In vitro assay for predicting renal proximal tubular cell toxicity
一种肾近曲小管、细胞的技术,应用在预测肾近曲小管细胞毒性的体外试验领域
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
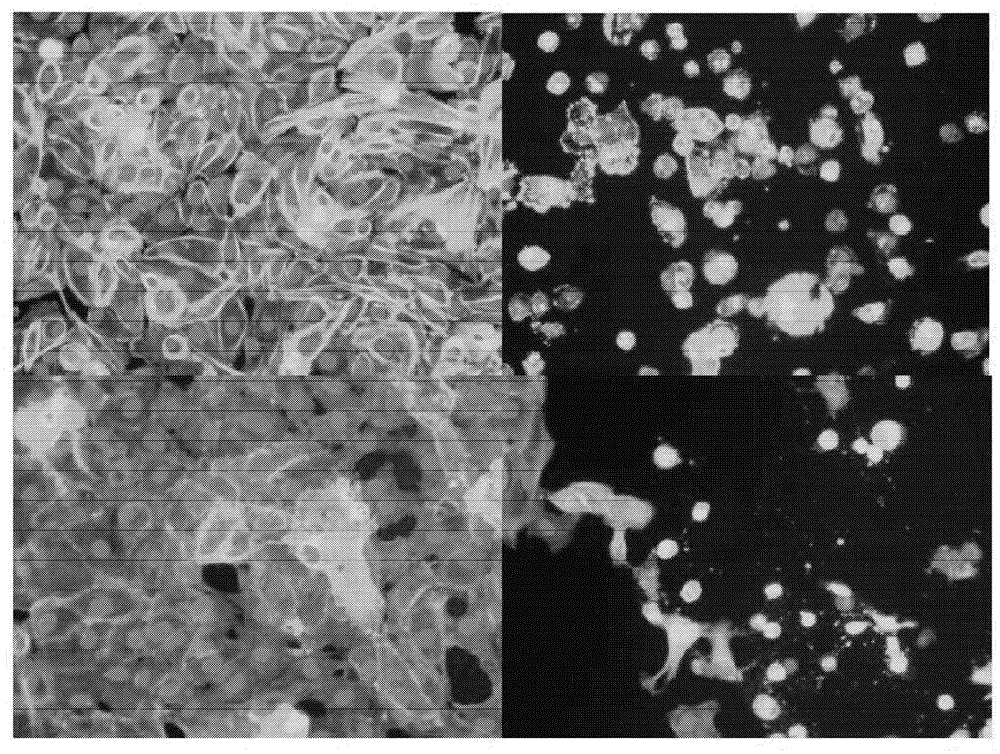
[0071] Human primary renal proximal tubular cells (HPTC) were observed to display marked changes in cell morphology when treated with nephrotoxic substances (see figure 1 ). Also, a reduction in the number of cells due to cell death was observed. The assay uses nuclei counts and changes in cell morphology (eg, cell area and roundness) to assess toxicity to HPTC.
[0072] First, cells were seeded into multi-well plates and cultured for 3 days. It was then exposed to the test compound for 16 hours. The cells used were commercially available HPTCs (American Type Culture Collection; "ATCC") and HPTCs isolated by the inventors from fresh human kidney samples.
[0073] Cells were left untreated or treated with 0.2 mg / ml of tetracycline (ATCC cells) or gentamicin (inventors isolate).
[0074] Cells were then fixed and stained, stained with and detected for F-actin. Treatment with these nephrotoxic substances resulted in morphological changes as follows: F-actin alignment, decrea...
Embodiment 2
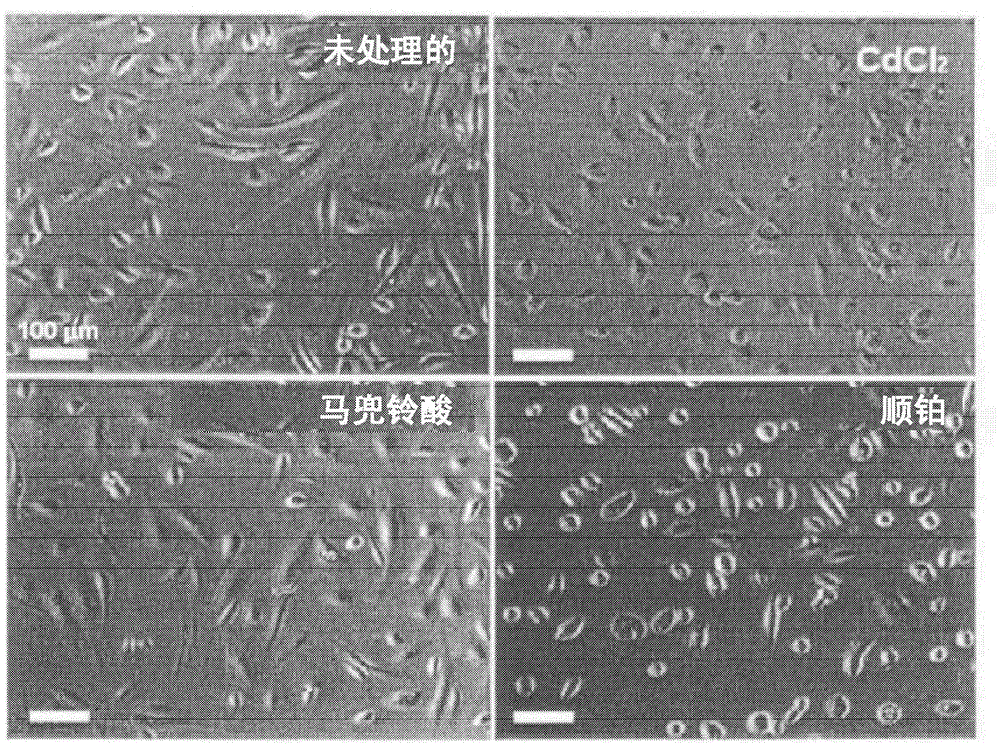
[0077] This example was performed using a commercially available HPTC (ATCC).
[0078] Cells were seeded into multi-well plates and cultured for 3 days. Then, the cells were left untreated, or treated with gentamicin (2.5 mg / ml), CdCl 2 (10 μg / ml), aristolochic acid (100 μg / ml), cisplatin (100 μg / ml) or DMSO (50 μg / ml).
[0079] After 24 hours, cells were imaged by phase-contrast microscopy ( figure 2 , gentamicin image and DMSO image not shown).
Embodiment 3
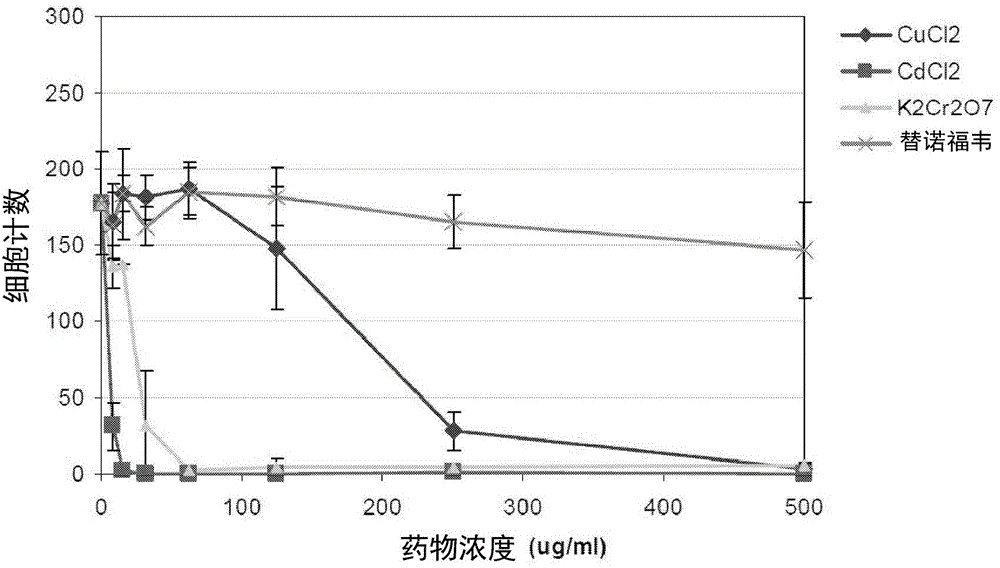
[0081] The following different types of renal proximal tubular cells were used: HPTC (ATCC), LLC-PK1 cells and HK-2 cells.
[0082] The cells were cultured and treated as described in Example 2, using 0-500 μg / ml of CuCl 2 , CdCl 2 、K 2 Cr 2 o 7 or tenofovir ( Figure 3-5 ) or gentamicin, tetracycline, 5-fluorouracil or As 2 o 3 ( Figure 6 and 7 )deal with. Cells were stained, imaged and counted. Different types of PTCs respond differently to compounds, and HPTC is the most sensitive ( Figure 3-5 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com