Method for adaptively routing underwater sensor network on basis of difference
An underwater sensor and routing technology, applied in the field of network communication, can solve the problems of long end-to-end delay of data collision, dynamic change of network topology, loss of routing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] In order to make the objectives, implementation solutions, and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
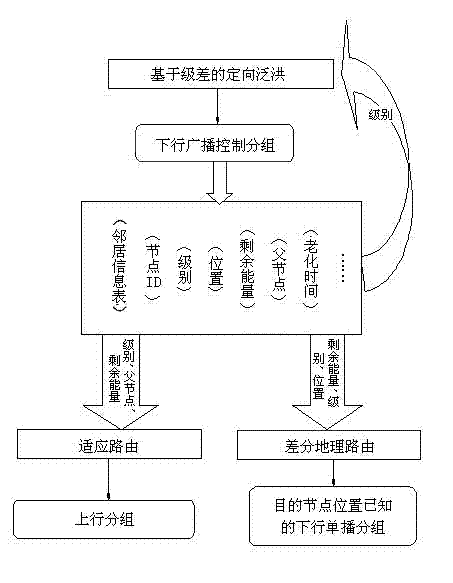
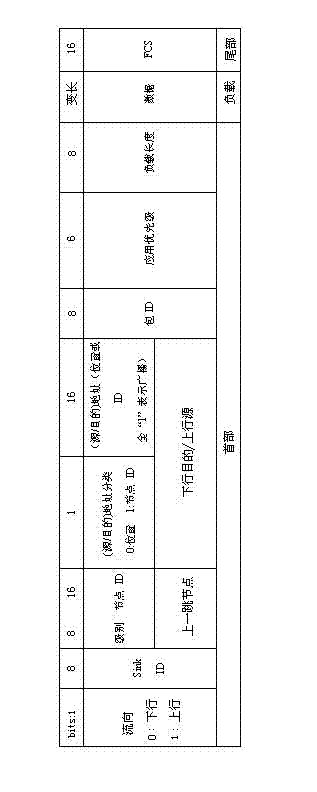
[0041] See figure 1 , To introduce the packet format used by the present invention to adapt to routing: (1) Packet format field: The length of the packet header is 9 bytes, the first bit is the flow direction field, and the bit is filled with 0, which means that the data packet is a beacon or control information sent from a SINK node to a common sensor node , Transmit along the downlink path; fill 1 means that the monitoring data from the sensor node is transmitted to the SINK node along the uplink path. The second field represents the SINK node ID. A UWSN network usually includes multiple SINK nodes to aggregate data. These SINK nodes are mutual backups and generate positioning groups for other nodes. The third field indicates the level of the sending no...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com