Novel method for evaluating potential of soil contaminated by phytoremediation radionuclide
A radionuclide and phytoremediation technology, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, etc., can solve the problem of not considering plant biomass and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0026] Select the sampling site, collect the dominant plants growing in the radionuclide-contaminated soil, and collect 6 plants for each plant; use polybutene sleeves, 30.5 cm in length, and 5 cm in diameter at the sampling points corresponding to plant growth. S-shaped stainless steel drilling tool to collect soil samples. The collected plant samples were first washed with tap water on the soil attached to the surface of their leaves and roots, and then washed with deionized water to separate the roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. After natural air-drying for 2 weeks, dry in an oven at 105 °C for 24 h, and then weigh the stems, leaves and fruits with an electronic balance after constant mass. The stems, leaves and fruits of the plants dried to a constant mass were crushed with a plant grinder, and passed through a 63 μm nylon sieve before being tested. For the collected radionuclide-contaminated soil samples, after removing plant residues and gravel, the soil at...
Embodiment 1
[0034] Phytoremediation coefficient (1).
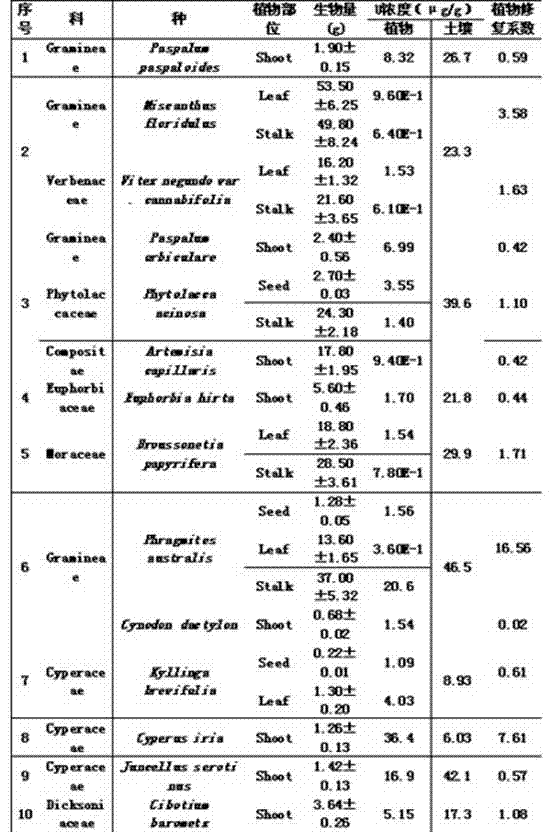
[0035] Table 1 Phytoremediation coefficients of 16 plants in radionuclide-contaminated soil of a uranium tailings pond and its surrounding areas to U
[0036]
Embodiment 2
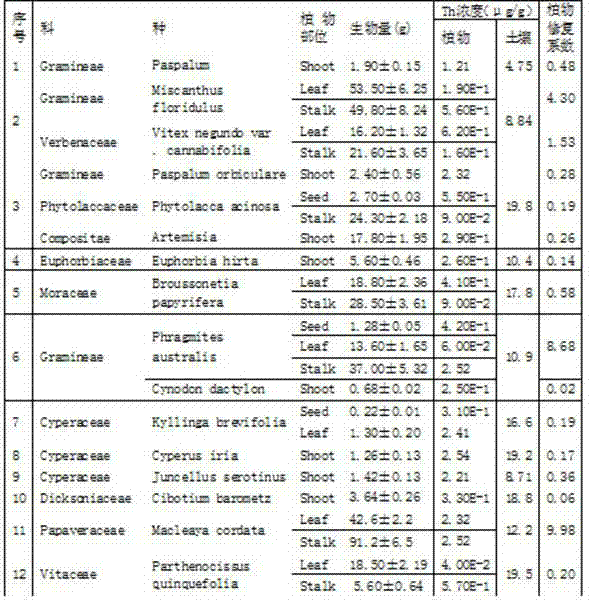
[0038] Collect 16 kinds of dominant plants and soil samples in the radionuclide-contaminated soil of a certain uranium tailings pool and surrounding areas, and measure the biomass of the aboveground parts of the plants, the Th concentration of the aboveground parts and the corresponding Th concentration in the soil, and According to formula (1), the phytoremediation coefficient of each plant to Th in radionuclide-contaminated soil was calculated, as shown in Table 2, according to the calculated phytoremediation coefficient, Macleaya cordata The restoration coefficient of Th in radionuclide-contaminated soil is the highest, which is 9.98. Therefore, among the 16 kinds of plants collected Macleaya cordata It has good remediation potential for Th in radionuclide-contaminated soil.
[0039] Phytoremediation coefficient (1).
[0040] Table 2 Phytoremediation coefficients of 16 plants in radionuclide-contaminated soil of a uranium tailings pond and its surrounding areas to Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com