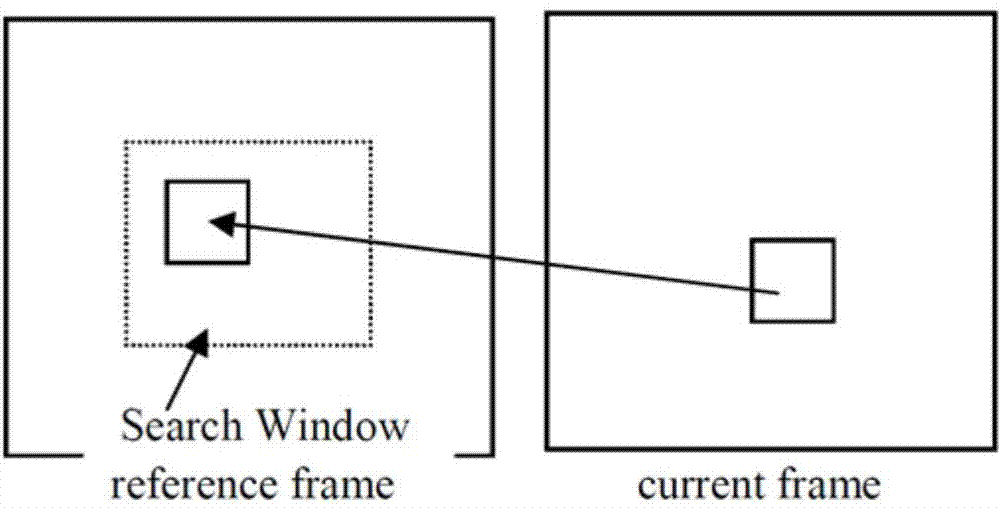
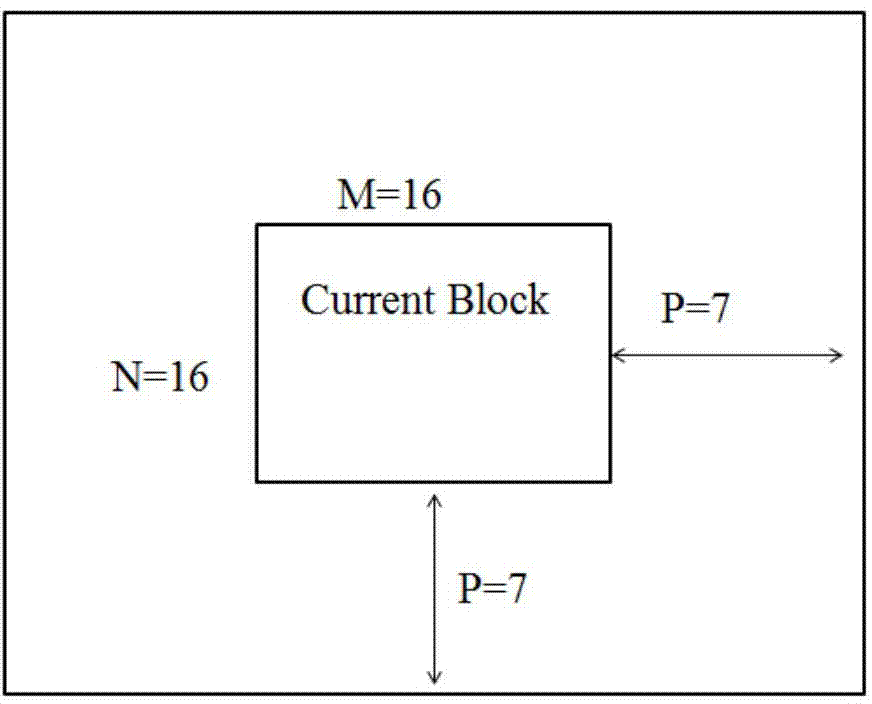
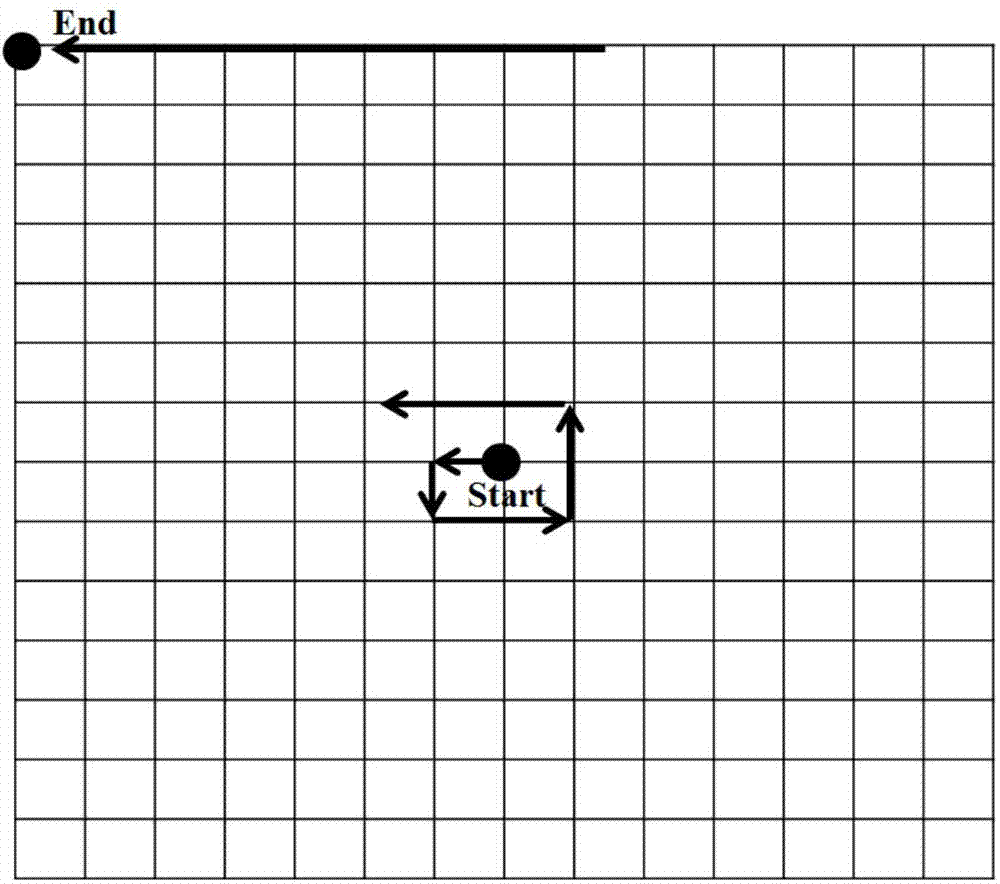
Method for motion estimation of video sequences based on block matching under different resolutions
A technology for video sequence and motion estimation, which is applied in the field of image processing and can solve the problem of lack of comparison of motion estimation accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0104] Embodiment 1: Video surveillance, video conferencing, etc. need to work at low resolution due to bandwidth limitations. Especially for video sequences with small motion ranges such as video conferencing, when the resolution is QCIF (176×144), the accuracy nearly equal to FS can be obtained by applying TSS or NTSS method.
Embodiment 2
[0105] Embodiment 2: Today's algorithms commonly use TSS to apply fast motion estimation. In fact, operations such as compression of fast motion sequences in QCIF format can apply the NTSS algorithm (because TSS is theoretically selected) to obtain higher PSNR and speed than TSS .
Embodiment 3
[0106] Embodiment 3: When motion estimation is performed on a video sequence with high resolution and fine picture quality, it is not necessary to use TSS (low resolution can be used). Because in high-resolution and fine-quality video sequences, reconstructed images tend to lose information, but low-resolution images do not lose information.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com