Map display method and device
A map and electronic map technology, applied in the field of geographic information, can solve problems such as affecting user experience, user visual fatigue, and blunt electronic map display, so as to improve user experience and reduce visual fatigue.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
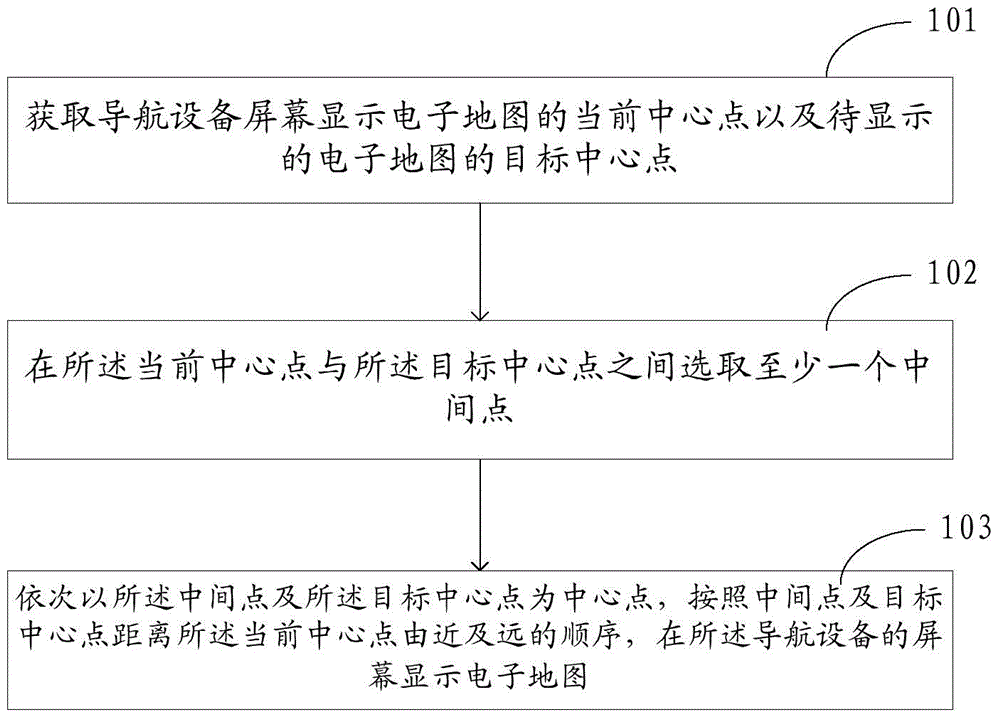
[0056] refer to figure 1 , is a flow chart of a map display method provided in Embodiment 1 of the present application. The method is applied to electronic devices such as navigation devices (such as navigators, mobile terminals (such as mobile phones) installed with navigation software), and the navigation The device includes a screen for displaying an electronic map, and the display screen may be a liquid crystal display or a touch display, and the method may include the following steps:
[0057] Step 101: Obtain the current center point of the electronic map displayed on the screen of the navigation device and the target center point of the electronic map to be displayed.
[0058] Wherein, the current center point refers to the center point of the electronic map currently displayed on the screen of the navigation device, and the target center point refers to the center point of the electronic map to be displayed on the screen of the navigation device.
[0059] Taking the n...
Embodiment 2
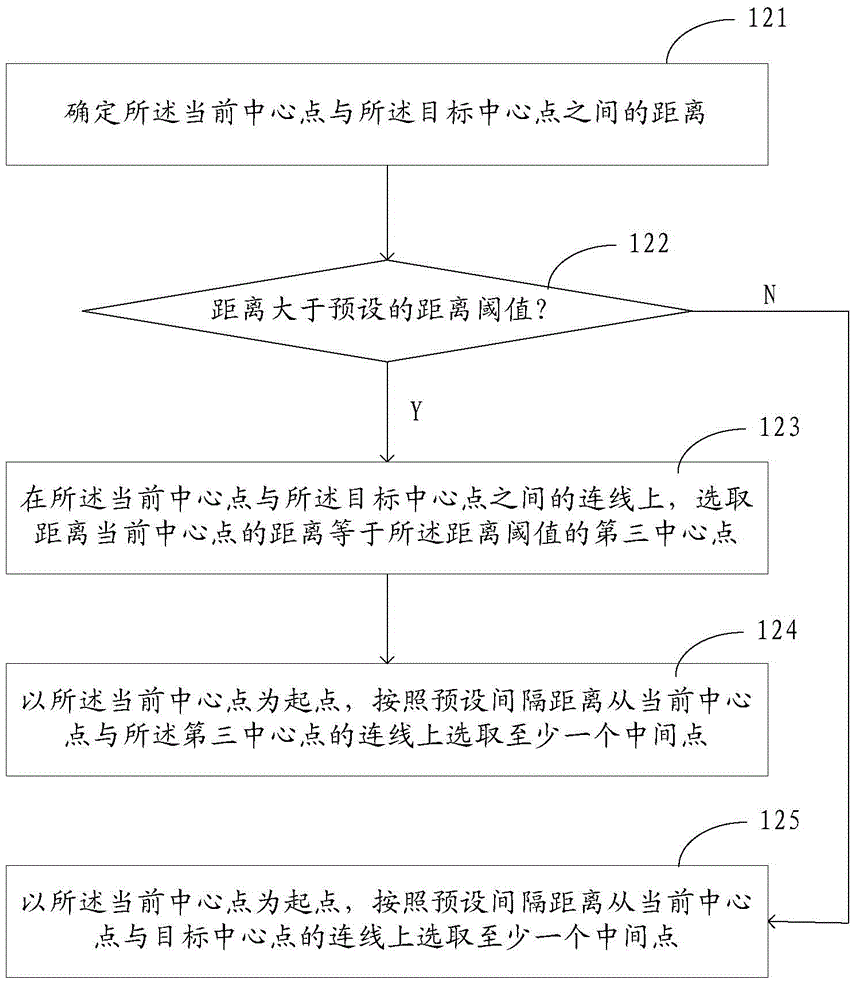
[0067] Compared with the map display method provided in Embodiment 1, the map display method provided in Embodiment 2 of the present application has figure 1 Step 102 in the flow chart shown is refined. refer to image 3 , is a flow chart of step 102, wherein said step 102 can be specifically implemented through the following steps:
[0068] Step 121: Determine the distance between the current center point and the target center point.
[0069] Step 122: Determine whether the distance is greater than a preset distance threshold, and when the distance is greater than the distance threshold, perform step 123; otherwise, perform step 125.
[0070] Step 123: On the connection line between the current center point and the target center point, select a third center point whose distance from the current center point is equal to the distance threshold, and perform step 124.
[0071] Step 124: Taking the current center point as a starting point, select at least one intermediate point...
Embodiment 3
[0079] In practical applications, in order to improve the acquisition and coherent display rate of the electronic map corresponding to the intermediate point and the target center point, the electronic map corresponding to each intermediate point and the target center point can be pre-drawn and cached, and displayed on the screen of the navigation device. When the intermediate point and the target center point are the electronic maps of the center point, the corresponding electronic map is directly obtained from the cache and displayed on the screen of the navigation device. Compared with the foregoing embodiment one and embodiment two, the difference between this embodiment three is that figure 1 Step 103 in the flow shown is refined. Therefore, refer to Figure 5 , is a flowchart of step 103, wherein said step 103 may include the following steps:
[0080] Step 131: Obtain the map data cached when generating the electronic map with the current center point as the center poi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com