Self-balanced quick load-reducing control method for microgrid
A control method and micro-grid technology, applied in the integration of power network operating system, AC network voltage adjustment, reducing/preventing power oscillation, etc., can solve the problems of micro-grid frequency collapse, load shedding error, small rotational inertia, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0071] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
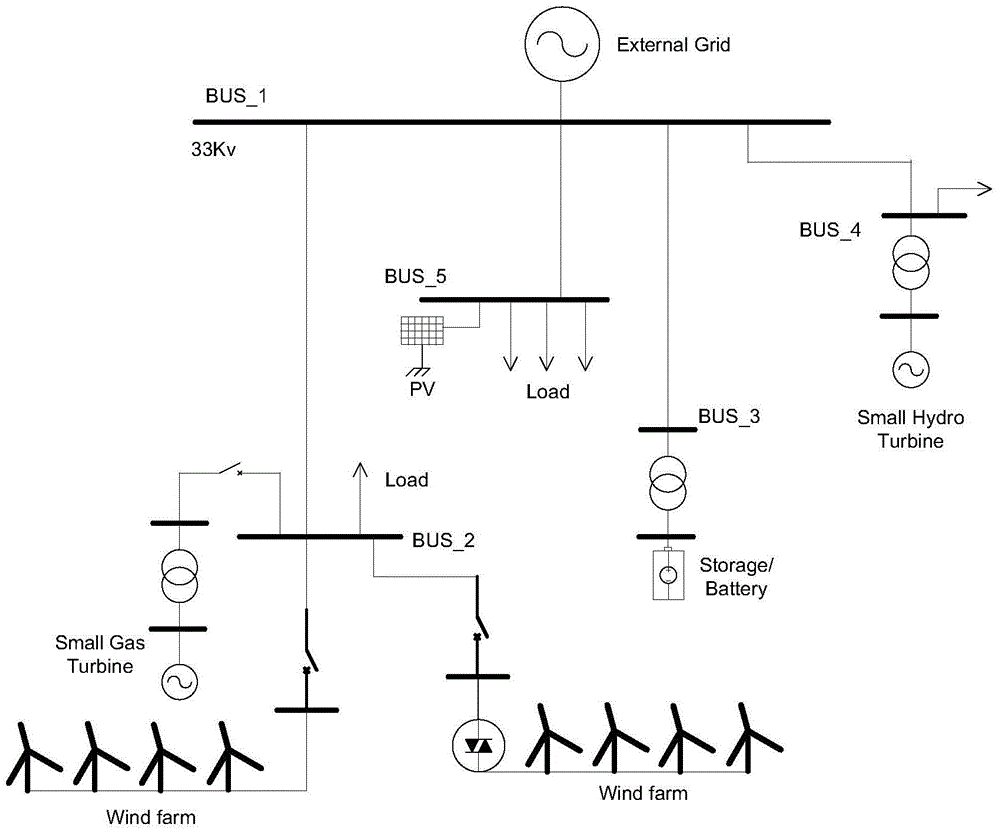
[0072] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a typical microgrid, including small hydropower units, gas turbines, wind farms, photovoltaic farms, energy storage batteries and partial loads.
[0073] 1. Estimate the disturbance magnitude of the microgrid online
[0074] The first stage is to estimate the magnitude of the disturbance in the microgrid, which includes two important steps, one is to determine the equivalent inertia constant of the microgrid, and the other is to calculate the power balance of the microgrid.
[0075] In a distribution network containing hybrid new energy generation, the inertia constant H can be defined by the following formula:
[0076]
[0077] But for different types of generators, the definition of inertia constant is different. H of synchronous generator SG
[0078]
[0079] Among them, J is the moment of inert...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com