Detection and quantitation of sample contamination in immune repertoire analysis
A technique for tissue samples and molecules, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., which can solve problems such as limitation, sensitivity cross-contamination, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The practice of the present invention will employ, unless otherwise indicated, conventional techniques and descriptions of molecular biology (including recombinant techniques), bioinformatics, cell biology, and biochemistry, which are within the skill of the art. Such routine techniques include, but are not limited to, sampling and analysis of blood cells, nucleic acid sequencing and analysis, and the like. Specific illustrations of suitable techniques can be found by reference to the Examples herein below. However, other equivalent conventional methods can of course also be used. Such general techniques and descriptions can be found in standard laboratory manuals such as Genome Analysis: A Laboratory Manual Series (Vol. I-IV); PCR Primer: A Laboratory Manual; and Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (all published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory );Wait.
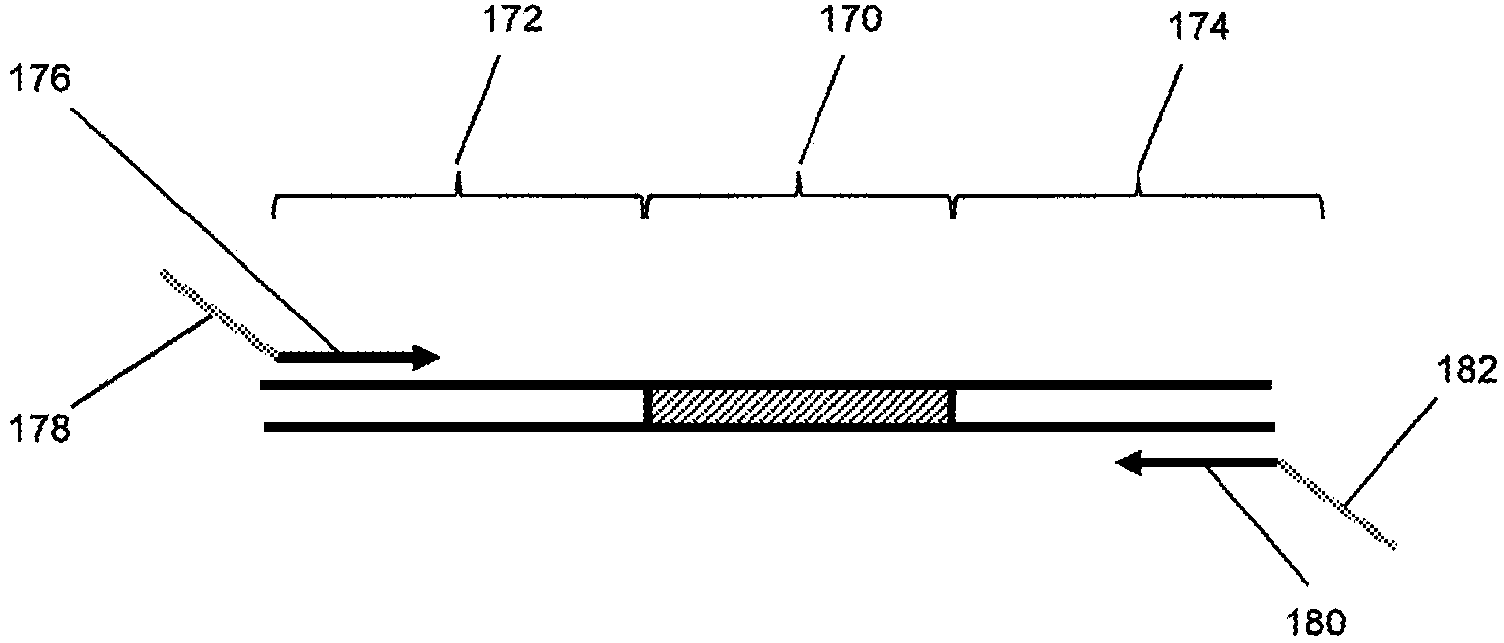
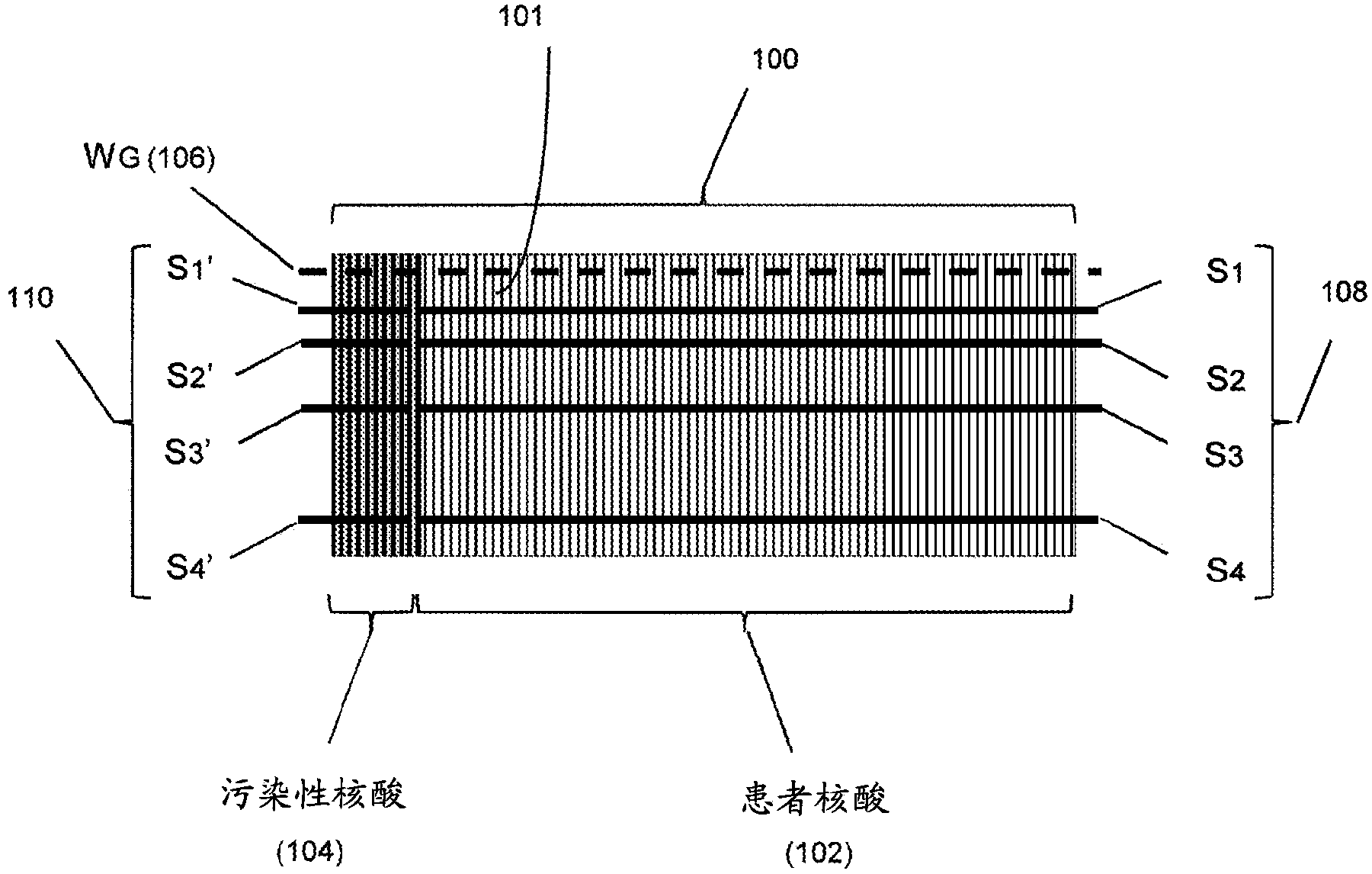
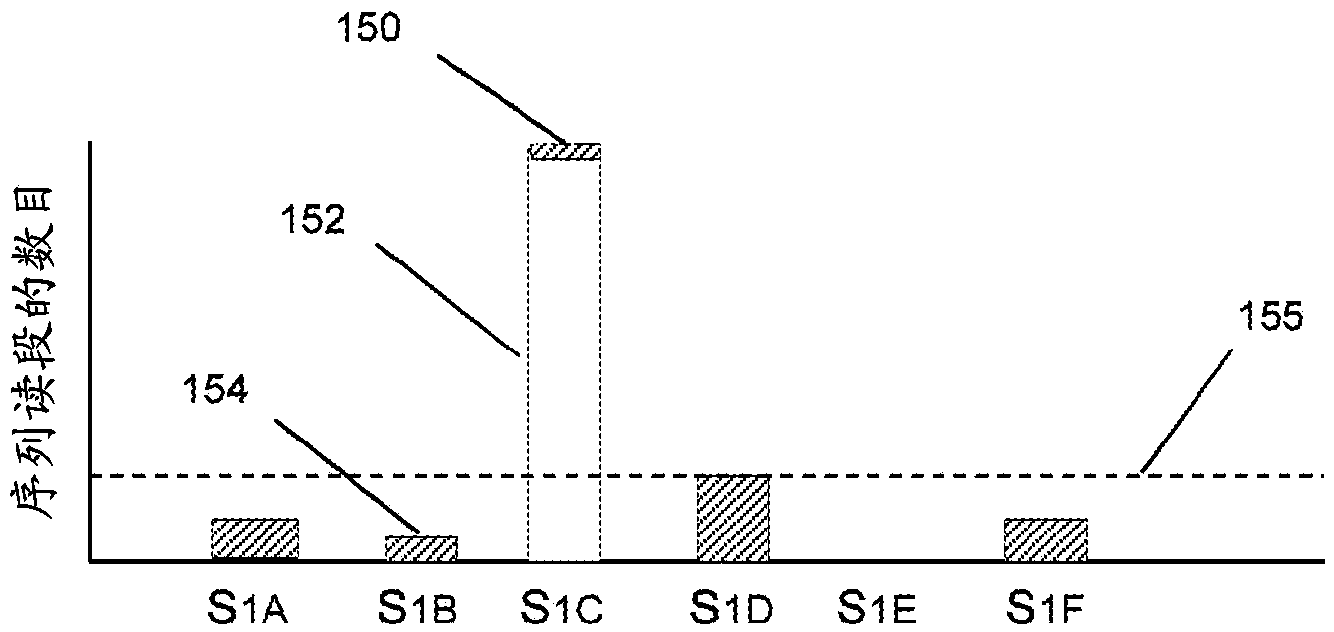
[0023] The present invention relates to a method for detecting and quantifying nucleic acid contamination in a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com