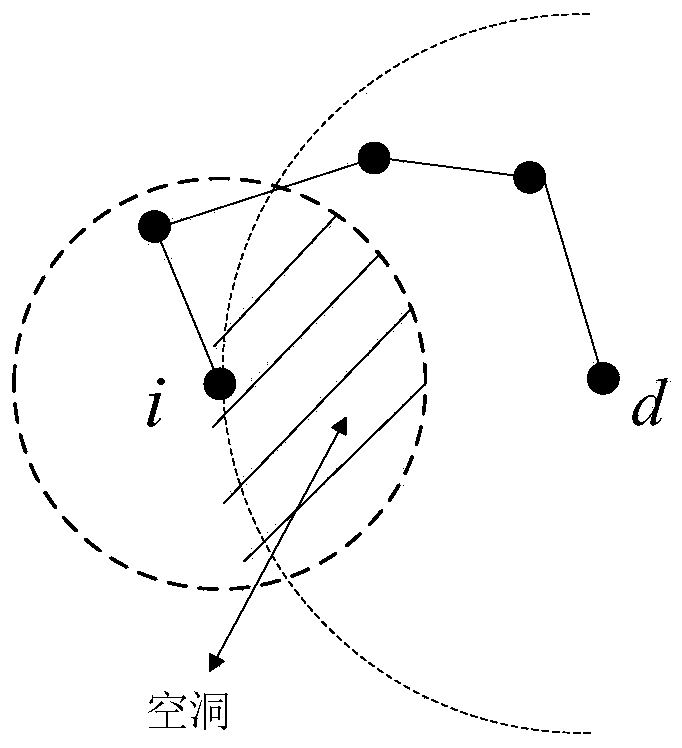
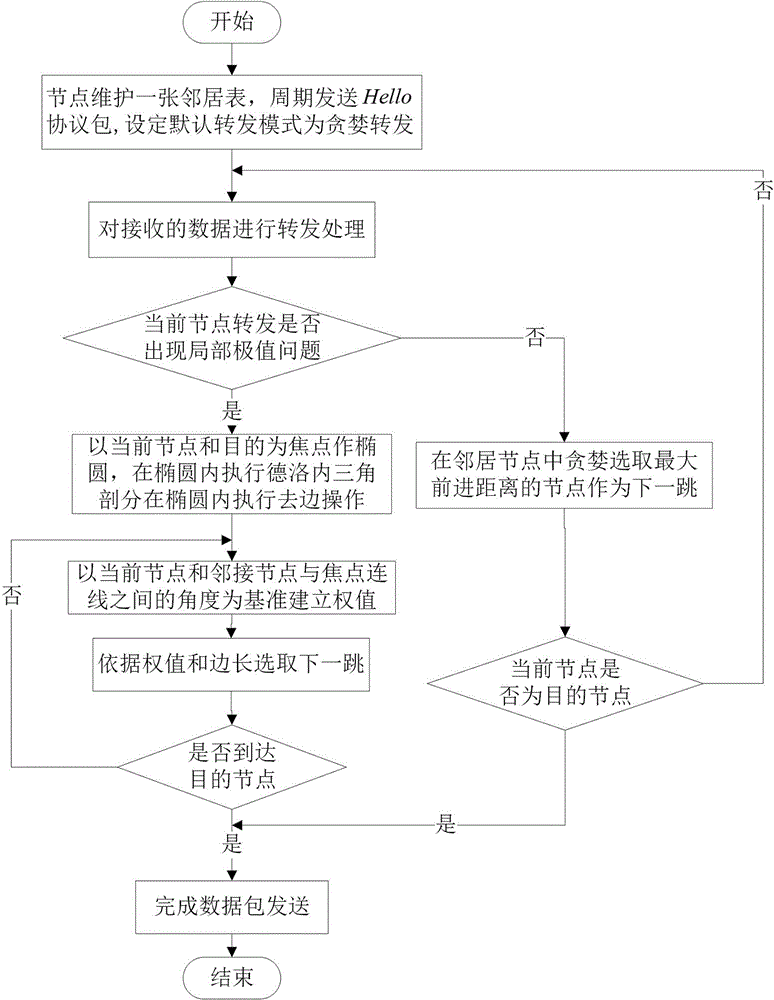
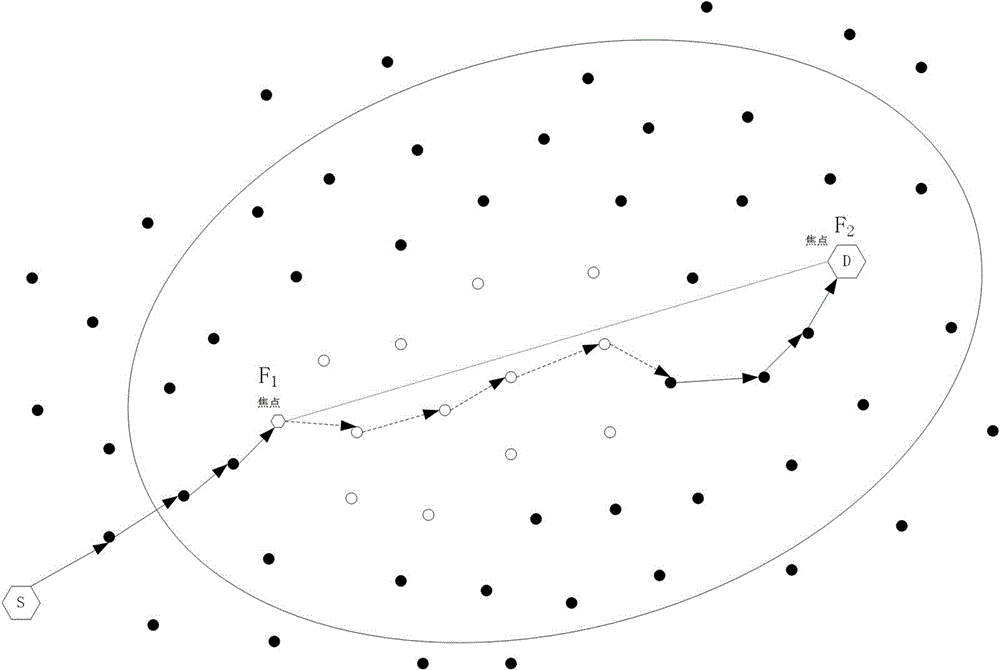
Cavity bypassing type geographical routing method based on Delauney triangulation
ActiveCN104703245ALow segmentation complexityIncrease routing hopsNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesTriangulationNetwork packet
The invention provides a cavity bypassing type geographical routing method based on Delauney triangulation. The cavity bypassing type geographical routing method based on Delauney triangulation is mainly used for solving the problem that a cavity appears during greedy transmission of existing routing and improving cavity bypassing routing efficiency. The cavity bypassing type geographical routing method based on Delauney triangulation comprises the basic steps that 1, each node maintains a neighbor table and broadcasts a hop of Hello protocol package with the delta t as the cycle, and the default data transmitting mode of the node is set to be the greedy mode; 2, the nodes process received data, a data packet is transmitted in the greedy mode, and transmission in the greedy mode fails, and step 4 is executed; 3, whether the data packet reaches a target node or not is judged, transmission is complete is yes, and the step 2 is executed again and data are continued to be transmitted if not; 4, if a local extreme value appears during transmission of the current node due to the existence of a cavity, and the next hop of Hello protocol package is transmitted in the peripheral transmission mode till the data packet reaches the target node.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
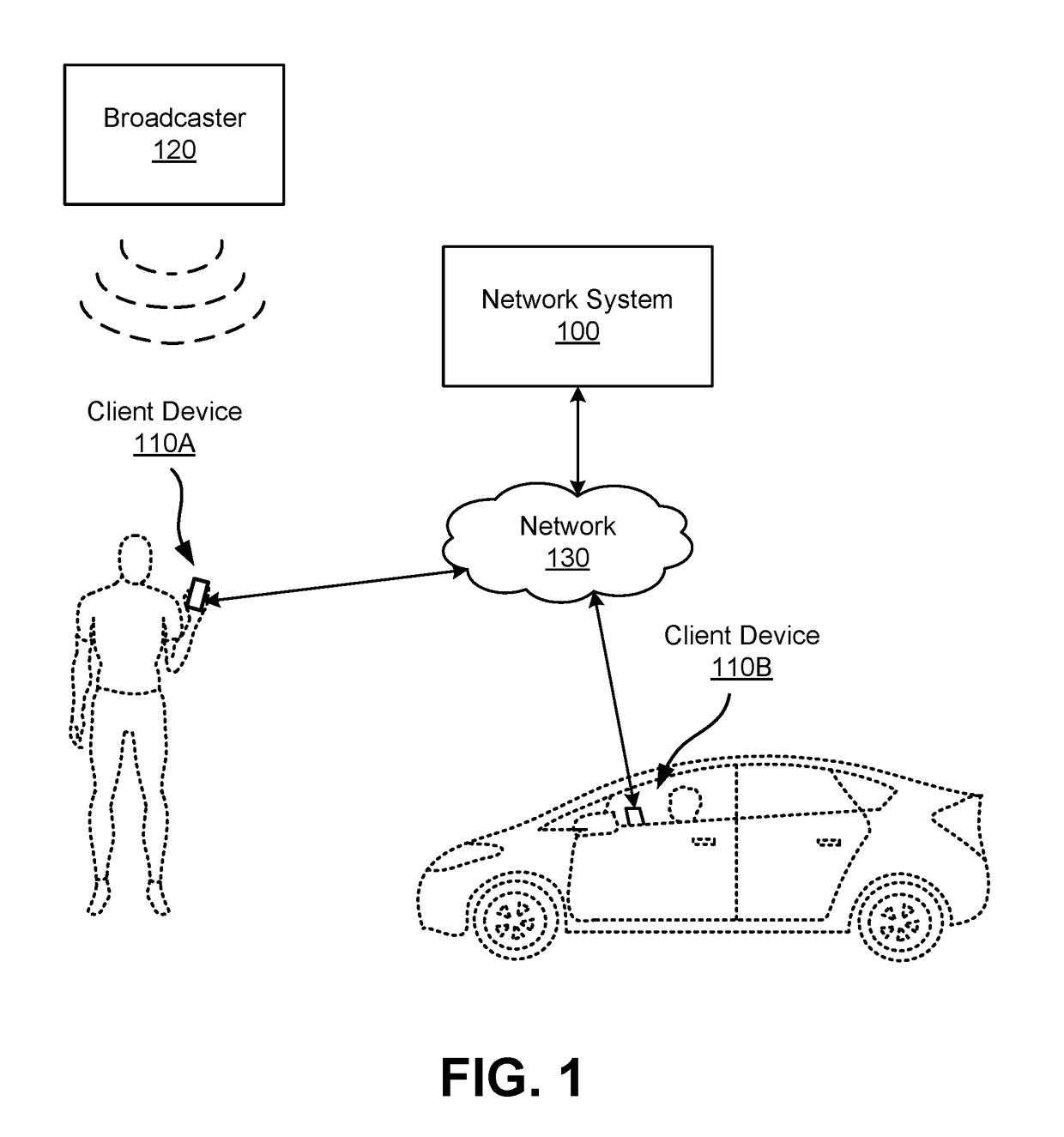
Geographic positioning using short-range transmissions
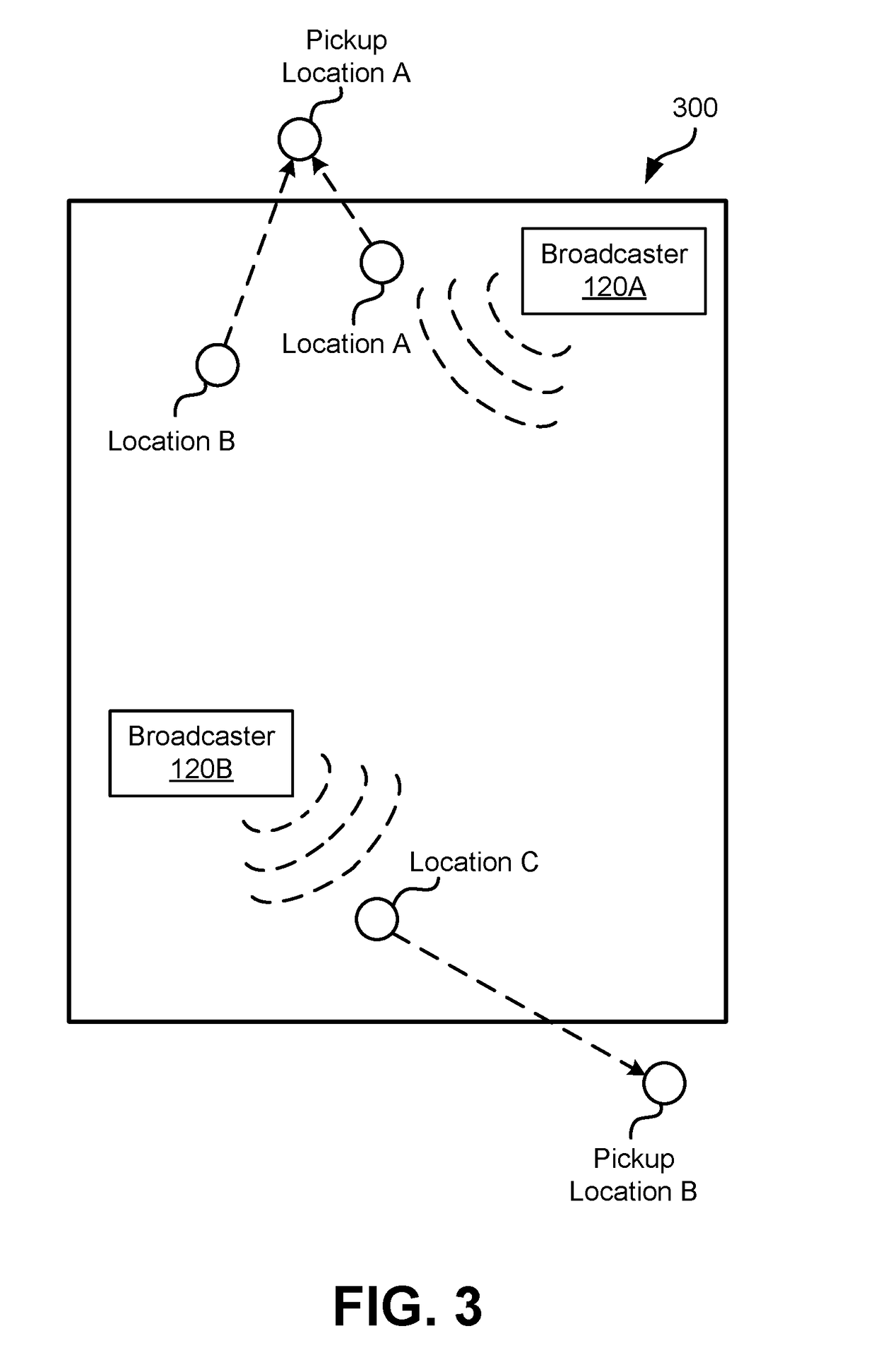
ActiveUS20190049552A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsWi-FiGeotargeting
A network system uses Wi-Fi signals or other types of short-range transmissions to determine pickup locations for users receiving services provided via the network system. The network system builds a database of search records mapping pickup locations to signatures of short-range transmission detected by users' client devices when they searched for the pickup locations. By comparing a signature detected by a given user's client device to the signatures in the database, the network system can check for similarities between the short-range transmissions. Responsive to finding a match, the network system predicts that the given user is likely to select a similar pickup location as other users whose client devices detected the signatures corresponding to the match. Accordingly, by leveraging the database, the network system can predict pickup locations without requiring the given user to input a search for a pickup location.
Owner:UBER TECH INC
Predictive low-delay geographical routing method
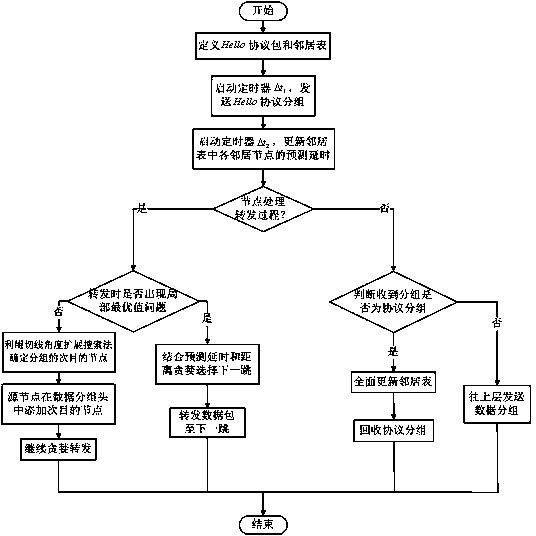
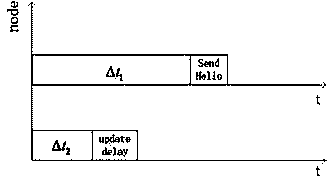
ActiveCN104394554AReduce energy consumptionAdd delay calculationPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork packetLow delay
The invention provides a predictive low-delay geographical routing method. The method is mainly used for solving the problem of unbalance between geographical routing delay and network energy consumption in the prior art, and the bypassing efficiency of a routing void is improved. The method comprises the following basic steps: (1) setting a Hello protocol packet and a neighbor table, and broadcasting a hop of protocol packet by regarding delta t1 as a cycle through each node; (2) locally updating the neighbor table by regarding delta t2 as a cycle through each node; (3) determining a receiving process or a forwarding process which needs to be processed by each node, and correspondingly executing the step (4) or the step (5); (4) judging the type of a packet, if the packet is the protocol packet, globally updating the neighbor table, and otherwise, transferring the packet to an upper layer of each node; (5) greedily forwarding a data packet by each node, and if a void is formed to generate a local extreme value in the forwarding process, selecting an anchor node to continuously perform greedy forwarding by utilizing a tangent angle spread searching method.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
A distributed hash table routing method fusing geographic positions
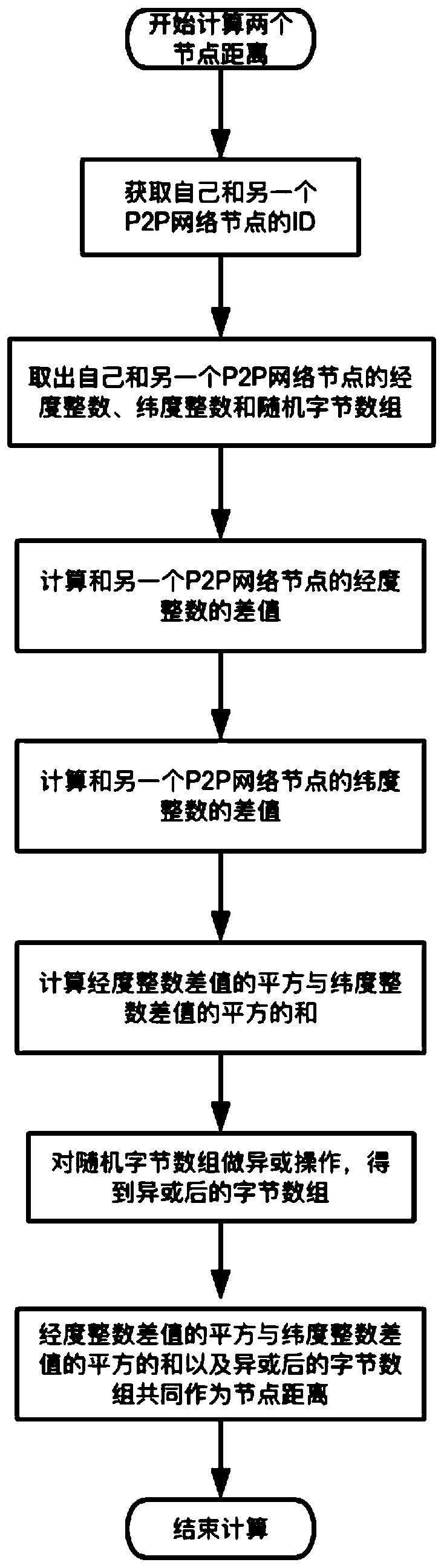
InactiveCN109743253AImprove data transfer efficiencyData switching networksGeographic siteGeolocation
The invention discloses a distributed hash table routing method f fusing geographic positions, which comprises the following steps that: P2P (Peer-to-Peer) network nodes use an ID (Identity) generation rule based on geographic positions to generate node IDs (Identities), and the distances among the nodes are calculated according to the IDs; The invention discloses a distributed hash table routingmethod fusing geographic positions. the advantages of the distributed hash table and geographic position information knowing are combined, The distributed hash table can be decentralized and is used for bottom layer network transmission of the block chain, geographic position information can be known, nodes close to geographic positions can be found more quickly, the communication speed between the nodes is higher, and the problem that the communication efficiency is low due to the fact that the distance between the nodes of the distributed hash table is too long is solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU QULIAN TECH CO LTD
Traffic-aware routing method applied to Internet of Vehicles
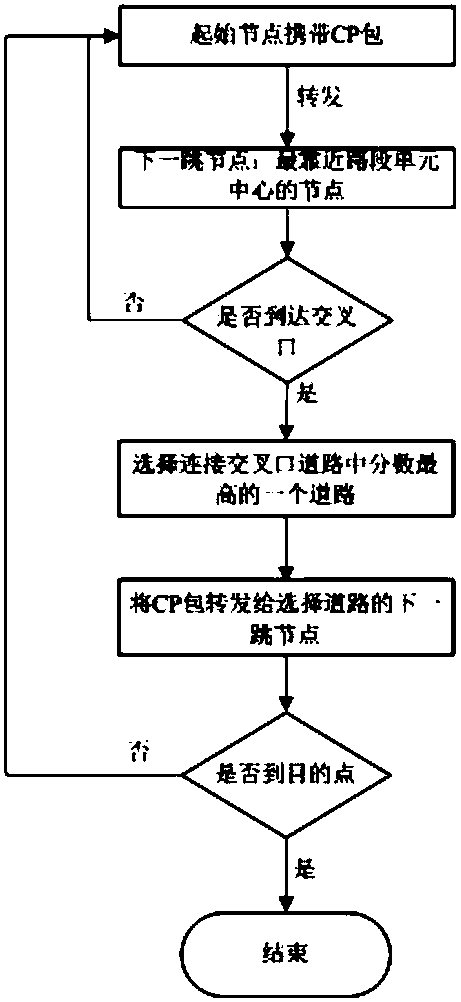
ActiveCN108391249AAvoid instability, large transmission delay and other problemsAvoid local optimum problemsParticular environment based servicesDetection of traffic movementLocal optimumThe Internet
The invention provides a traffic-aware routing method applied to Internet of Vehicles. A data packet is transmitted from a starting point to a destination point through forwarding between nodes, wherein the forwarding of the data packet comprises data packet forwarding at an intersection and data packet forwarding in a straight road section, and an intersection road section needs to be selected according to road condition information of each road section which is broadcast by a data collection package at the intersection when the forwarding is carried out at the intersection. According to themethod, the problems of unstable link and large transmission delay are avoided, and the local optimum problem in the geographic routing is solved.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Multipath geographic routing optimization method for on-demand movement of sink node in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN106162790AReduce the amount of updatesImprove performanceNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesPathPingRoute search
The invention discloses a multipath geographic routing optimization method for on-demand movement of a sink node in a wireless sensor network. The method adopts hierarchical logical structure design and is respectively divided into three stages of establishing a neighbor table, establishing a path table and establishing a routing table. The movement of the sink node is constrained by parameters, such as residual energy, time and a target function, in order to avoid frequent updating of the neighbor table due to frequent movement of the sink node, so that the neighbor table can be selectively updated by the node. The neighbor table and the path table adopt a separate establishment process, so that the updating amount caused by sink movement is reduced; during a route search stage, a global optimum path set is searched by adopting an improved taboo search algorithm; routing is conducted in the optimum path set, and the health index of a path link is measured by a short slab principle in order to avoid invalid routes; when the health index is lower than a computing threshold, the link is a critical path, the sink node moves towards the short slab path, so that the on-demand movement of the sink node is realized, the network energy consumption is effectively balanced, and the network lifetime is prolonged.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
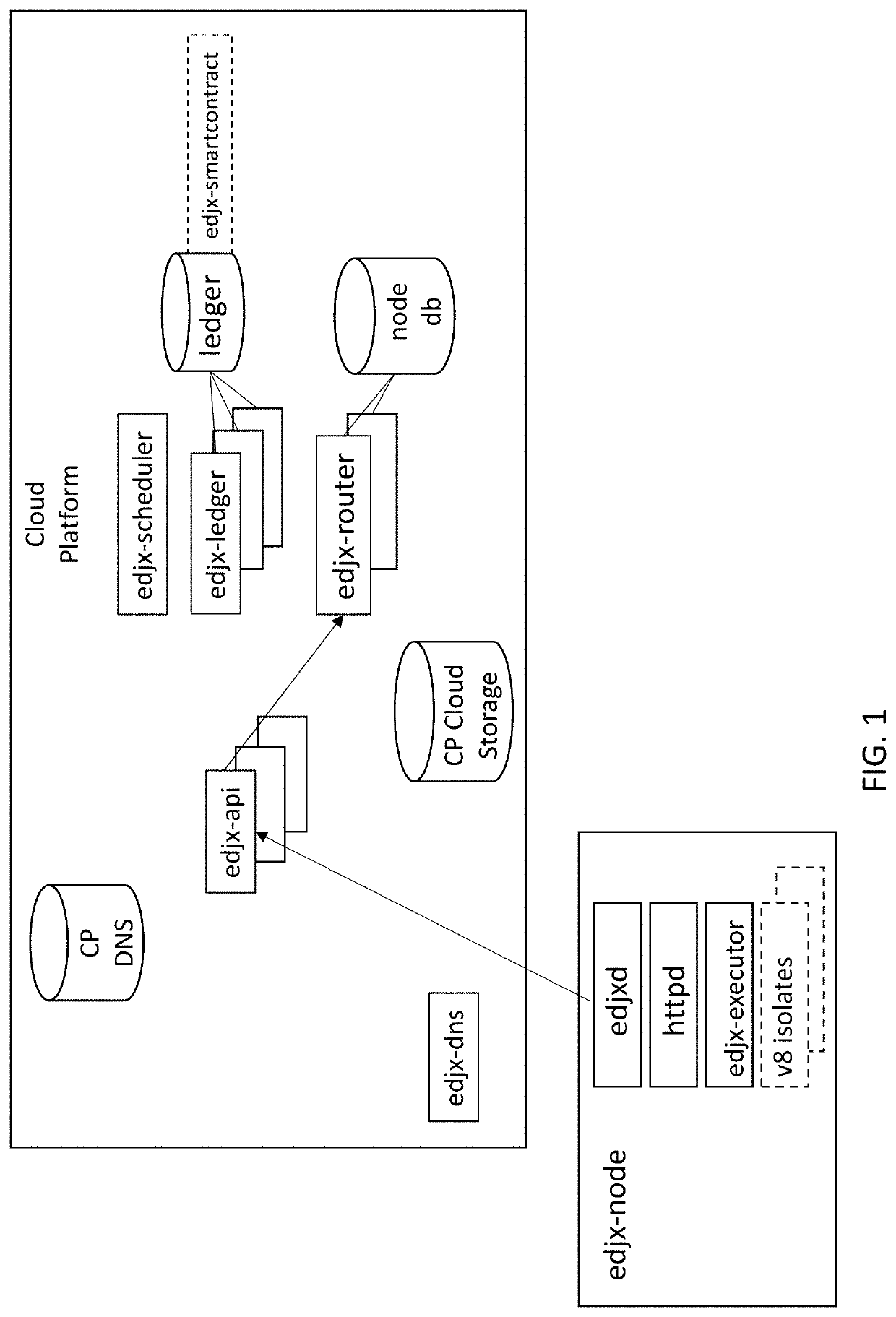
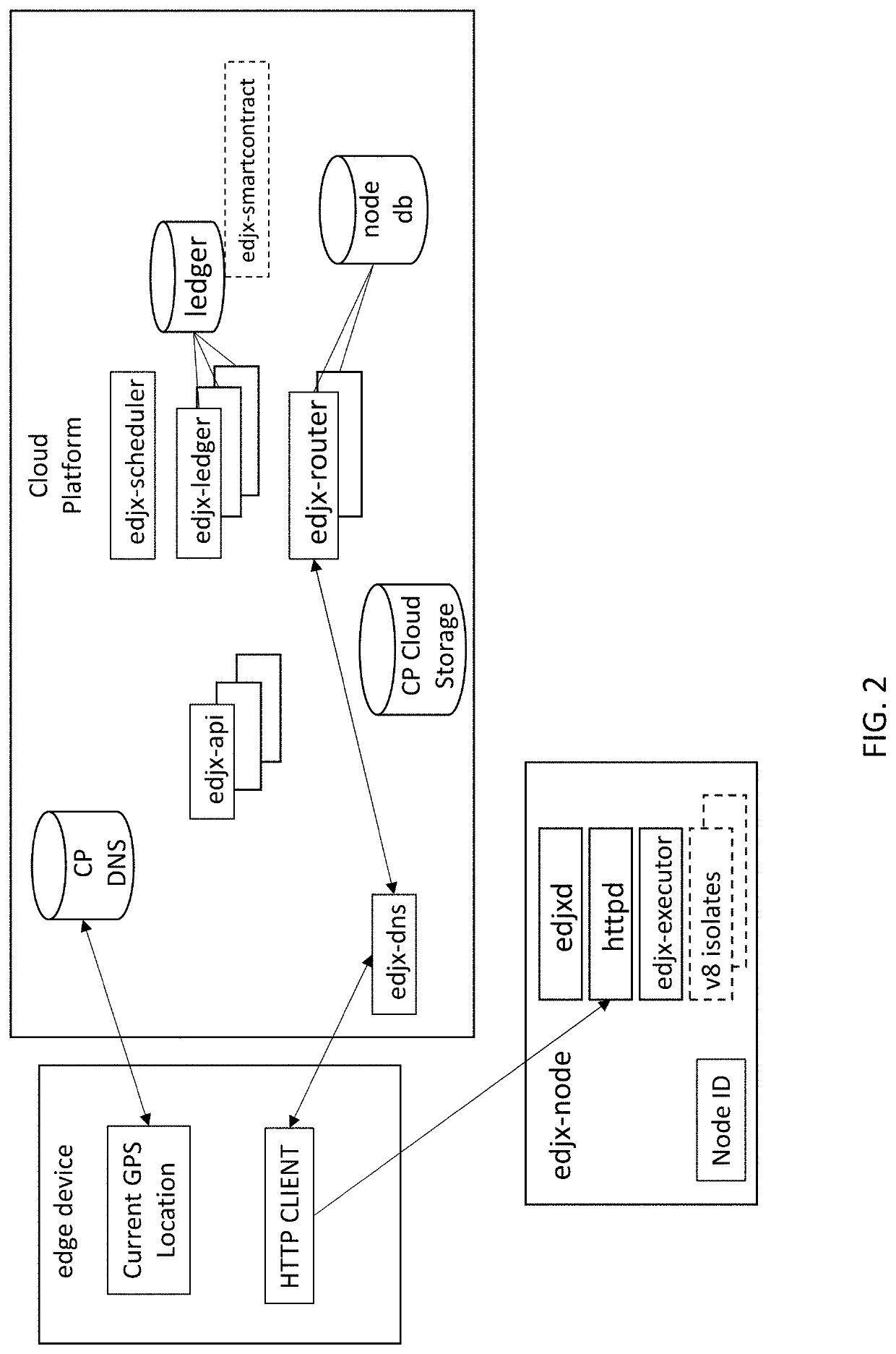
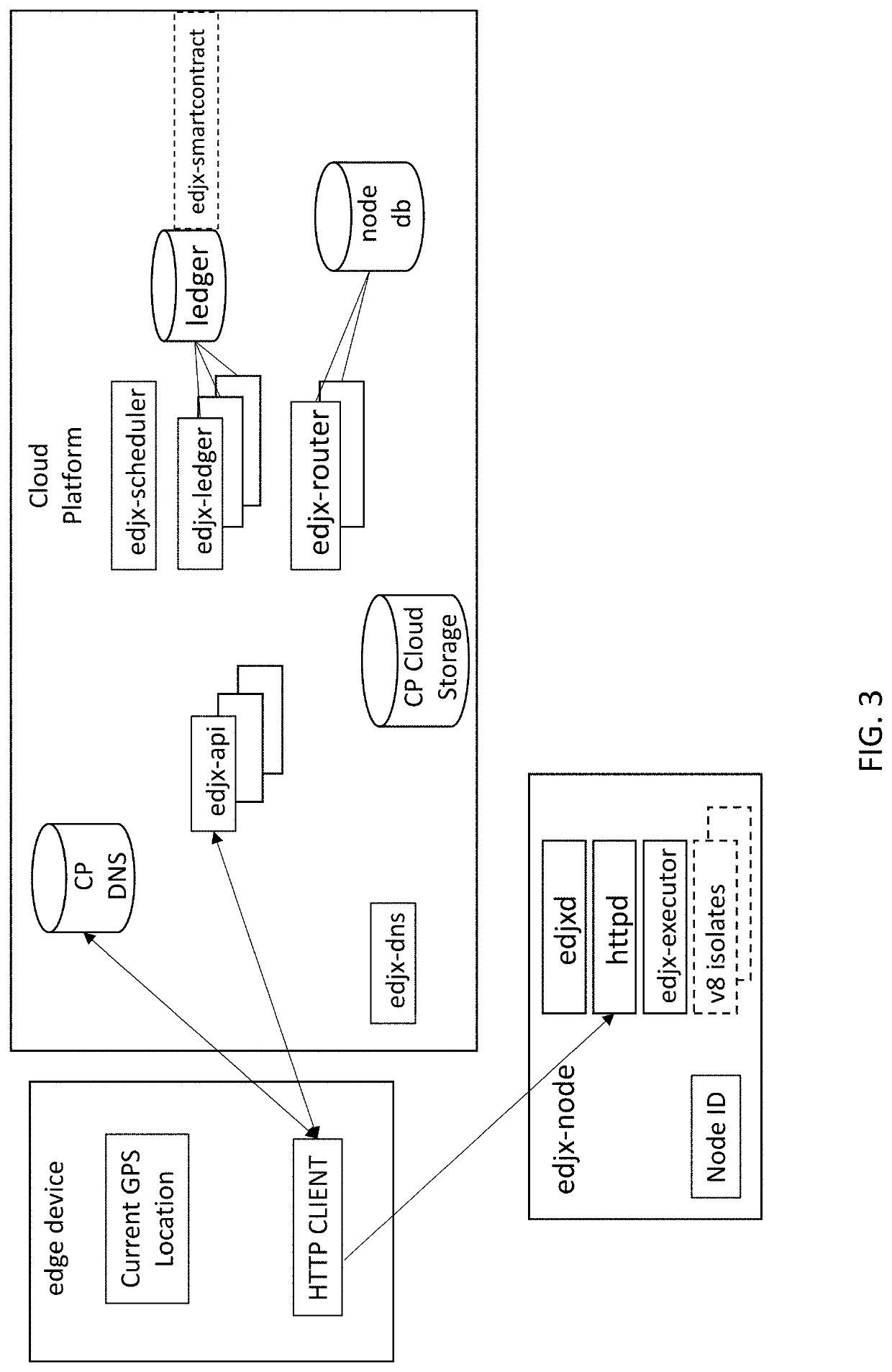
Systems and methods for locating server nodes in close proximity to edge devices using georouting
Systems and methods for locating server nodes in close proximity to edge devices using georouting. Microservers automatically form a global peer-to-peer network to serve edge functions and content to edge devices. Edge devices use HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to execute serverless functions or otherwise retrieve data from edge nodes located in close proximity to the HTTP client. Serverless functions are implemented in secure, isolated environment utilizing a blockchain.
Owner:EDJX INC
Prediction-based routing method at intersection in vehicle self-organizing network
InactiveCN102137462BShort transmission distanceGuaranteed normal transmissionAssess restrictionData switching networksIn vehicleTransmission time delay
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
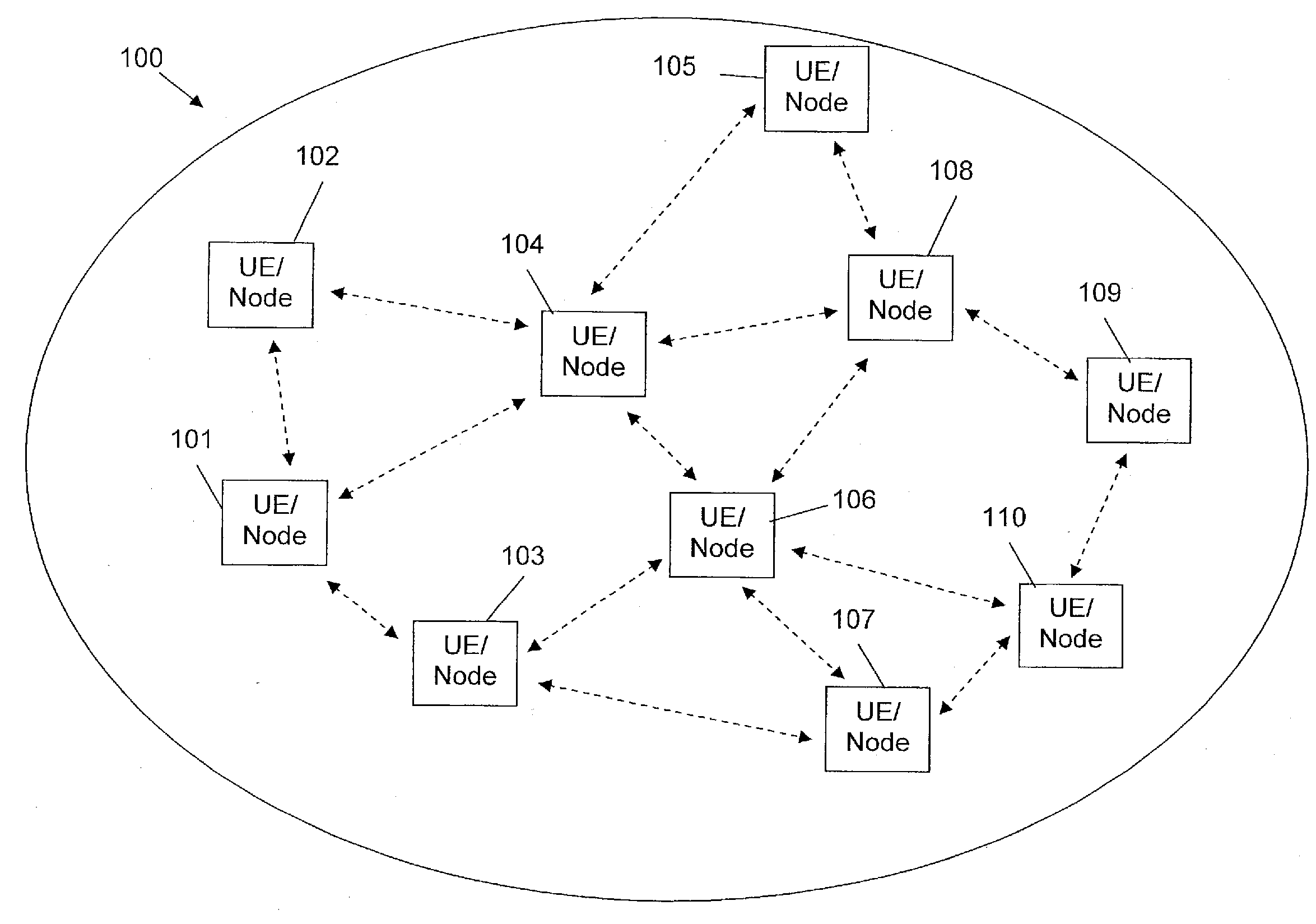
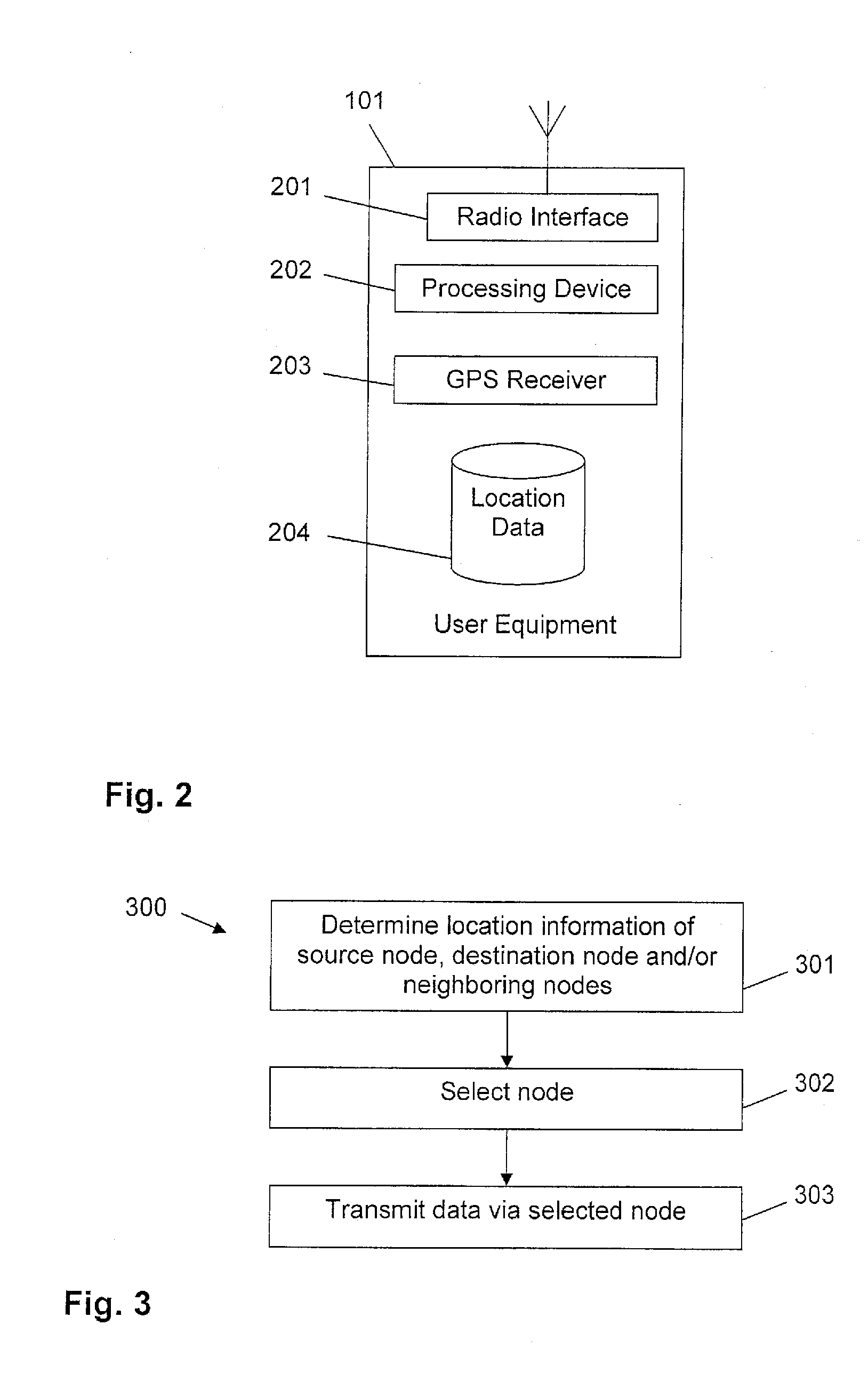
Operating a user equipment in a wireless mesh radio network
InactiveUS20160309392A1Efficient routingEasily and efficiently advertizedNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkRadio networks
The present invention relates to a method for operating a user equipment in a wireless mesh radio network. The wireless mesh radio network comprises a plurality of neighboring nodes arranged within a direct radio frequency communication range of the user equipment, and a destination node. Communication data is to be routed from the user equipment to the destination node through the wireless mesh radio network. According to the method, a location information of the user equipment defining a geographic location at which the user equipment is currently located is determined. Furthermore, for each neighboring node a corresponding location information defining a geographic location at which the corresponding neighboring node is currently located is determined. Additionally, a location information of the destination node is determined. Based on the determined location information of the user equipment, the destination node and the neighboring nodes one neighboring node selected and the communication data to be routed from the user equipment to the destination node is transmitted to the selected neighboring node.
Owner:SONY CORP
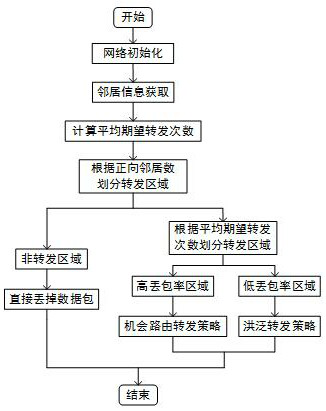
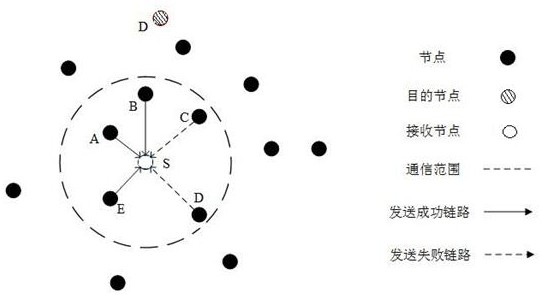
Geographical routing protocol method applied to underwater acoustic sensor network
ActiveCN112235845AReduce waiting timeSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionHigh level techniquesTrunkingEngineering
The invention provides a geographical routing protocol method applied to an underwater acoustic sensor network, which comprises the following steps that each node acquires neighbor node information and calculates an average expected forwarding frequency for dividing a routing forwarding area; and each relay node divides an area in a communication range into a low packet loss rate area, a high packet loss rate area and a non-forwarding area according to the node degree and the packet loss rate, wherein the node in the low packet loss rate area uses an opportunistic routing forwarding strategy,and the node in the high packet loss rate area uses a flooding forwarding strategy, the node in the non-forwarding area does not participate in forwarding the data packet. According to the method, theadvantages of an opportunistic routing forwarding strategy and a directional flooding forwarding strategy are integrated, and compared with other underwater acoustic sensor network routing protocols,the energy consumption can be obviously reduced, and the packet loss rate and the end-to-end delay are reduced.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
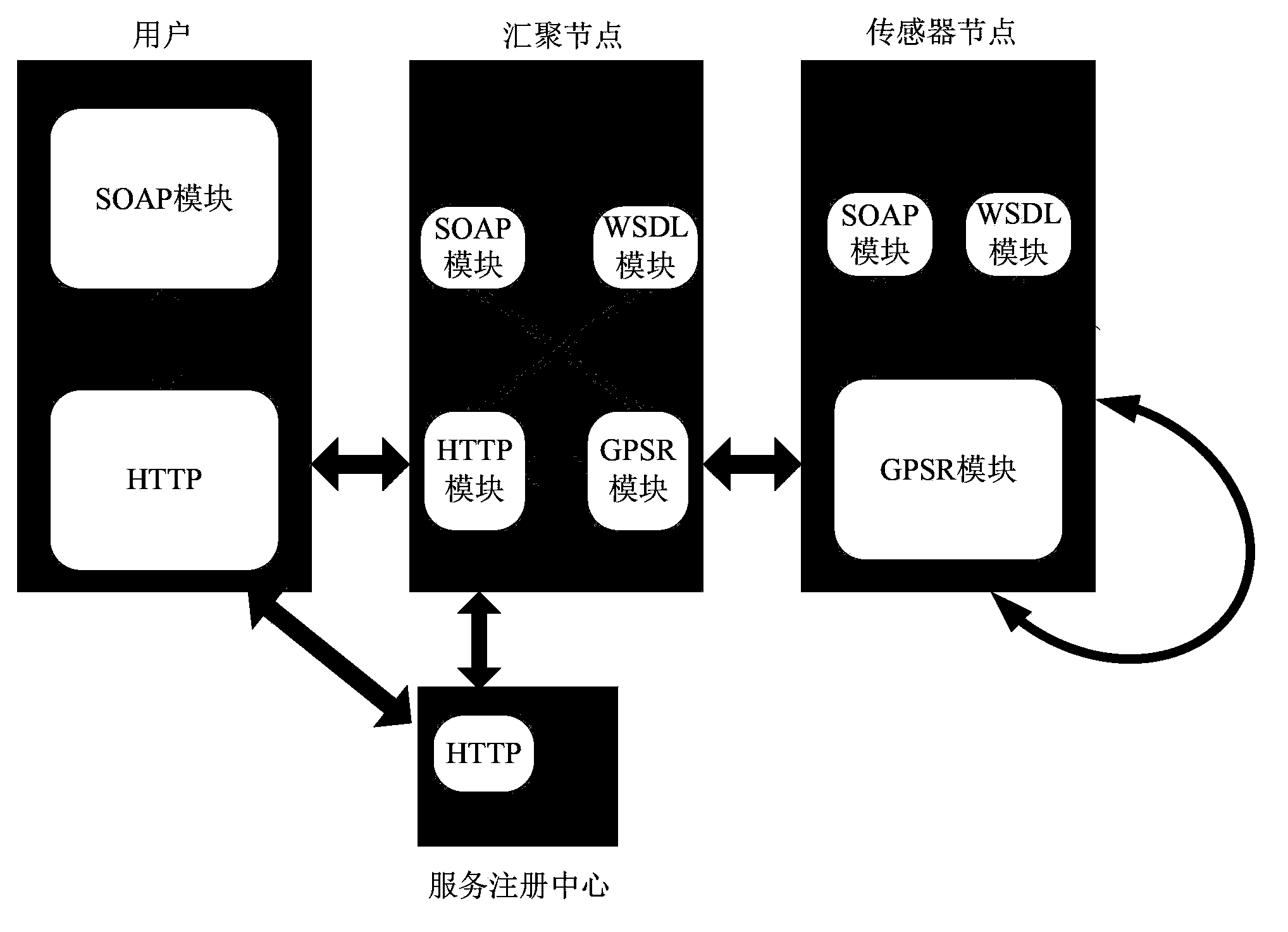
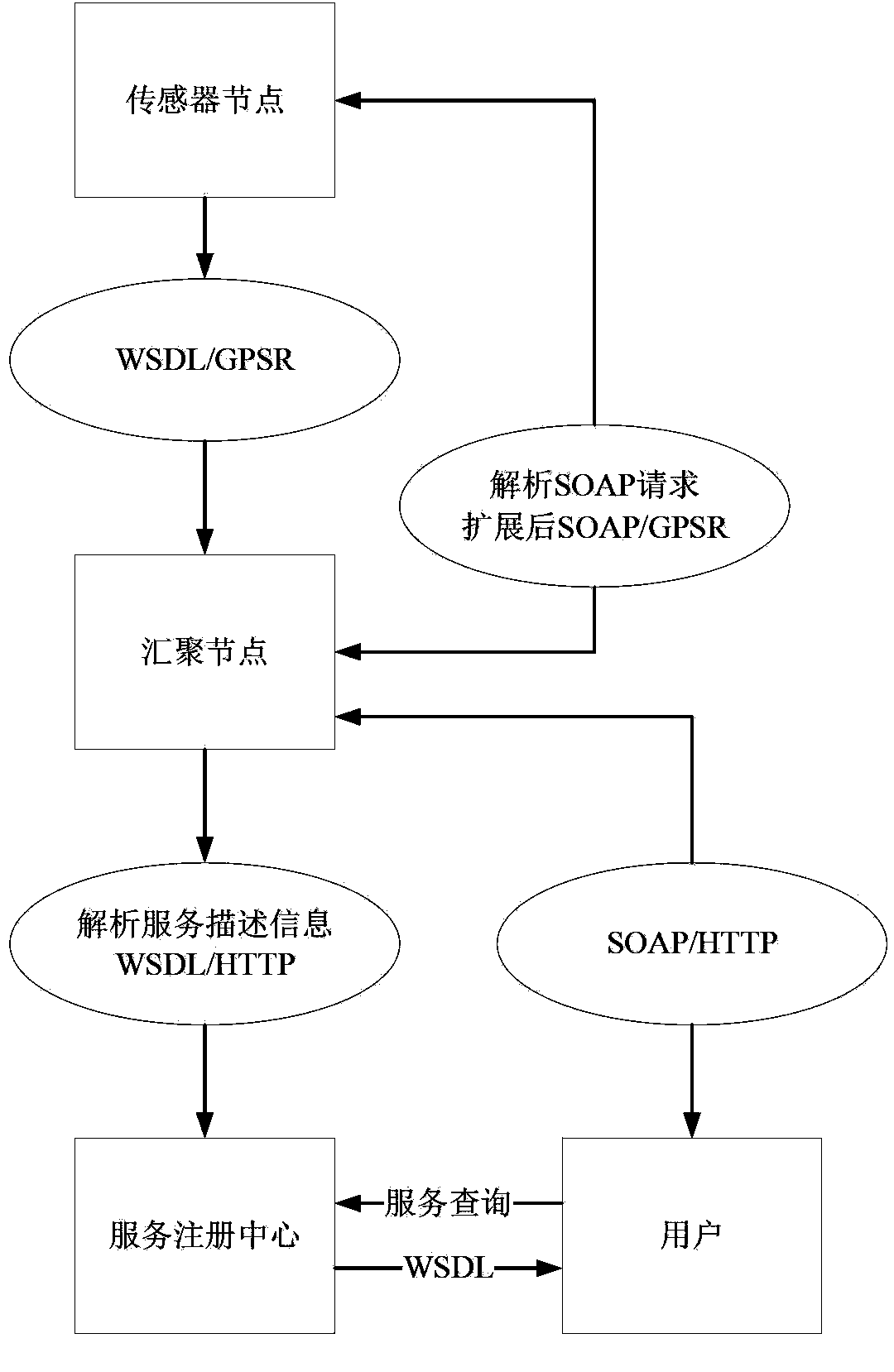
GPSR and SOAP interaction-based service network in building and construction method of service network
InactiveCN103780593ASolve problems such as deficienciesSolve problems such as exhaustionTransmissionGeolocationSensor node
The present invention relates to a GPSR and SOAP interaction-based service network in a building and a construction method of the service network. The network includes an aggregation node, a registration service center and a plurality of sensor nodes distributed in the building; the aggregation node is used for distributing services provided by the sensor nodes to the registration service center, forwarding received service requests of users to sensor nodes that can provide services for the users; the registration service center is used for registering the services of the sensor nodes and acquiring the information of the sensor nodes that can provide services according to self service description information of the users which is received by the registration service; a sensor network geographic routing protocol is adopted between the aggregation node and each sensor node as a communication carrier, and the geographic position information of the sensor nodes and the aggregation node when the sensor network geographic routing protocol is adopted are determined according to a three-dimensional coordinate system which is constructed in the building in which the above nodes are located, and the addresses of the sensor nodes are determined through adopting the coordinates of the sensor nodes in the constructed three-dimensional system.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com