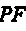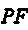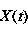Vehicle model audio feature extracting method based on LMD (local mean decomposition) and energy projection methods
A technology of audio features and extraction methods, applied in speech analysis, speech recognition, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the difference of signal frequency components, unable to directly and effectively identify signal characteristic frequencies, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037]Step 1: Use the sound sensor to measure the moving truck and obtain the audio signal of the truck , the sampling frequency is 44100, and the number of sampling points is 4096;
[0038] Step 2: Analyze the collected truck audio signal by local mean decomposition (LMD) method To decompose, the steps are as follows
[0039] (1) Find the local mean function . find truck audio signal All local extreme points , find the average value of all adjacent local extremum points
[0040]
[0041] Among them, i=1,2,...M; M is the number of local extremum points of the original signal. Then, all adjacent mean points Connected by a straight line and smoothed by the moving average method, we get
[0042] (2) Find the envelope estimation function . The envelope estimate is
[0043]
[0044] All two adjacent envelope estimates Connected by a straight line, and then smoothed by the moving average method to obtain .
[0045] (3) The local mean function from th...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Step 1: Use the sound sensor to measure the driving tractor and obtain the audio signal of the tractor , the sampling frequency is 44100, and the number of sampling points is 4096;
[0076] Step 2: Analyze the collected tractor audio signal by local mean decomposition (LMD) method To decompose, the steps are as follows
[0077] (1) Find the local mean function . Find out the tractor audio signal All local extreme points , find the average value of all adjacent local extremum points
[0078]
[0079] Among them, i=1,2,...M; M is the number of local extremum points of the original signal. Then, all adjacent mean points Connected by a straight line and smoothed by the moving average method, we get
[0080] (2) Find the envelope estimation function . The envelope estimate is
[0081]
[0082] All two adjacent envelope estimates Connected by a straight line, and then smoothed by the moving average method to obtain .
[0083] (3) The local mean ...
Embodiment 3
[0111] Step 1: Use the sound sensor to measure the moving car and obtain the audio signal of the car , the sampling frequency is 44100, and the number of sampling points is 4096;
[0112] Step 2: Decompose by local mean Method for the collected car audio signal To decompose, the steps are as follows
[0113] (1) Find the local mean function . find car audio signal All local extreme points , find the average value of all adjacent local extremum points
[0114]
[0115] Among them, i=1,2,...M; M is the number of local extremum points of the original signal. Then, all adjacent mean points Connected by a straight line and smoothed by the moving average method, we get
[0116] (2) Find the envelope estimation function . The envelope estimate is
[0117]
[0118] All two adjacent envelope estimates Connected by a straight line, and then smoothed by the moving average method to obtain .
[0119] (3) The local mean function from the original signal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com