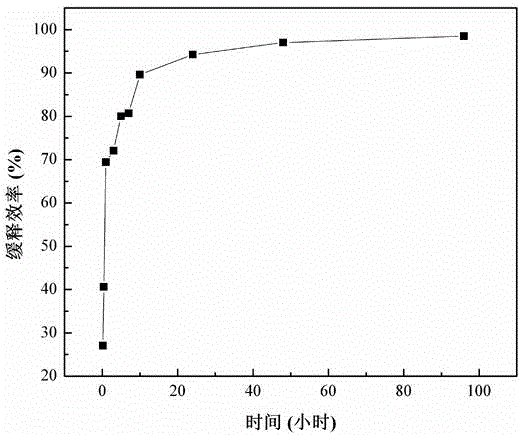
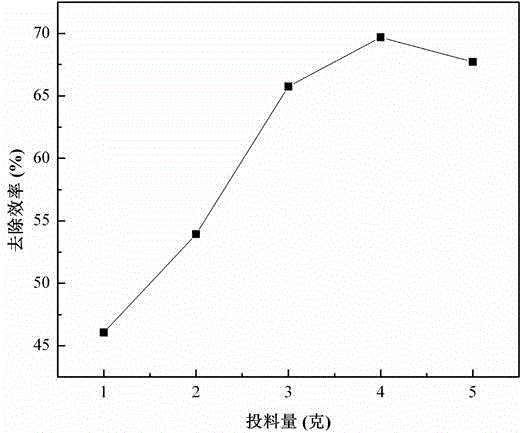
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Radionuclide contamination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiation exposure also occurs after internal contamination, i.e., when a radionuclide is ingested, inhaled or absorbed into the blood stream. This kind of exposure stops only if the radionuclide is totally eliminated from the body, with or without treatment.
Method and device for treating radioactive wastes
ActiveCN102157215AAvoid pollutionImprove corrosion resistanceRadioactive decontaminationPlasma techniqueRefractoryRadioactive waste
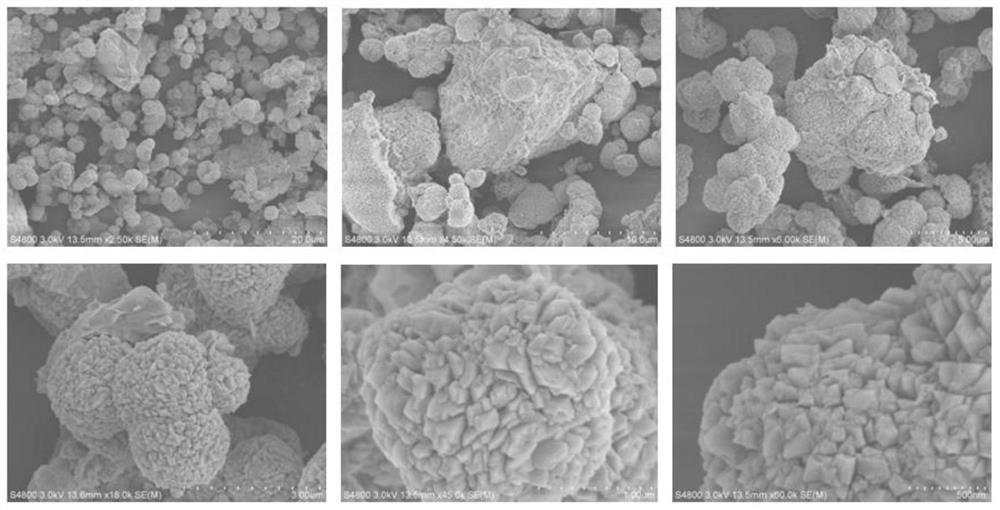
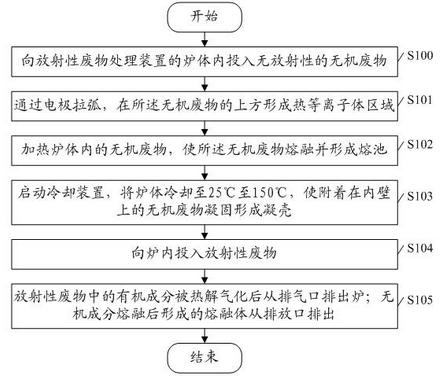
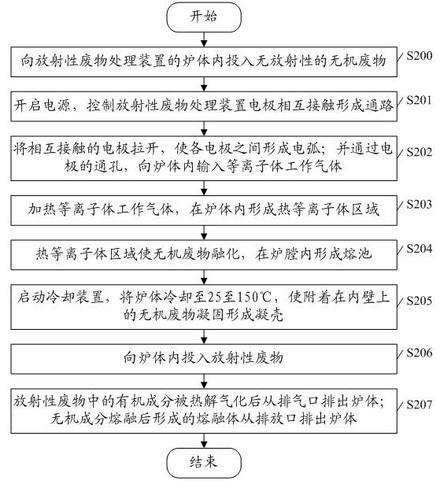
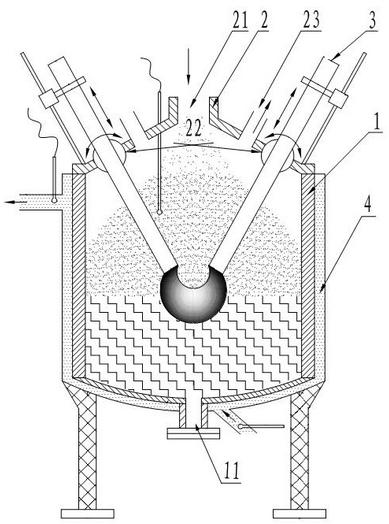
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for treating radioactive wastes. The method comprises the following steps of: putting nonradioactive inorganic wastes into a furnace body of a radioactive waste treatment device to form a thermal plasma area above the inorganic wastes by electrode arcing, and heating the putted inorganic wastes to form a molten pool; starting a coolingdevice to cool down the furnace body to a temperature of 25-150 DEG C so as to make the inorganic wastes attached to the inner wall of the furnace body be solidified to form a shell; putting radioactive wastes into the furnace body to pyrolyze organic elements of the radioactive wastes, and then exhausting the generated gas from the furnace body; and charging inorganic elements of the radioactivewastes into the molten pool to be molten, and discharging the molten inorganic elements out of the furnace body. During the implementation of the method and device disclosed by the invention, the furnace body does not need refractory materials, and the molten body is solidified in an area near the inner wall of the furnace to form the shell, thus the inner wall of the furnace does not directly contact with the molten body, radioactive nuclides are prevented from polluting the inner wall of the furnace, the device can be used for treating various wastes, the service life of the device is long and the amount of residual wastes is small.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD
Orofacial radiation detection device for detection of radionuclide contamination from inhalation
InactiveUS20090159807A1Cathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesSolid-state devicesElectricityMicrocomputer
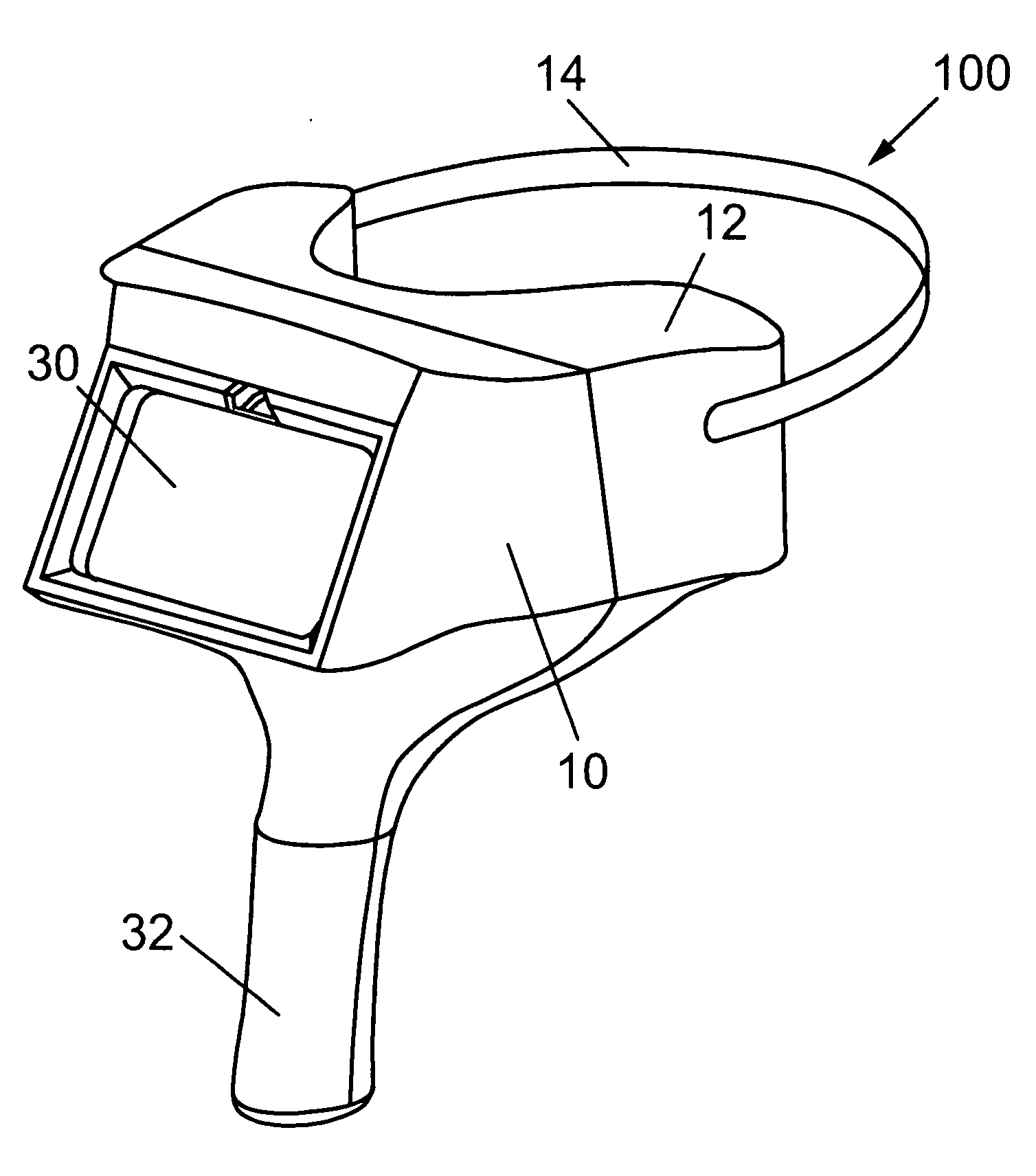
The present invention provides an orofacial radiation detection device for detection of radionuclide contamination from inhalation. The device includes a face mask including a support frame and an adjustable head strap connected to the support frame. Mounted on the frame are radiation detectors in selected locations so that when being worn by a person, the detectors are located in close proximity to the orofacial region of the person including their nose and mouth. The device includes an electronic controller connected to the detectors for controlling operation of the radiation detectors. The device includes a microcomputer mounted on the support frame and electrically connected to the electronic controller for processing signals from the detectors for allowing input from an operator, performing data analysis and detection algorithms, and outputting results. The detectors include beta and gamma detectors that, utilizing appropriate hardware processing and software algorithms, are able to determine if radionuclides are present in the orofacial area of a person suspected to have been exposed to airborne contamination.
Owner:UNIV OF ONTARIO INST OF TECH
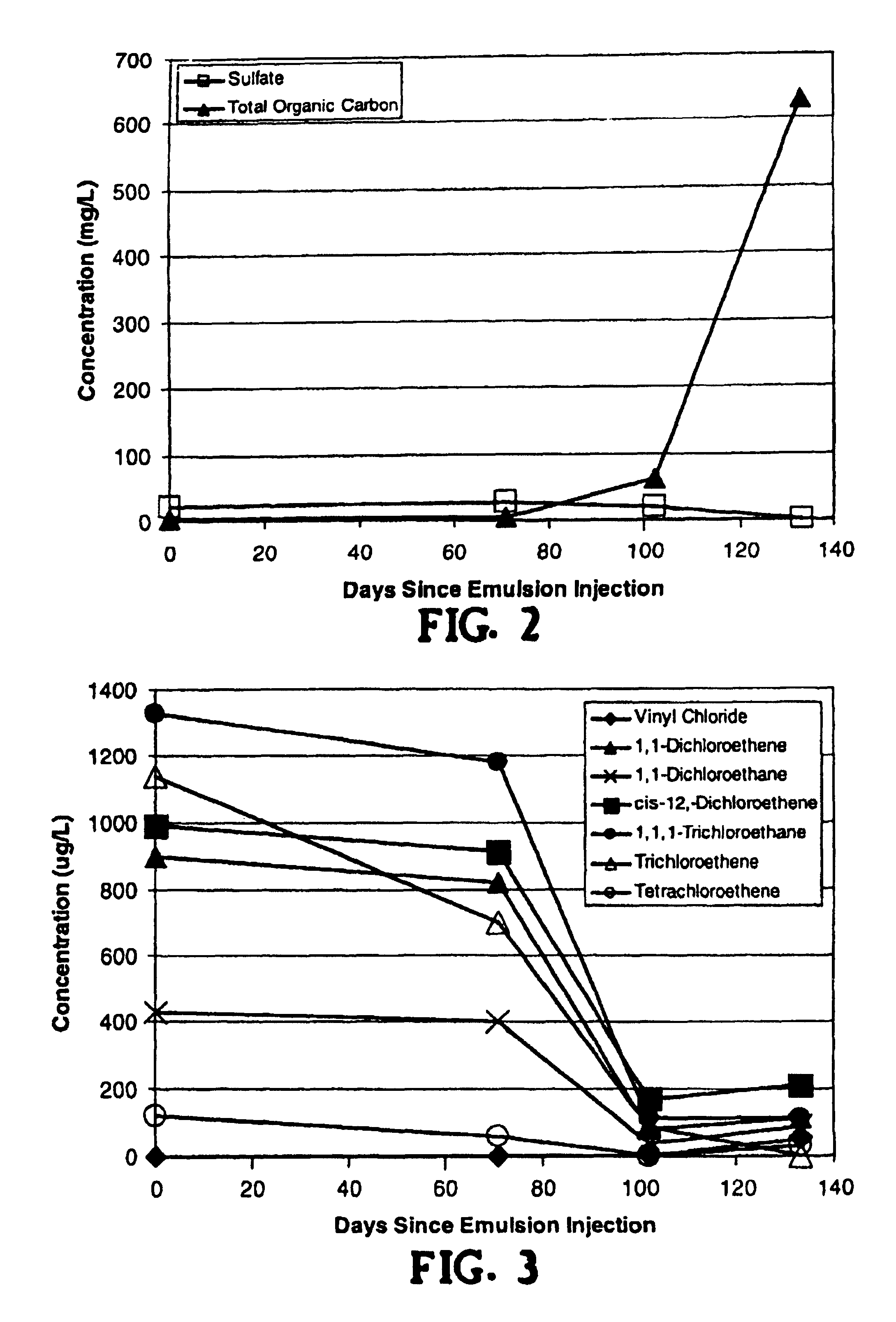
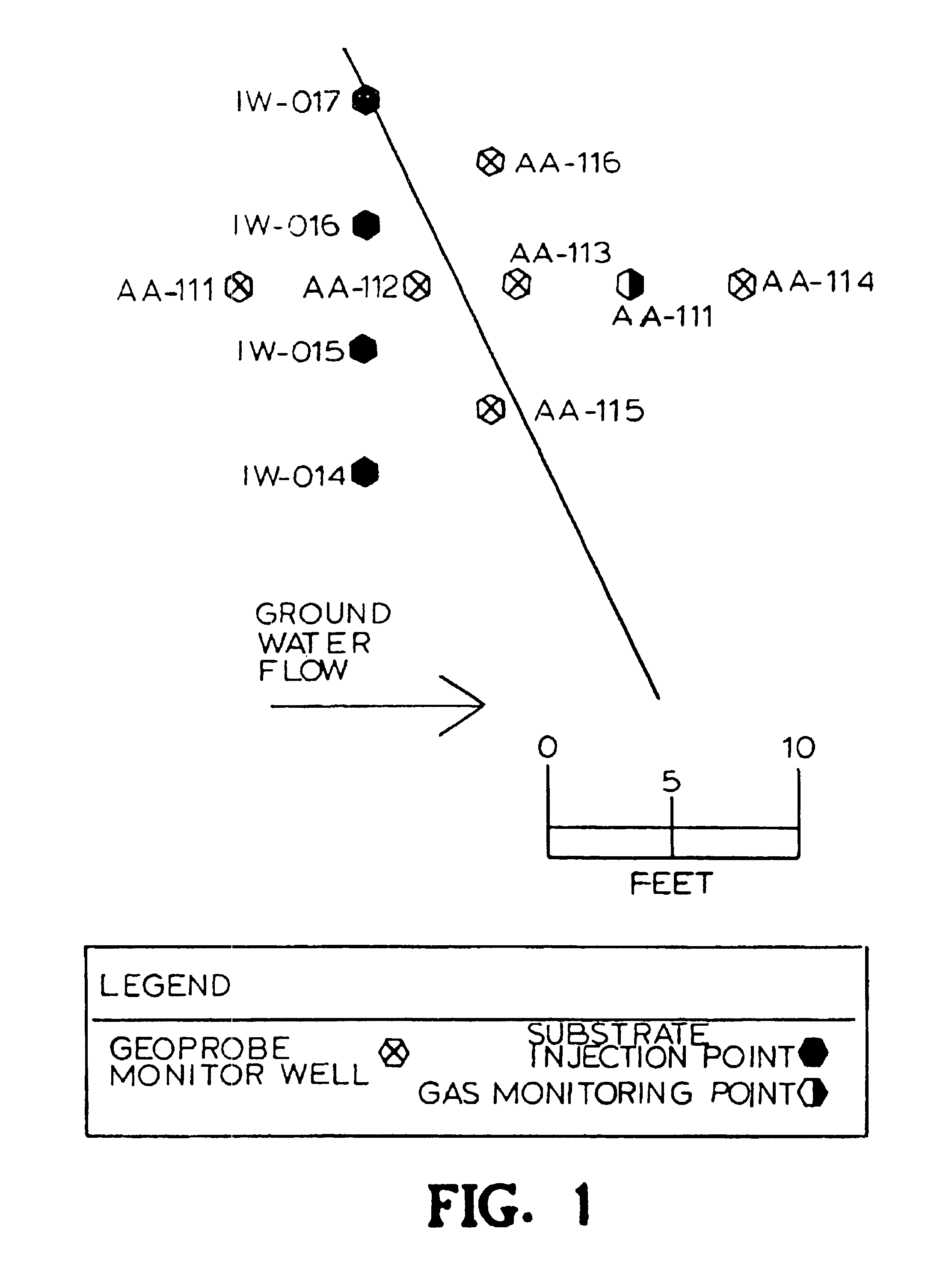
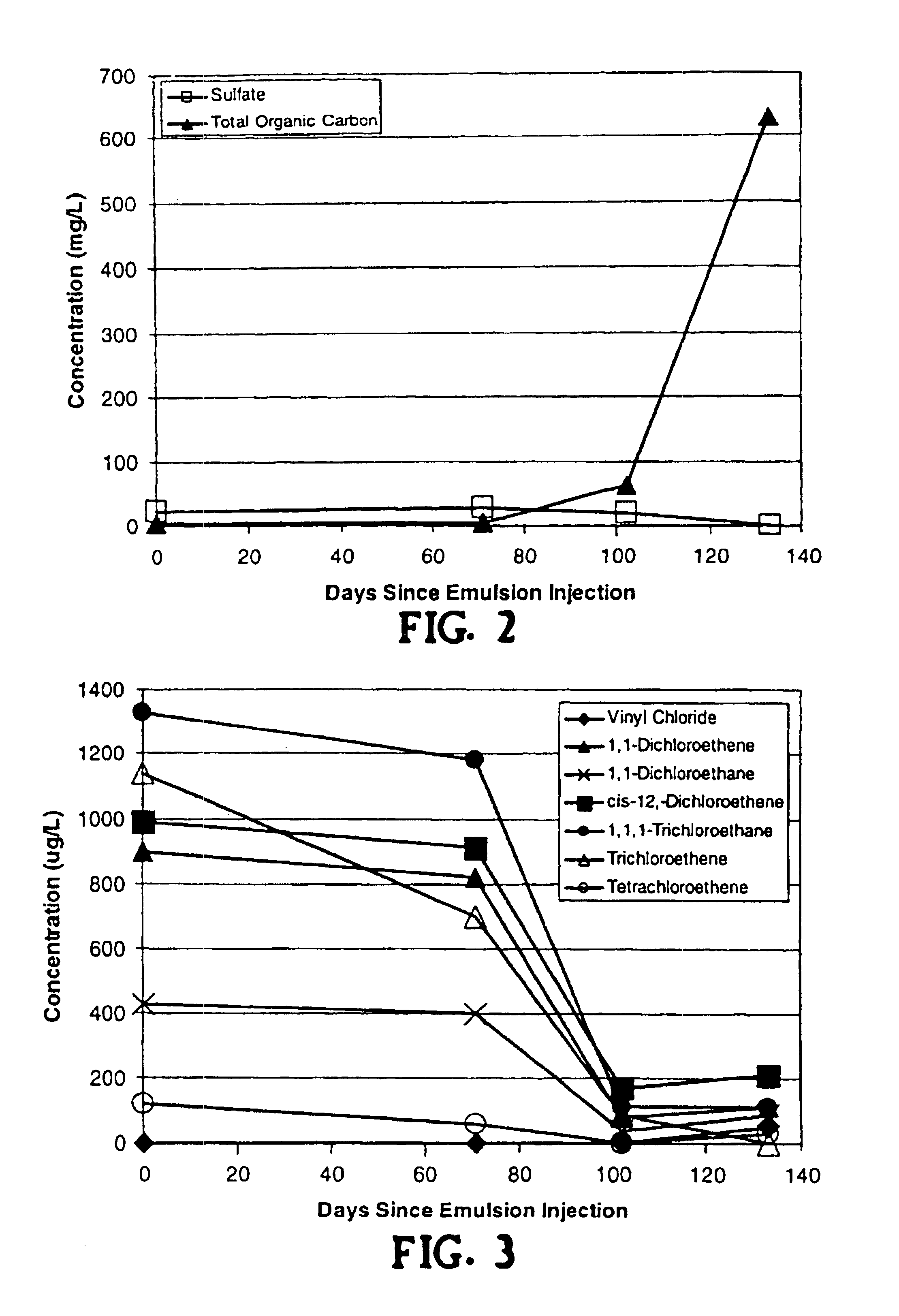
Method for remediation of aquifers
InactiveUSRE40734E1Improve mobilityWater treatment compoundsSolid waste disposalFood gradeInorganic compound
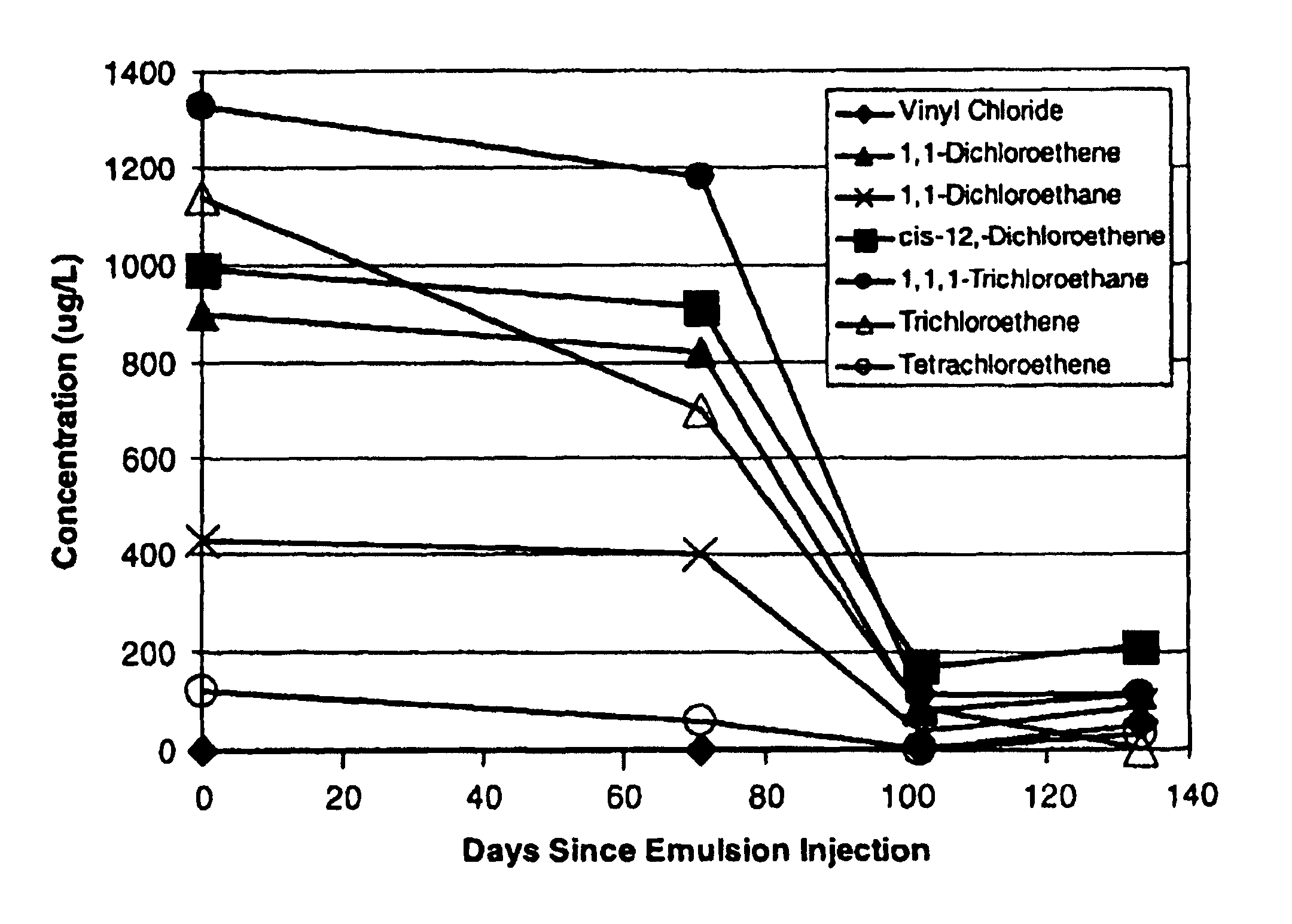
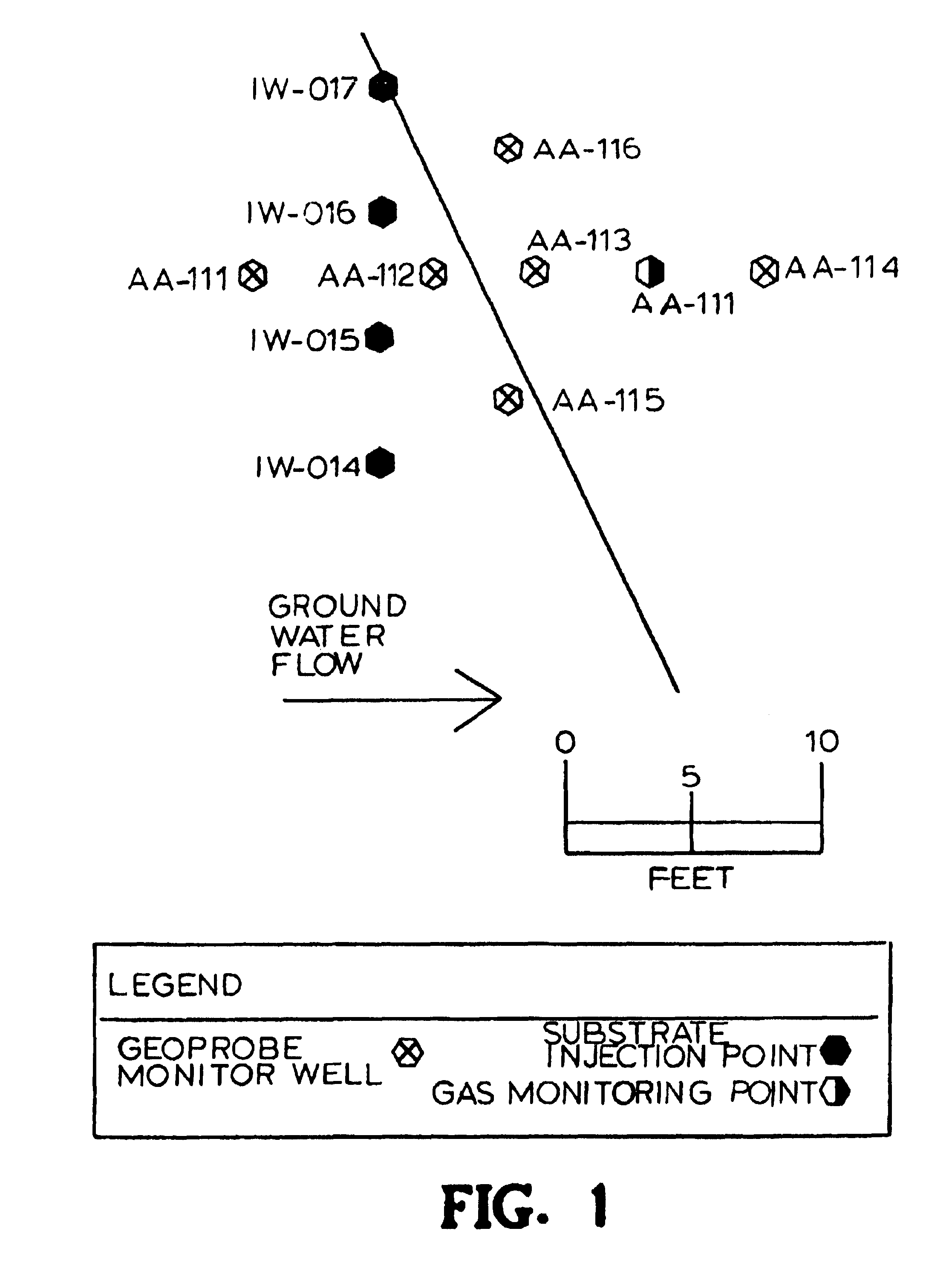
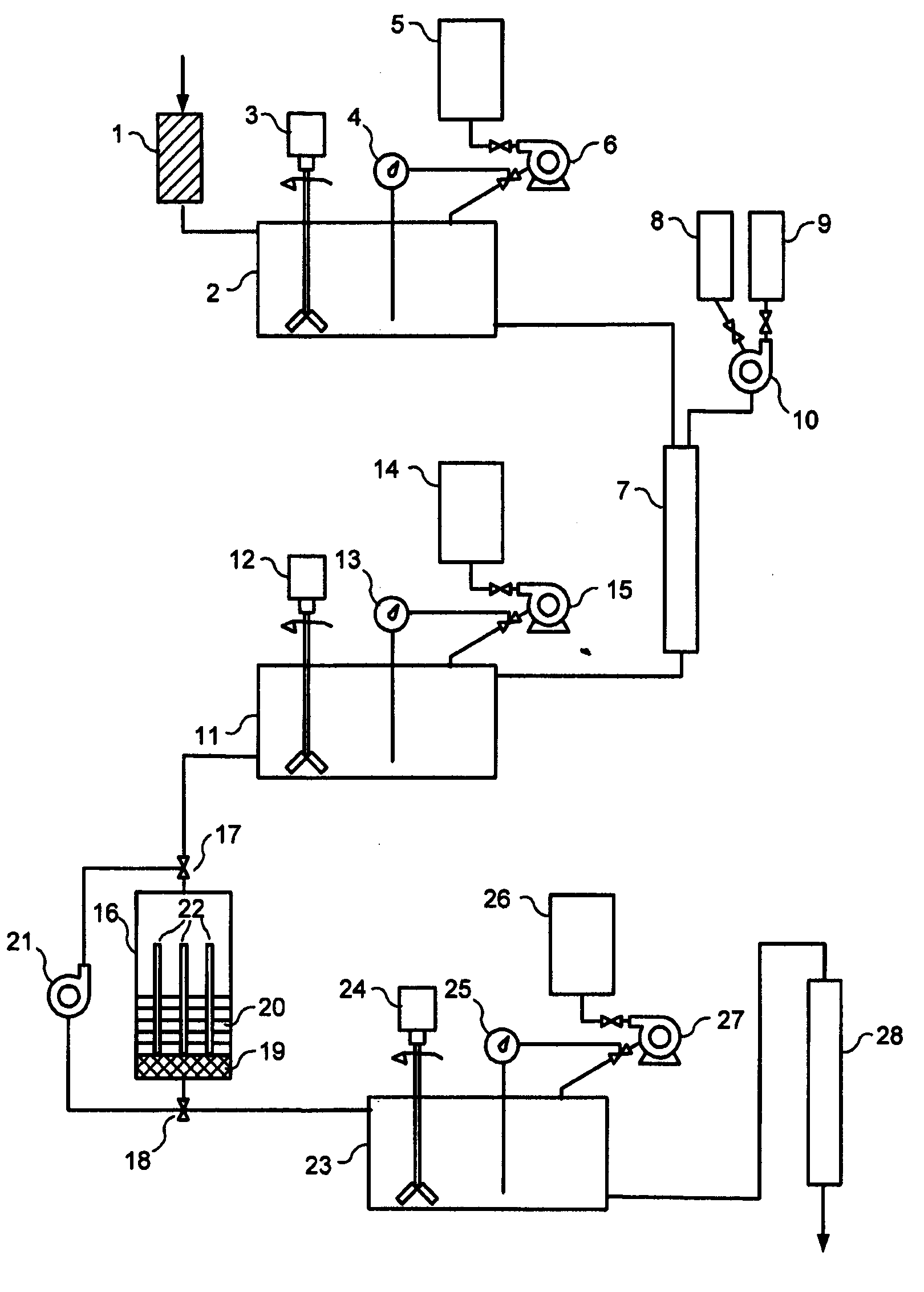
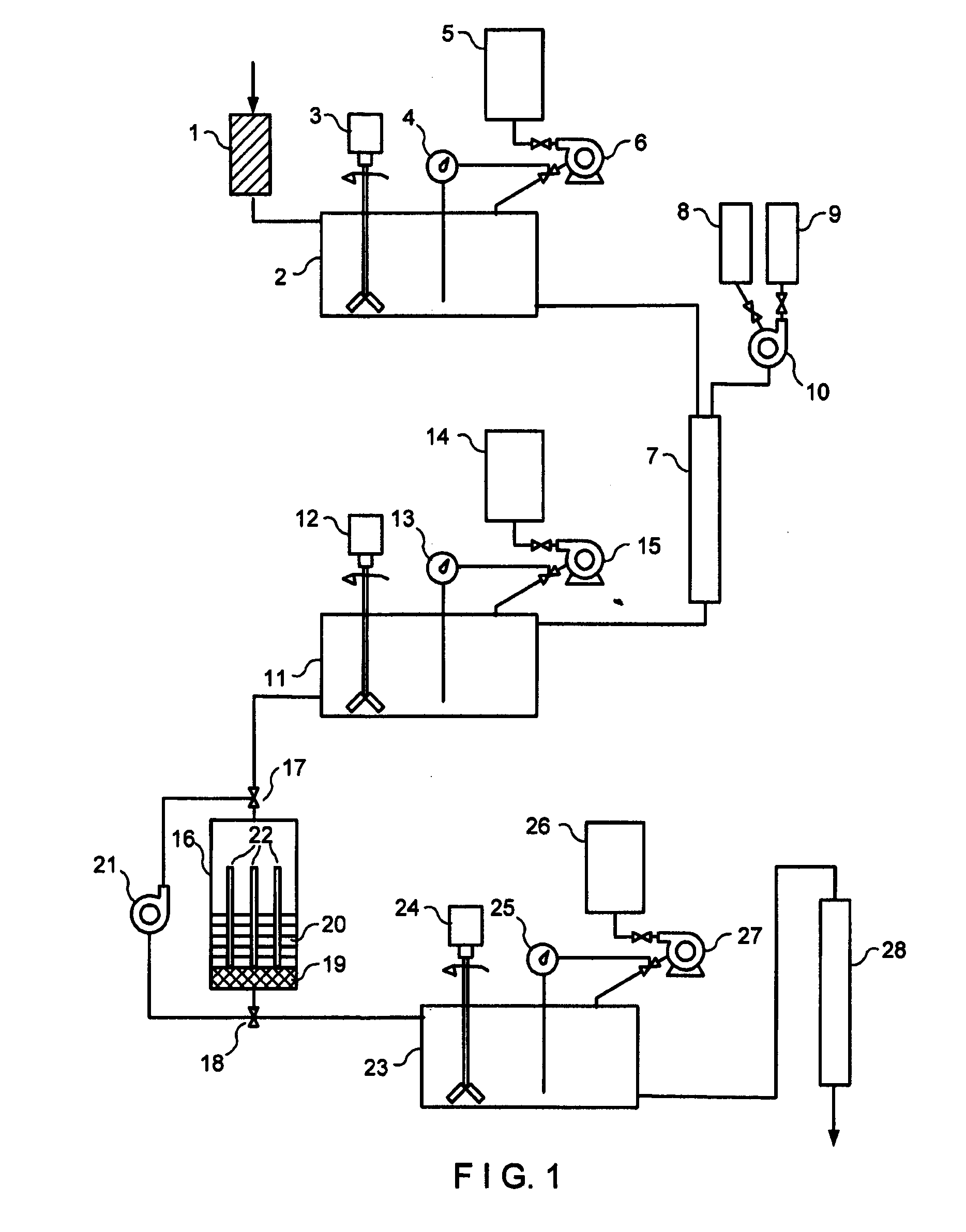
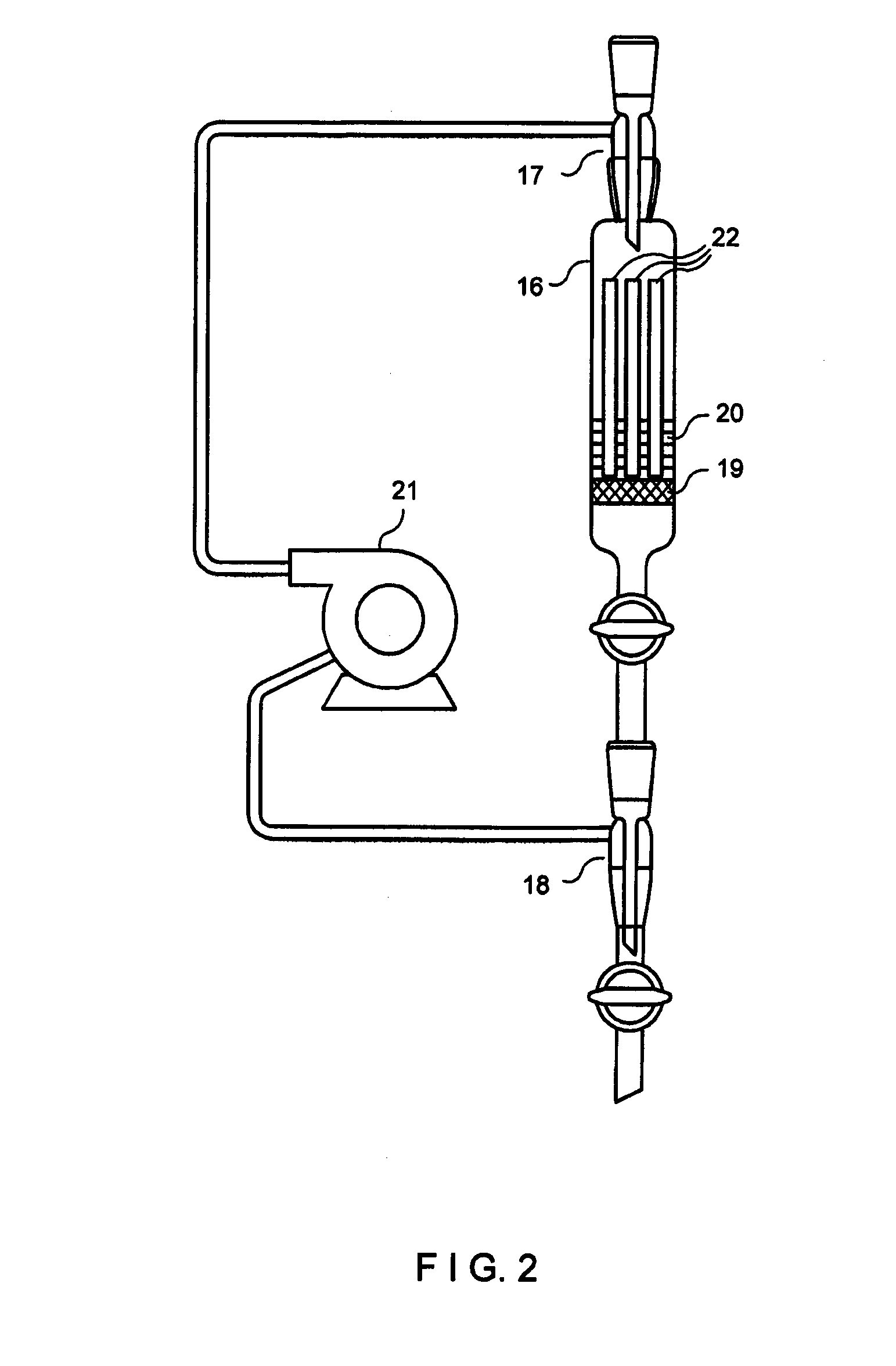
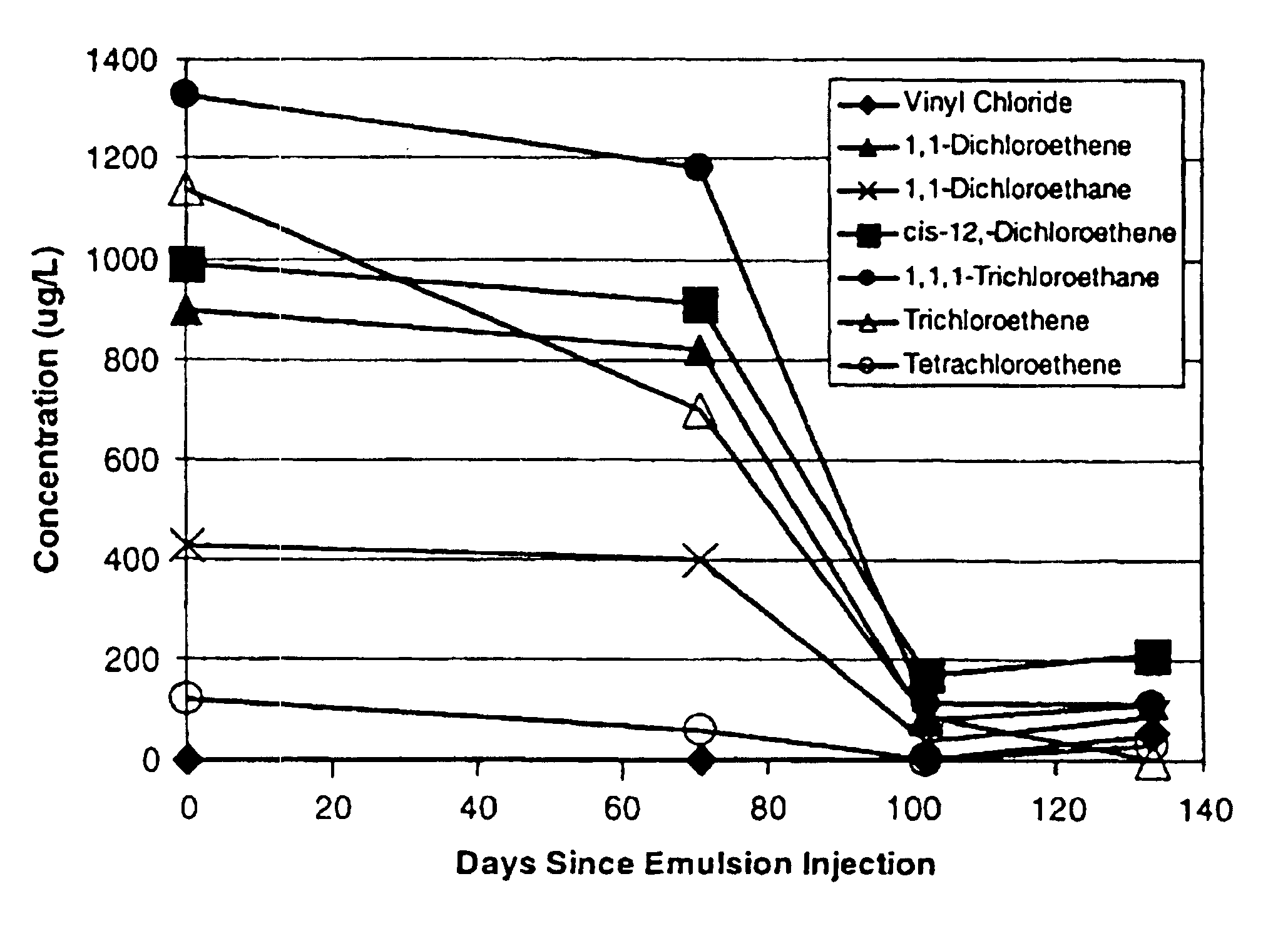
A method for remediating aquifers and groundwater contaminated, for example, by toxic halogenated organic compounds, certain inorganic compounds, and oxidized heavy metals and radionuclides, using the introduction of an innocuous oil, preferably an edible, food grade oil such as soybean oil, formulated into a microemulsion preferably by mixing with a natural food-grade emulsifier (such as lecithin) and water.
Owner:SOLUTIONS IES
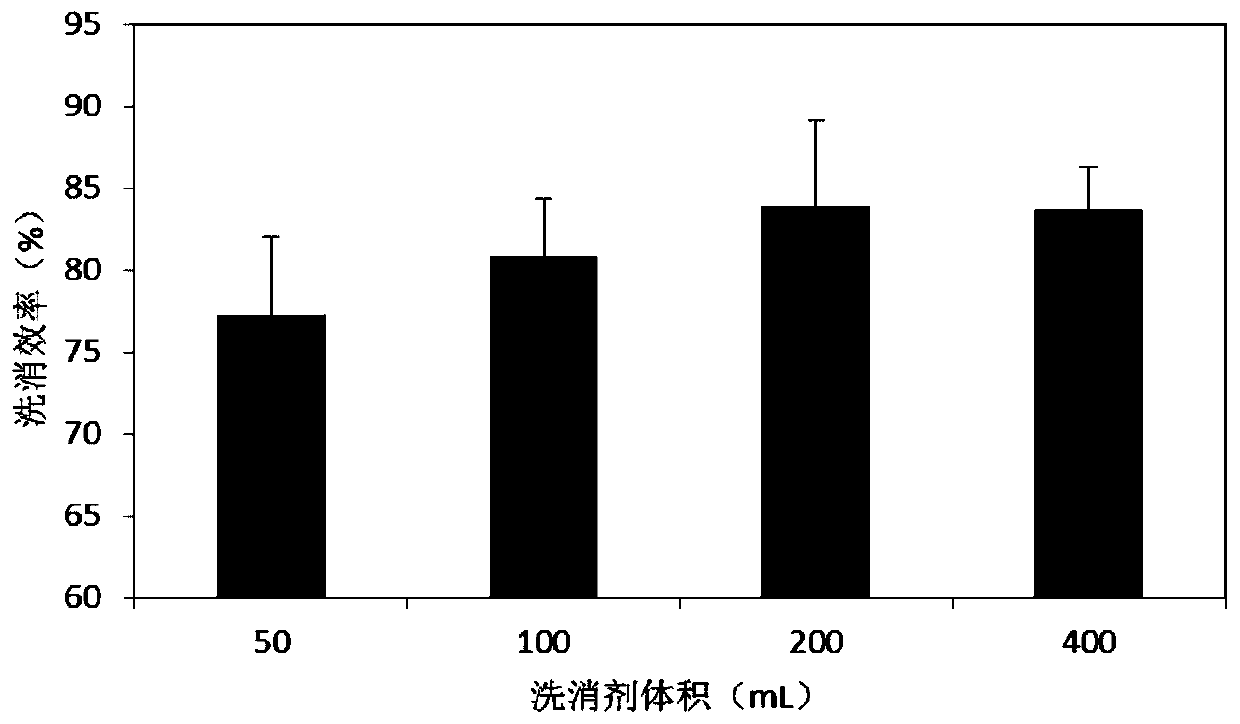
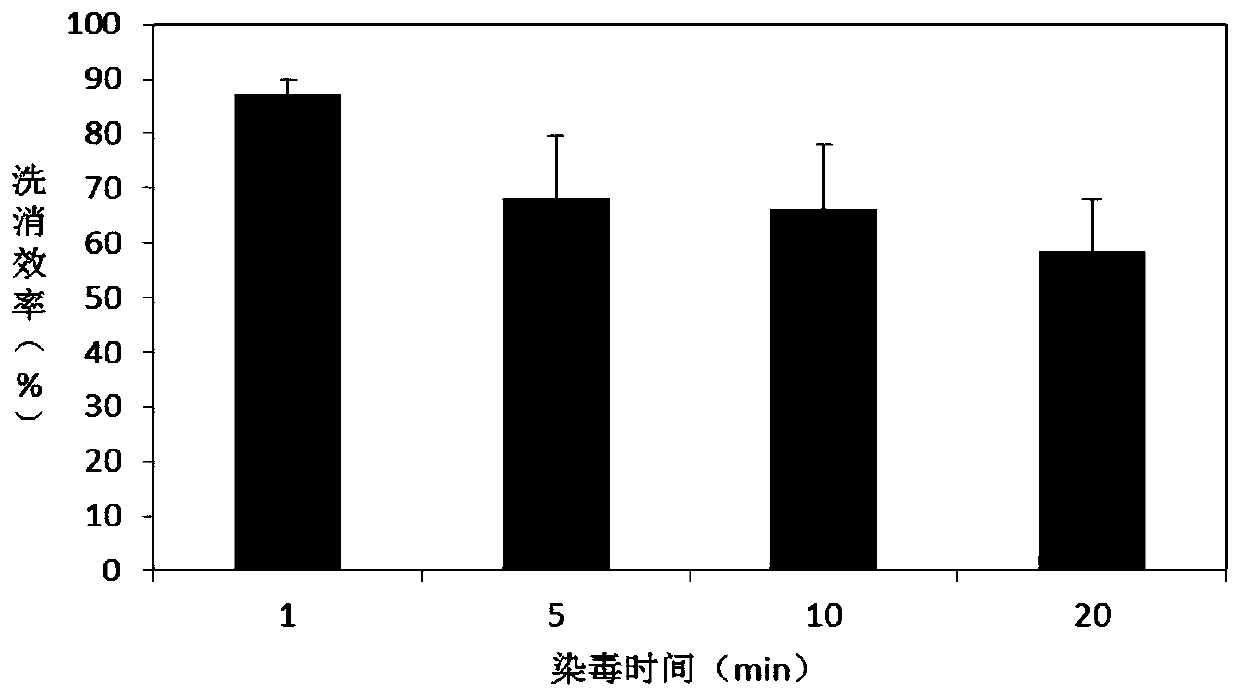
Washing-disinfecting liquid and disinfecting-washing bag thereof for radioactive skin contamination
InactiveCN101732341AEasy to useEasy to packOrganic active ingredientsDermatological disorderNuclear reactorNuclear power
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, in particular to a washing-disinfecting liquid and a disinfecting-washing bag thereof for skin and wounds with radionuclide contamination. The invention discloses a washing-disinfecting liquid for radioactive skin contamination, which is characterized in that the washing-disinfecting liquid contains 0.5 to 10 percent of EDTA, 0.5 to 10 percent of citric acid, 0.5 to 10 percent of super sodium chloride, and 0.5 to 10 percent of aqueous solution of fatty alcohol sodium sulfate. The invention also discloses a washing-disinfecting bag for radioactive skin contamination, which is characterized in that the washing-disinfecting bag comprises the washing-disinfecting liquid. The washing-disinfecting liquid has the advantages of high decontamination rate and no stimulation to skin or wounds. The washing-disinfecting bag adopting disposable packaging has the characteristics of small volume, convenience for carrying and storage and convenient quick use. When the radionuclide contamination of the skin and the wounds is removed, the washing-disinfecting liquid and the disinfecting-washing bag need no washing, produce little secondary pollution, and ensure good decontamination effects, so the washing-disinfecting liquid and the disinfecting-washing bag can be allocated to personnel engaged in nuclear power, nuclear reactors, radiation devices and other radiation work in the army or local places in order to implement radioactive washing and disinfecting in nuclear accident emergency.
Owner:NAVY MEDICINE RES INST OF PLA
Method and device for decontaminating water which contains metal and/or is radioactively contaminated
InactiveUS7070685B2Simple and easyLow costFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricitySemimetalRadioactive contamination
The invention relates to an efficient process and device for the decontamination of waters polluted with heavy metals, semimetals and / or radionuclides by cation exchange and electrochemical deposition of the anions.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Method for remediation of aquifers
InactiveUSRE40448E1Improve mobilityWater treatment compoundsSolid waste disposalOrganic compoundGroundwater pollution
A method for remediating aquifers and groundwater contaminated, for example by toxic halogenated organic compounds, certain inorganic compounds, and oxidized heavy metals and radionuclides, using the introduction of an innocuous oil, preferably an edible, food grade oil such as soybean oil, formulated into a microemulsion preferably by mixing with a natural food-grade emulsifier (such as lecithin) and water.
Owner:SOLUTIONS IES
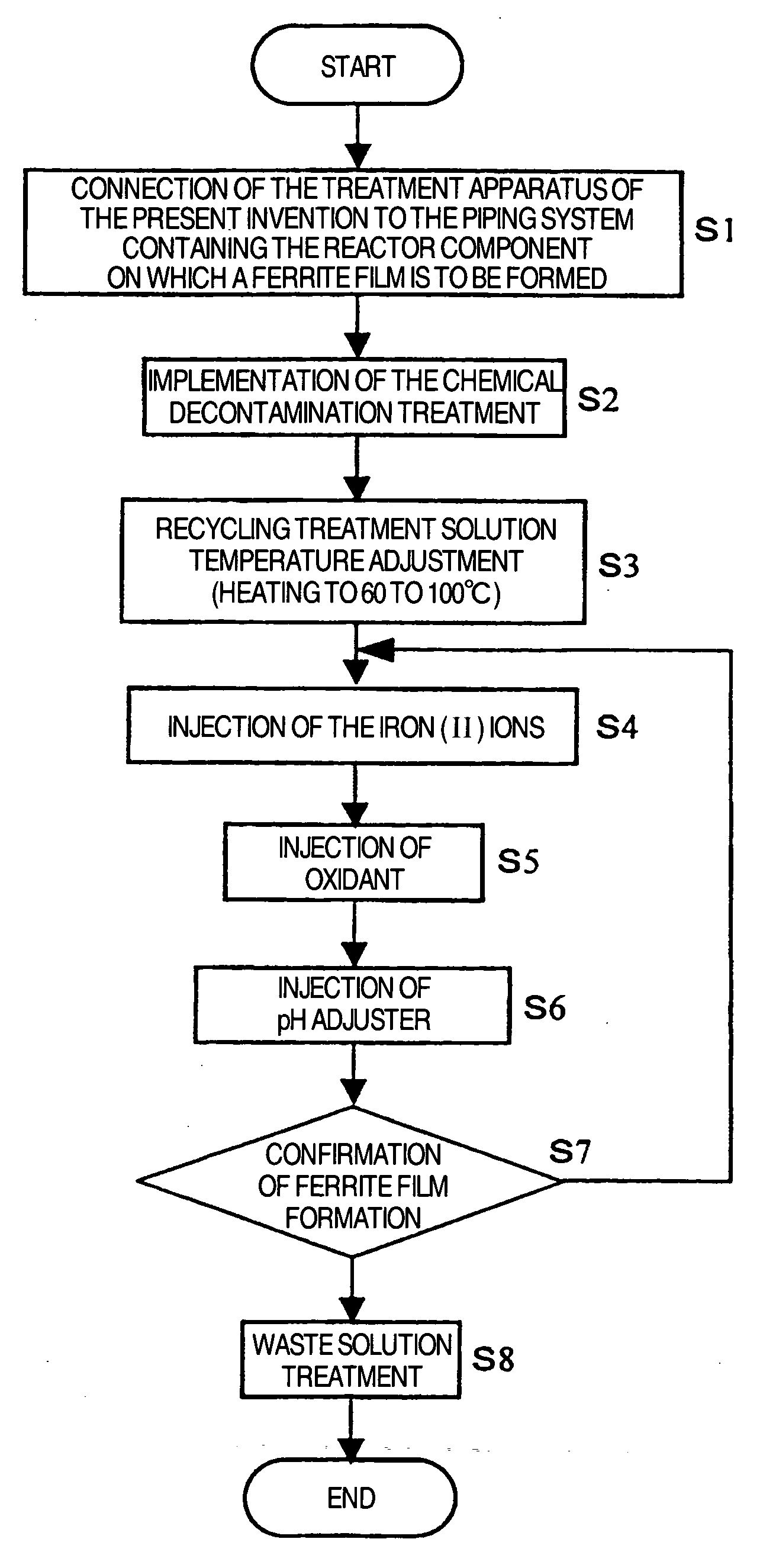
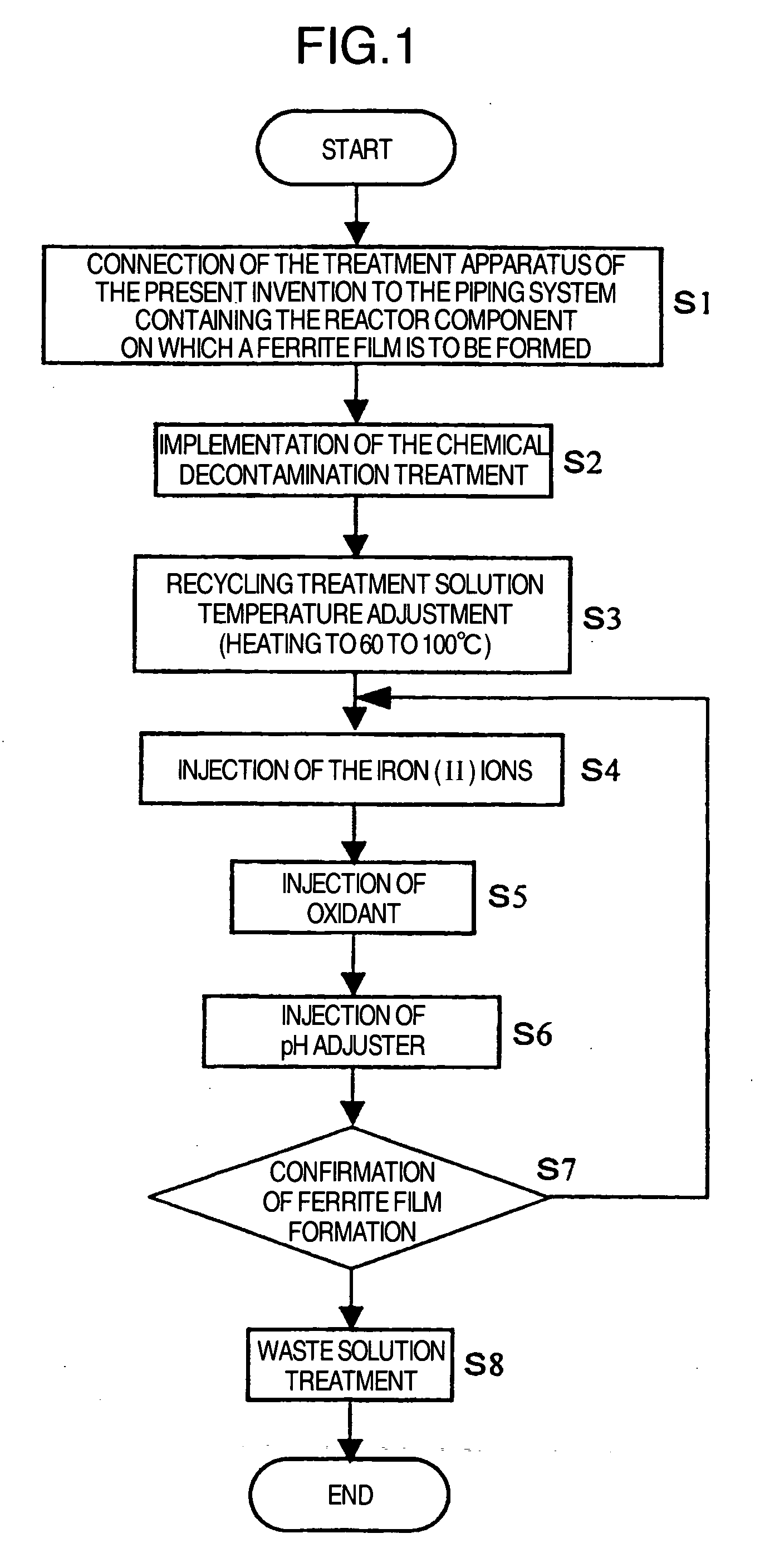
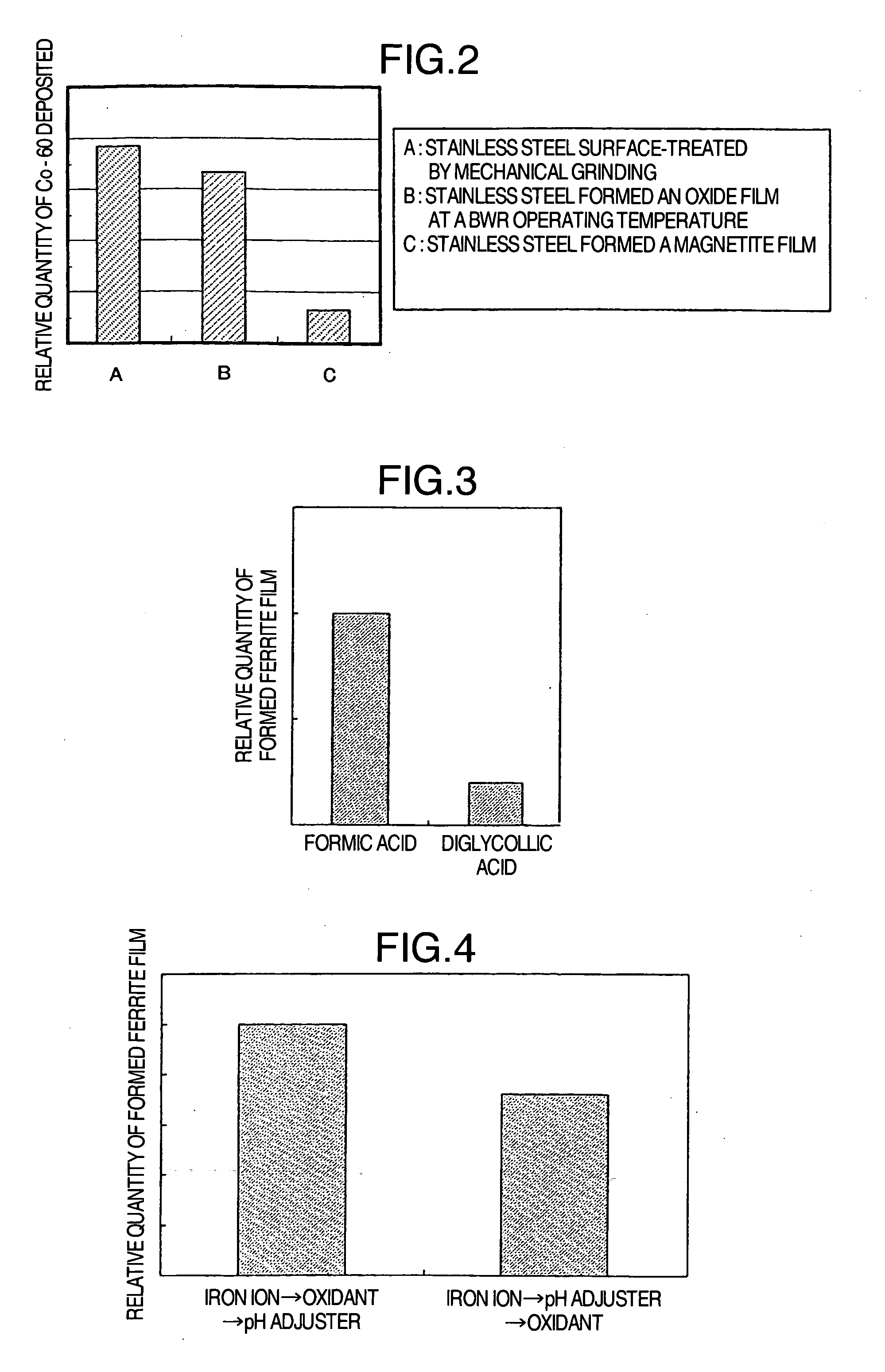
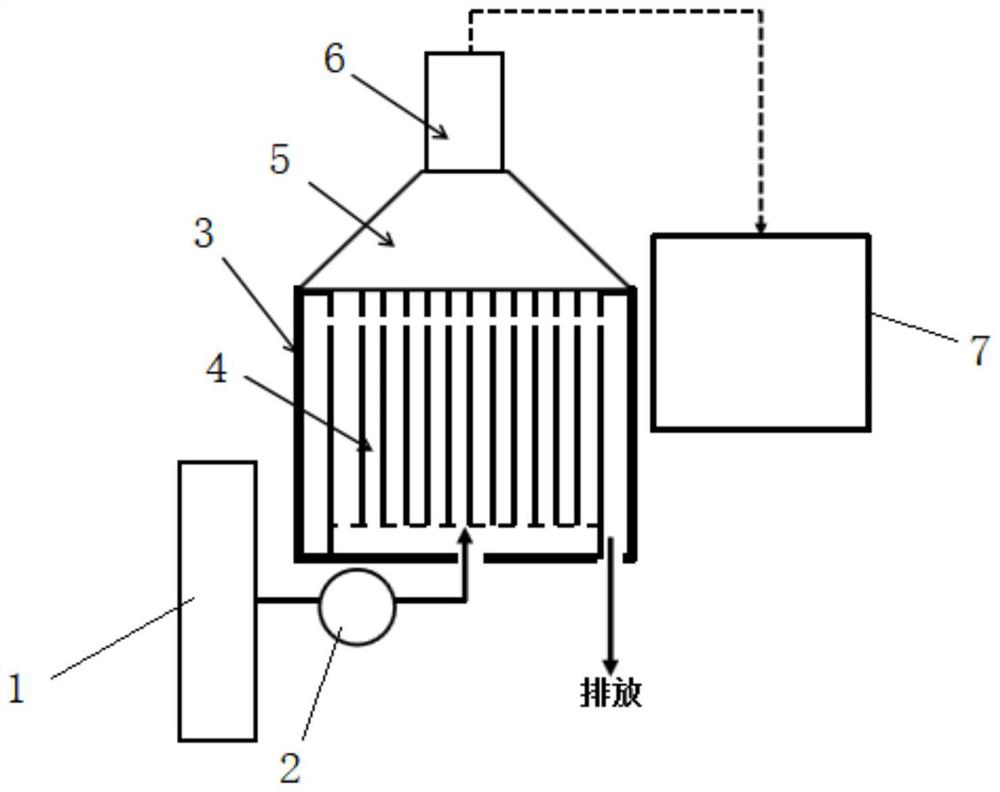
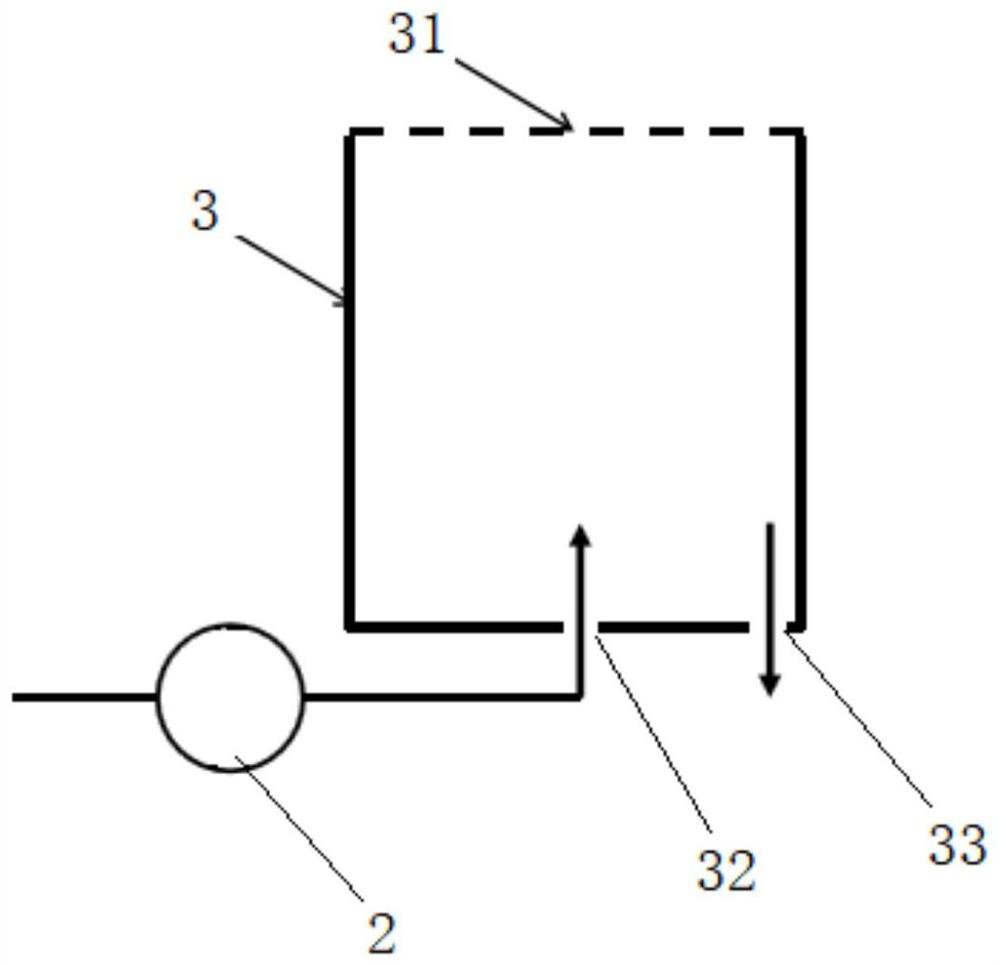
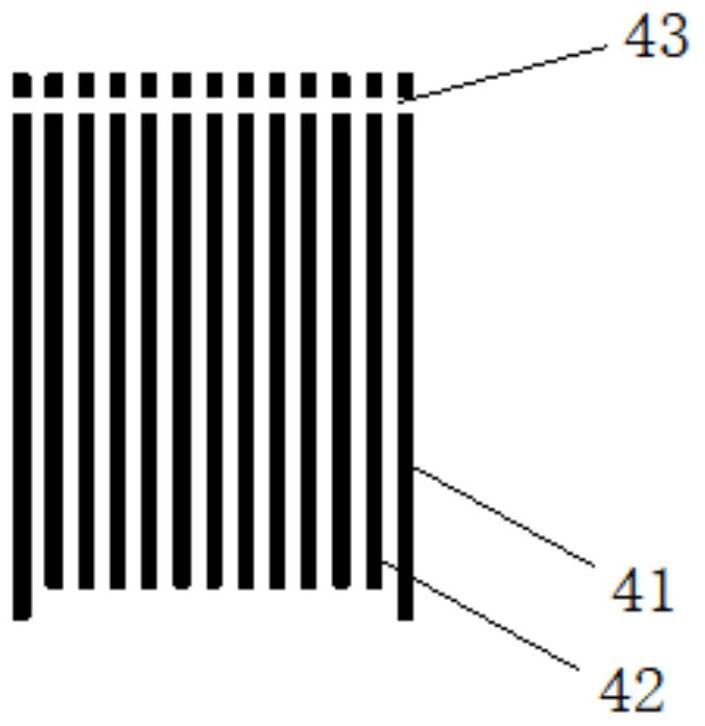
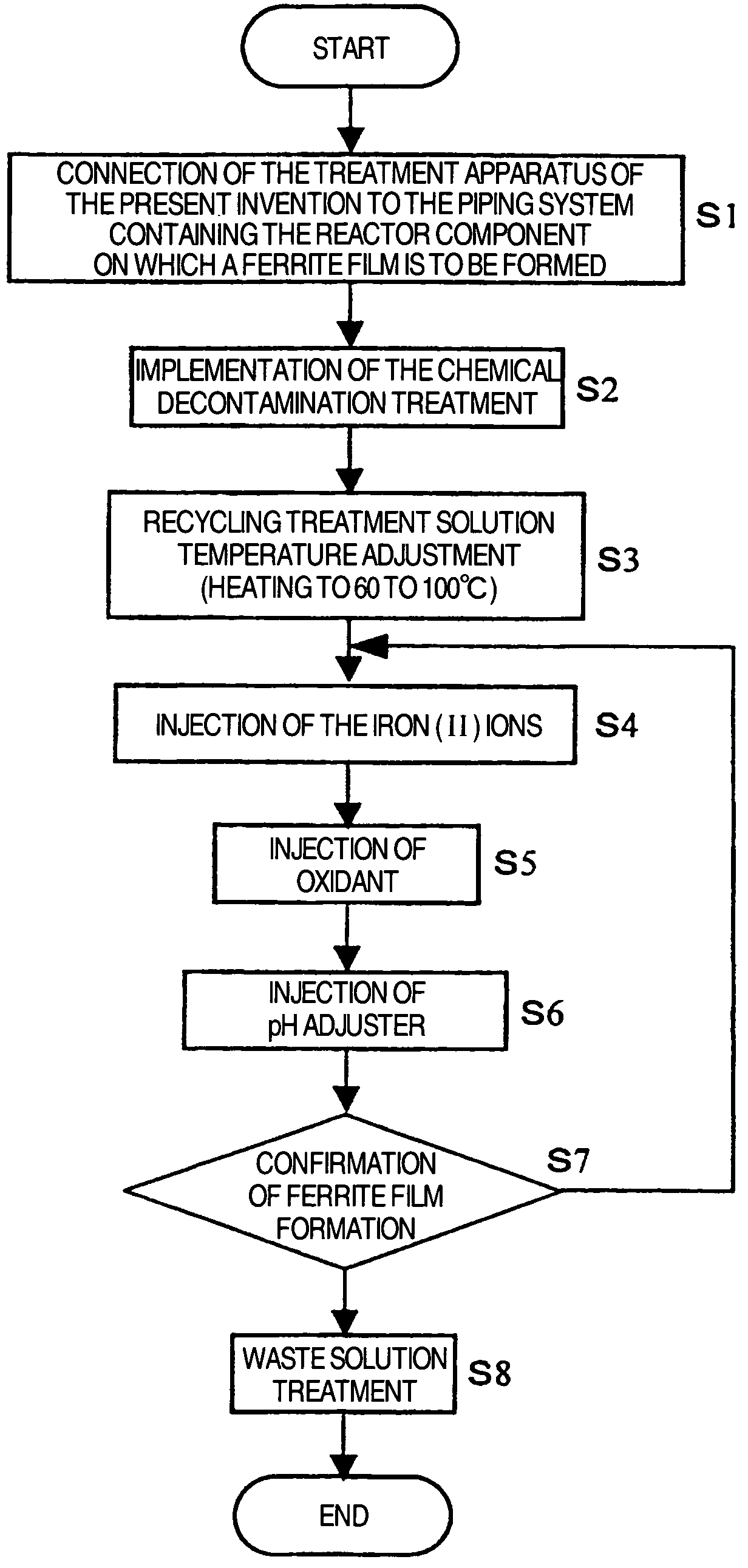
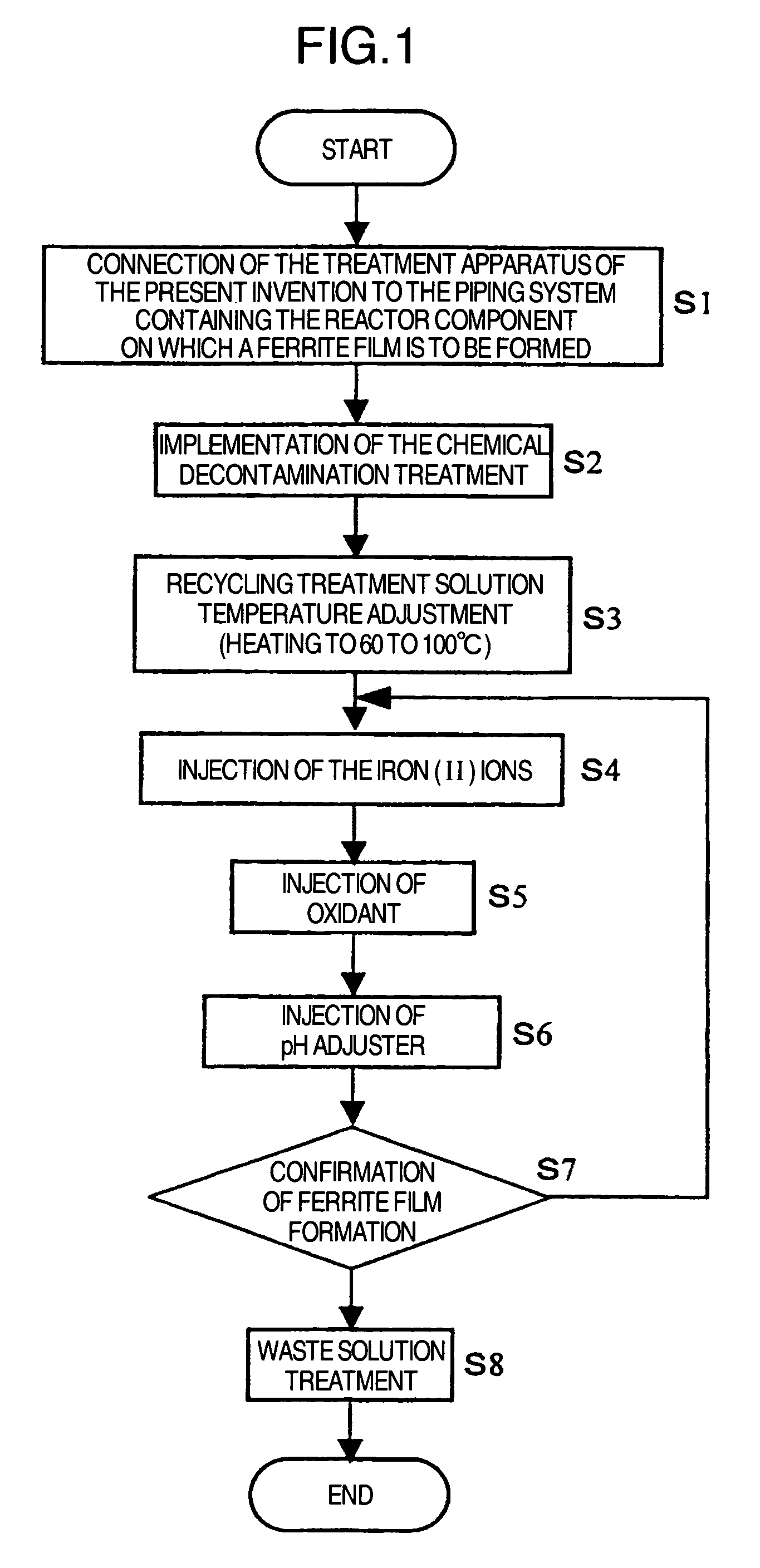
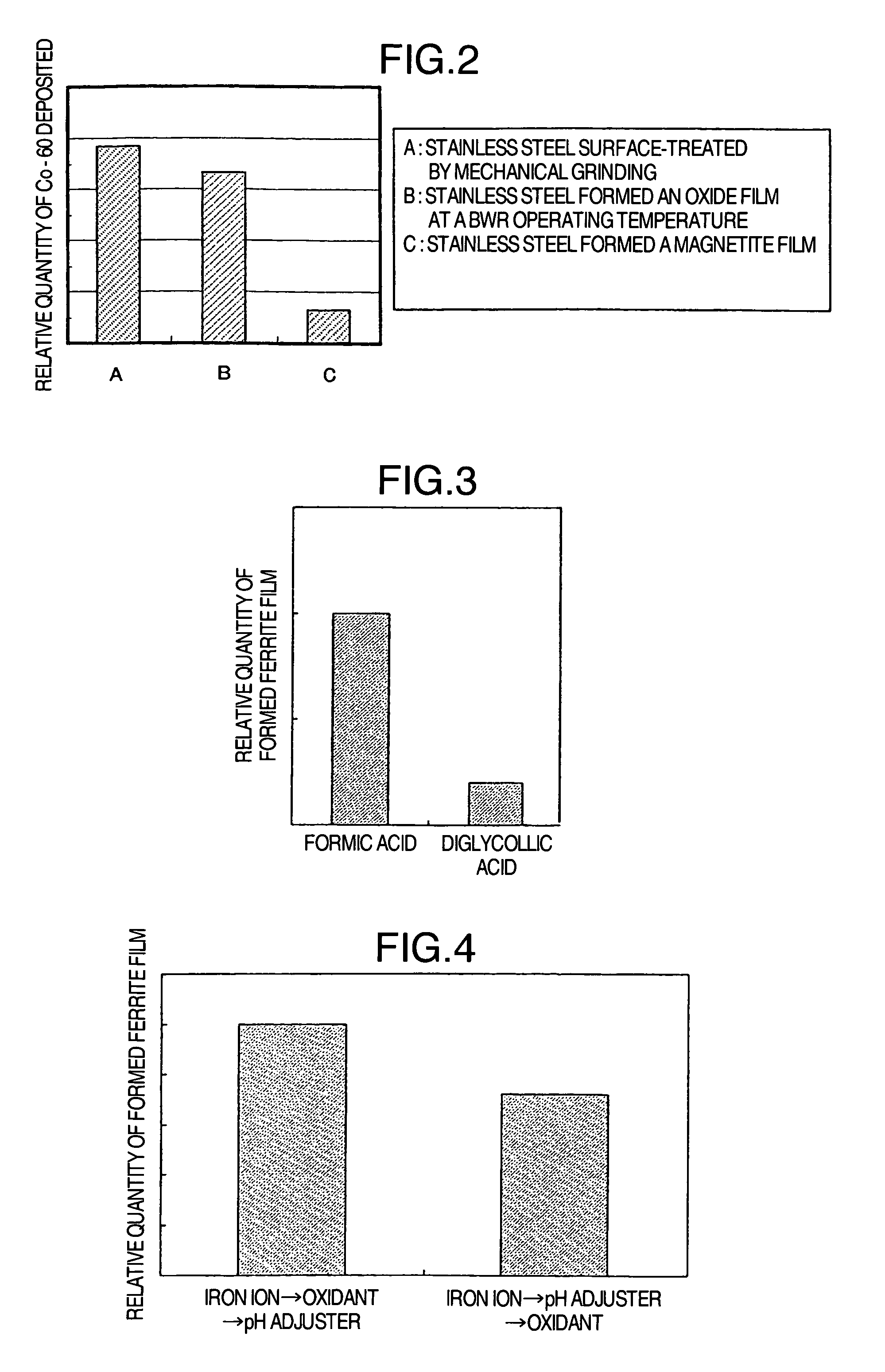
Suppression method of radionuclide deposition on reactor component of nuclear power plant and ferrite film formation apparatus
ActiveUS20070127619A1Efficiently suppress radionuclide depositionNuclear energy generationSolid state diffusion coatingNuclear plantNuclear engineering
It is an object of the present invention to efficiently suppress radionuclide deposition on a reactor component of nuclear power plant. Radionuclide deposition on the surface of a metallic reactor component of nuclear power plant is suppressed by forming a ferrite film on the component, wherein the film is formed, after decontamination for removing radionuclides contaminants from the component surface is completed and before the plant is started up, by contacting a treatment solution which mixes a first agent containing the iron (II) ions, a second agent for oxidizing the iron (II) ions into the iron (III) ions and a third agent for adjusting pH level of a solution to 5.5 to 9.0 in this order with the reactor component surface.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Decontamination bag for skin radioactive contamination
InactiveCN102499941AEasy to useEasy to packDermatological disorderAluminium/calcium/magnesium active ingredientsNuclear reactor coreNuclear power
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments and in particular relates to a decontamination bag for radionuclide contamination of skin and wounds. The invention discloses a decontamination bag for skin radioactive contamination, which comprises a water absorbent pad and a decontamination liquid. The invention is characterized in that the decontamination liquid is an aqueous solution containing 0.5% to 10% of EDTA, 0.5% to 10% of citric acid, 0.5% to 20% of bleaching powder and 0.5% to 10% of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate. The decontamination bag is available in disposable package and has the characteristics of having a small size and being convenient to carry and store and convenient to use. The decontamination bag can eliminate radionuclide contamination of skin and wounds without needing water washing, reduces secondary contamination, has good decontamination effects, and is applied to workers of nuclear power, nuclear reactors and radiation devices in both army and local areas for radiation decontamination in case of nuclear emergency.
Owner:NAVY MEDICINE RES INST OF PLA
Textile surface adhesive staining nuclide detergent and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110452779ASynergistic decontaminationMeets Nuclear Industry SpecificationsInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsNon destructiveAdhesive
The invention relates to the technical field of nuclear power decontamination, in particular to a textile surface adhesive staining nuclide detergent and a preparation method thereof. The textile surface adhesive staining nuclide detergent is prepared from, by weight, 12-18% of a composite surfactant, 15-20% of a complexing agent, 8-14% of an enzyme preparation, 5-8% of an enzyme stabilizer, a pHregulator and the balance water. The textile surface adhesive staining nuclide detergent can meet the requirement for decontamination of nuclear power textiles, especially has an excellent decontamination effect on radionuclide contamination, does contain harmful ingredients, and has environment friendliness, and after decontamination is completed, the textile surface adhesive staining nuclide detergent is non-destructive to fabrics, easy to rinse, and free of residues.
Owner:郑州华核新材料科技有限公司
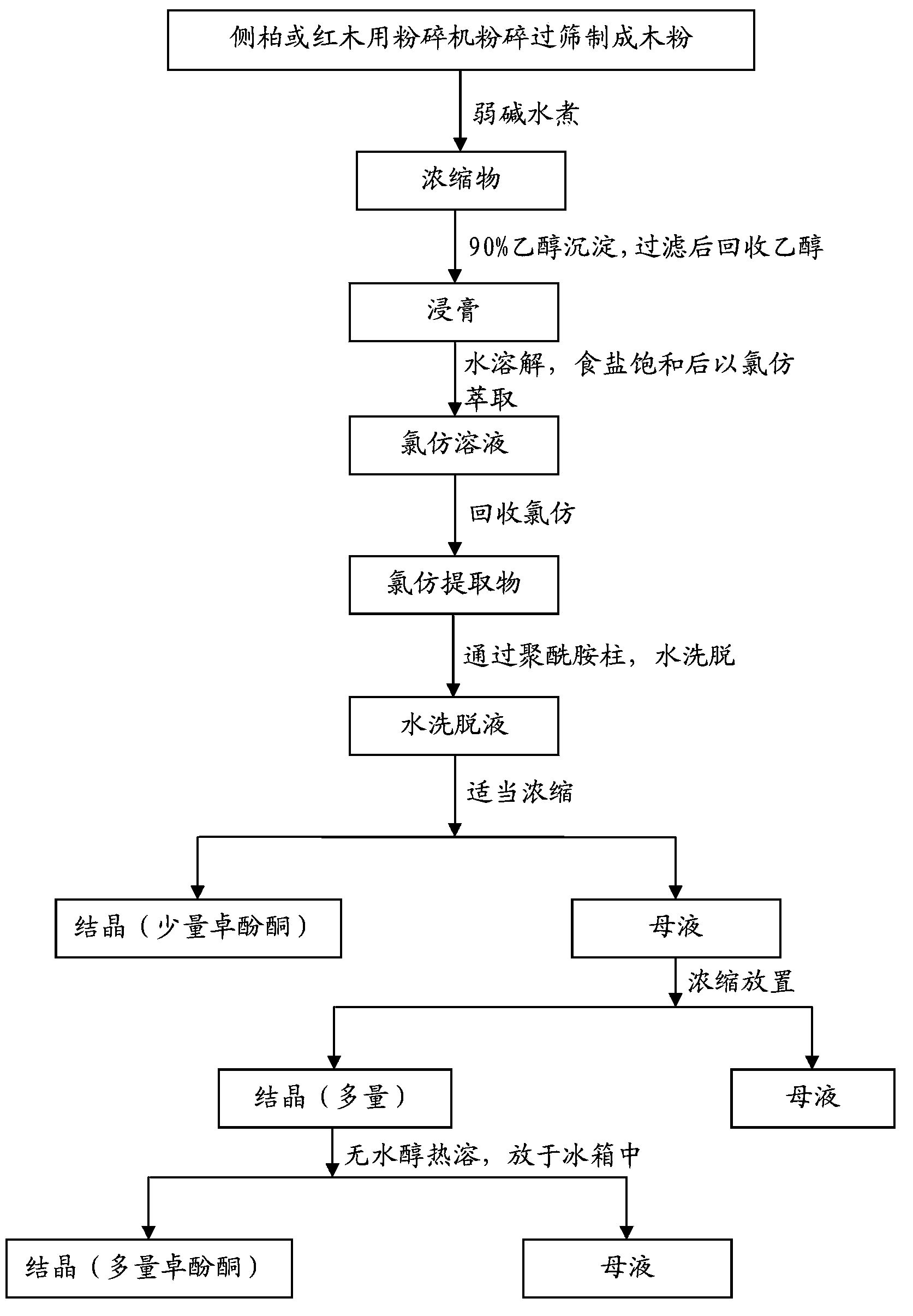
Traditional Chinese medicine extract for irradiated body radionuclide excretion promotion and extraction method of traditional Chinese medicine extract
ActiveCN103565852AOvercome complexation deficienciesAvoid Deficiency SyndromeAntinoxious agentsConiferophyta medical ingredientsAdditive ingredientExcretion process
The invention relates to a preparation technology of radioactive excretion promotion medicines and particularly relates to a traditional Chinese medicine extract for irradiated body radionuclide excretion promotion and an extraction method of the traditional Chinese medicine extract. The method comprises the following steps: with platycladus orientalis and rosewood core materials of cupressaceae as extracting raw materials, extracting with weak alkali water or alcohol, and recovering an extraction solvent, wherein the extraction components comprise tropolone, resins and volatile essential oil. The traditional Chinese medicine extract can be used for complexing excretion promotion medicines and wound-cleaning medicines of personnel suffering from radionuclide contamination and also can be applied to a clean recovery complexing agent in a radioactive experiment site.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
A treatment method for radionuclide-containing pollutants
The invention provides a treatment method for radionuclide-containing pollutants. Firstly, if the pollutants are liquid or particles with the size less than 70 microns, the method comprises the steps of adding zeolite, a flocculant, and a coagulant aid in the liquid state pollutants, adjusting the PH value, stirring the mixture for 5-60 minutes, separating solids and liquid, obtaining supernate, and repeating the above-mentioned steps many times until obtained supernate meets requirements. Secondly, if the pollutants are particles with the size greater than 70 microns, the method comprises the steps of cleaning the pollutants with a cleaning fluid, separating solids and liquid and treating the obtained liquid substance with the method mentioned in the first part. Thirdly, if the pollutants are large-area solid pollutants, the method comprises the steps of applying livering cleaning liquid on the solid pollutants, standing the pollutants on the condition of exclusion of water, performing rinsing, collecting the cleaning agent on the solid pollutants and performing treating with the method mentioned in the first part. The method can effectively remove radionuclide in solids, particles, powder and waste water, is good in treatment effect, and can reduce the cost consumed in the radionuclide removing process, shorten the treatment time and reduce the treatment cost.
Owner:武汉网绿环境技术咨询有限公司
Radionuclide pollution decontamination agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109700826AExtensive coordination abilityGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsSide effectPhosphate
The invention relates to a radionuclide pollution decontamination agent and a preparation method and an application thereof. The decontaminant comprises the following components by mass percentage: 1.0%-20% of EDTA.Na2, 0.1%-0.4% of carboxymethyl chitosan, 0.05%-0.3% of sodium alginate, 0.5%-2.0% of lidocaine hydrochloride, and balance of pure water or phosphate buffer, wherein a pH value is 6.9-7.0. The preparation method comprises the following steps: EDTA-Na2, carboxymethyl chitosan, sodium alginate and lidocaine hydrochloride are accurately weighed according to the proportion, the EDTA-Na2is heated and dissolved under alkaline conditions, and then the carboxymethyl chitosan and sodium alginate are dissolved, and then the two are mixed and stirred uniformly, a lidocaine hydrochloride solution is added, the pH is adjusted to 6.7-6.9 with HCl, the material is dissolved while stirring, and metering a volume. The decontamination agent has a chelate adsorption function on a plurality ofradionuclides, has no toxic and side effects, and can be used as the low-toxic and high-efficiency radionuclide pollution decontamination agent.
Owner:中国人民解放军海军特色医学中心
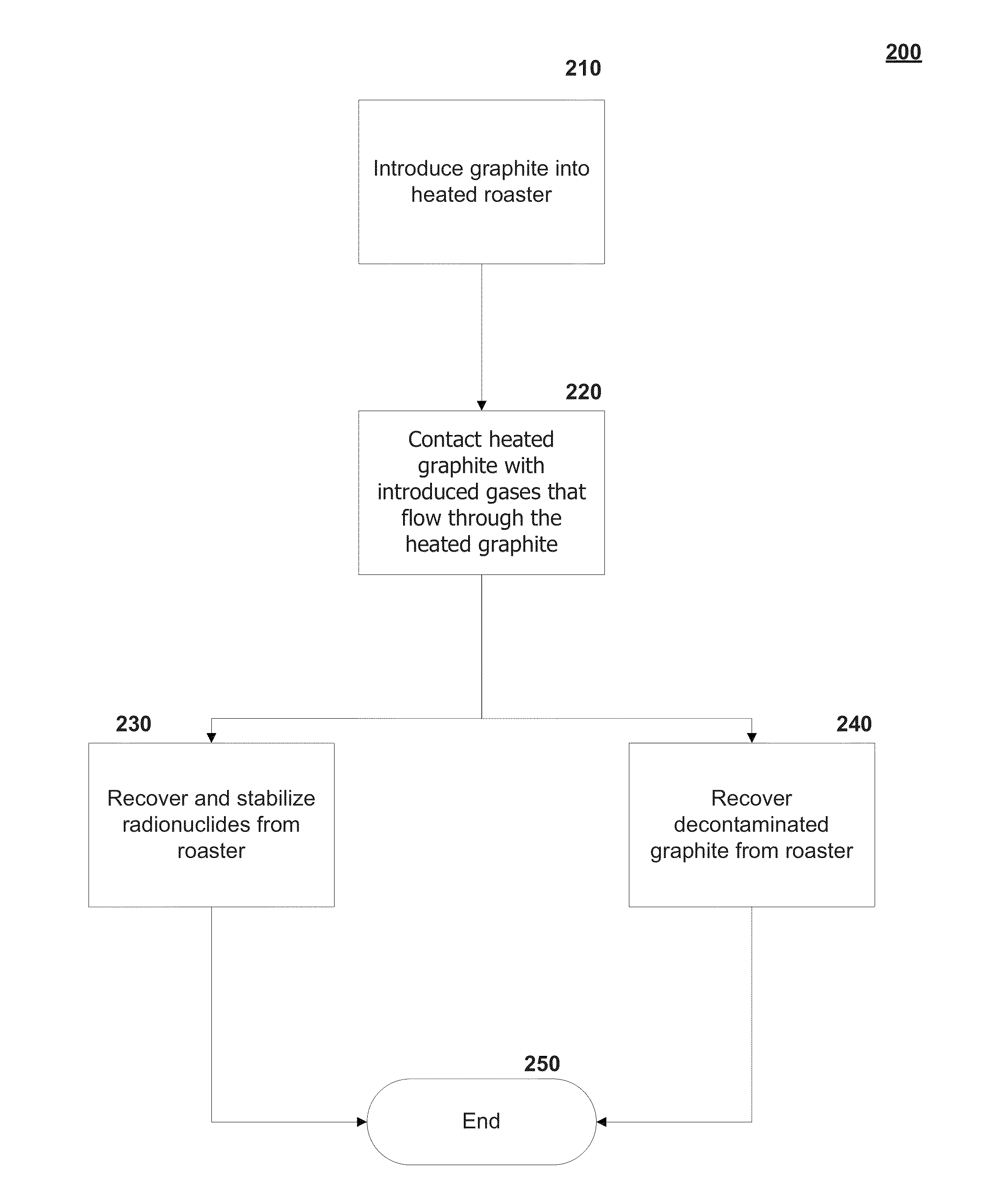
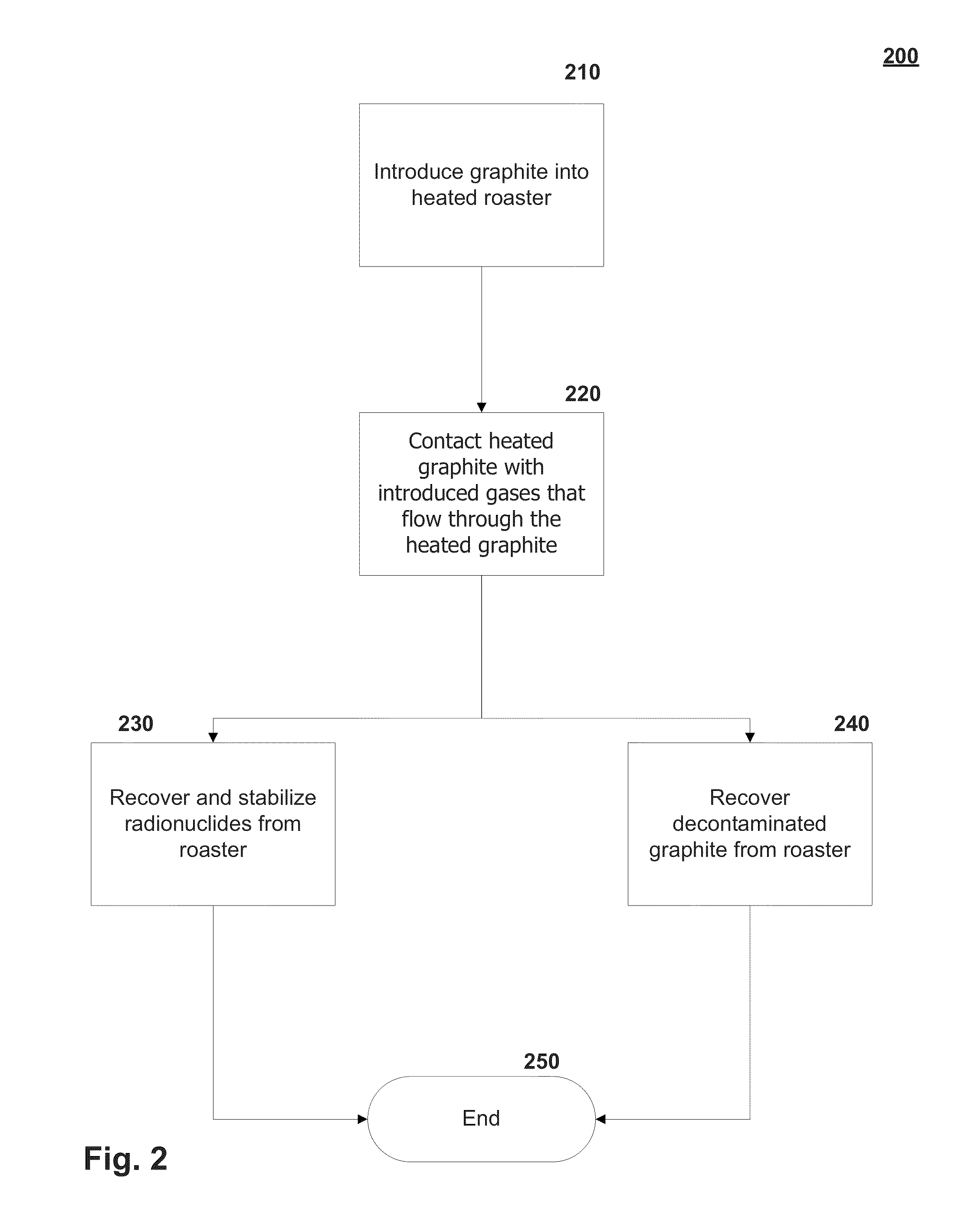
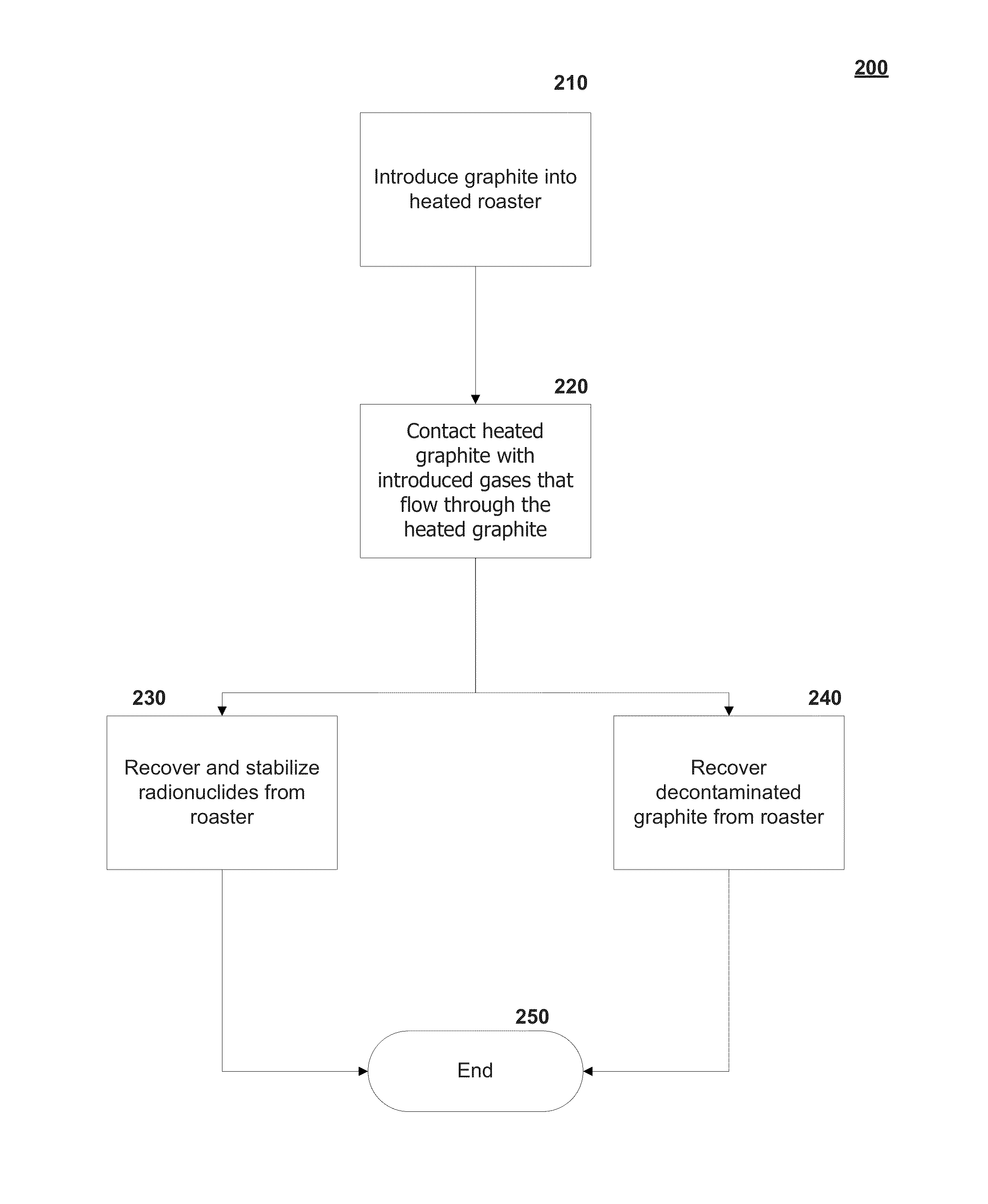
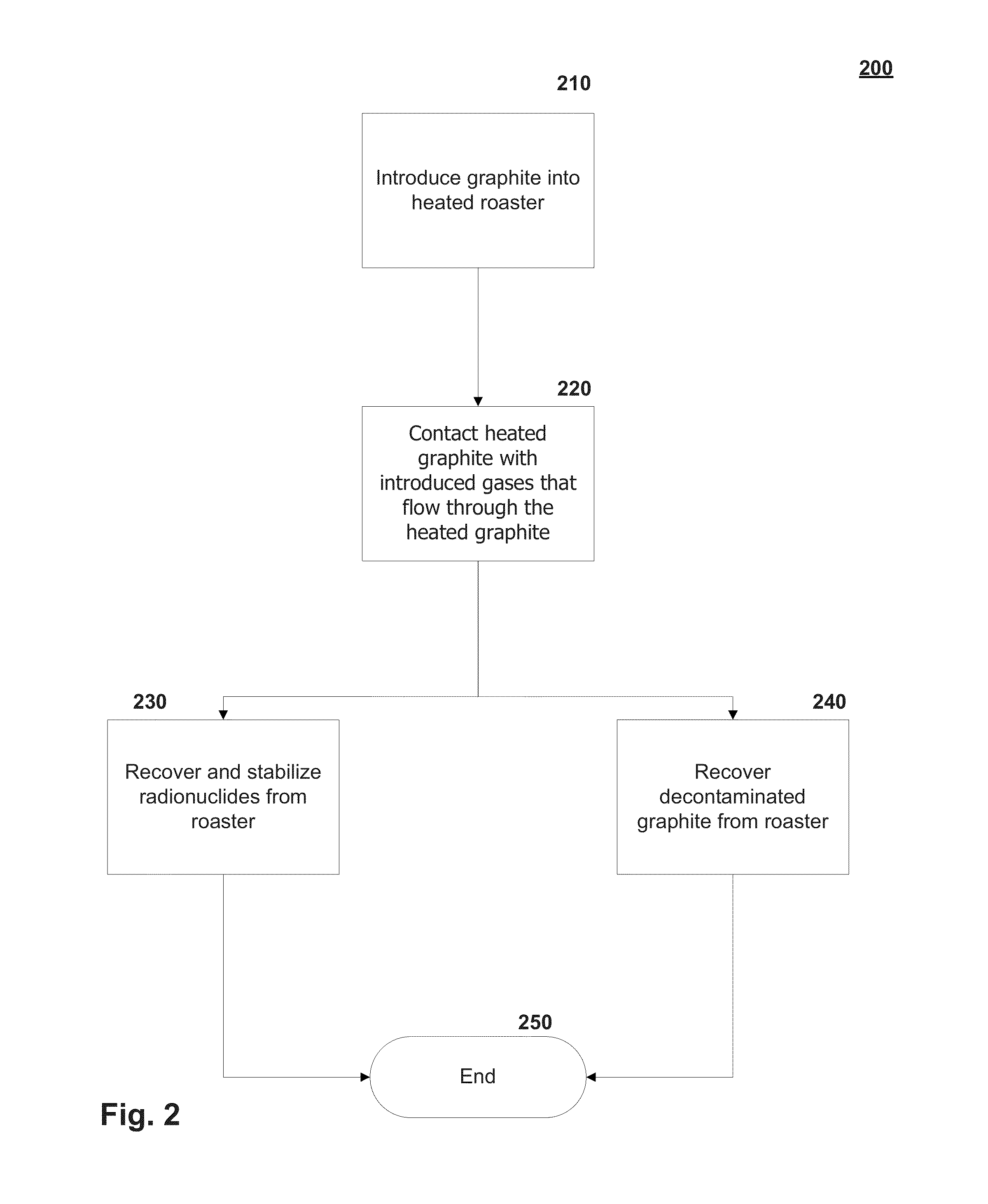
Graphite thermal decontamination with reducing gases
Providing a roaster that operates at temperatures in the range of 800° Celsius to 2000° Celsius with inert, optional oxidizing and reducing gases to treat graphite contaminated with radionuclides including tritium, carbon-14, and chlorine-36. The combination of temperatures and gases allow for the removal of most to substantially all the carbon-14 within the graphite while substantially limiting gasifying the bulk graphite.
Owner:ELECTRICITE DE FRANCE
Curing process method for radioactive nuclide polluted sandy soil
ActiveCN102610288AIncrease the content of glass phaseImprove uniformityRadioactive decontaminationBLENDER/MIXERMass ratio
The invention provides a curing process method for radioactive nuclide polluted sandy soil, which comprises the steps of thermite preparation and curing process. Aluminum powder, ferric oxide powder and auxiliaries 1 are weighed by mass ratio of 0.33-0.66:1.00-2.00:0.01-0.30 and sequentially placed in a blender mixer to be stirred for 30-60 minutes at the speed of 60-120 r / min under the normal temperature and the constant pressure till the mixing is even. The curing process comprises the steps of mixing, dumping and embedding, ignition and post-processing. The mixing step is that the sandy soil with grain size smaller than 1cm and with SiO2 as a main component, thermite, auxiliaries 2 and simulate radioactive nuclide are mixed by mass ratio of 1.0:1.6-3.0-0.01-0.35:0.01-0.20 and stirred for 90-120 minutes at the speed of 45-60 r / min under the normal temperature and the constant pressure till the mixing is even. The dumping and embedding step is that a mixture obtained in the mixing step are dumped and embedded in a steel container or a cement pool with a cover plate and a gas filtering device at the top, dry sand with the depth of 15-50cm is dumped and embedded around the mixture, and dry sand with the depth of 50-100cm is covered on the mixture and then covered by the cover. The ignition step is that an ignition device is installed at the upper portion or the lower portion of the mixture, is powered on to perform ignition and is powered off to measure resistance and confirm the igniting effect. The post-processing step is that a cured body is taken out or embedded on the spot when cools to the environmental temperature.
Owner:63653 FORCES PLA
Preparation method of dictyophora-loaded vulcanized nano zero-valent iron and application
InactiveCN109821508AEvenly dispersedNot easy to reuniteOther chemical processesRadioactive decontaminationWastewaterChemical stability
The invention discloses a preparation method of dictyophora-loaded vulcanized nano zero-valent iron. The method includes the following steps: (1) soaking dictyophora in ultrapure water, heating the obtained solution in a reaction kettle, washing until the solution is neutral, and grinding the dried solid into powder for later use; (2) mixing and dissolving FeSO4*7H2O, Na2S2O4 and the dictyophora material obtained in step (1) in water, and adding NaBH4 for reaction; and (3) performing solid-liquid separation, washing and drying on the product obtained in the step (2) by using a magnet to obtaina dictyophora-loaded vulcanized nano zero-valent iron material. The dictyophora-loaded vulcanized nano zero-valent iron prepared by the method can be used for efficiently removing radionuclide uranium in wastewater, and has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, good removal effect, high chemical stability, cleanness, no pollution, no toxic effect on the environment, and wide application prospect in the field of radionuclide pollution control.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
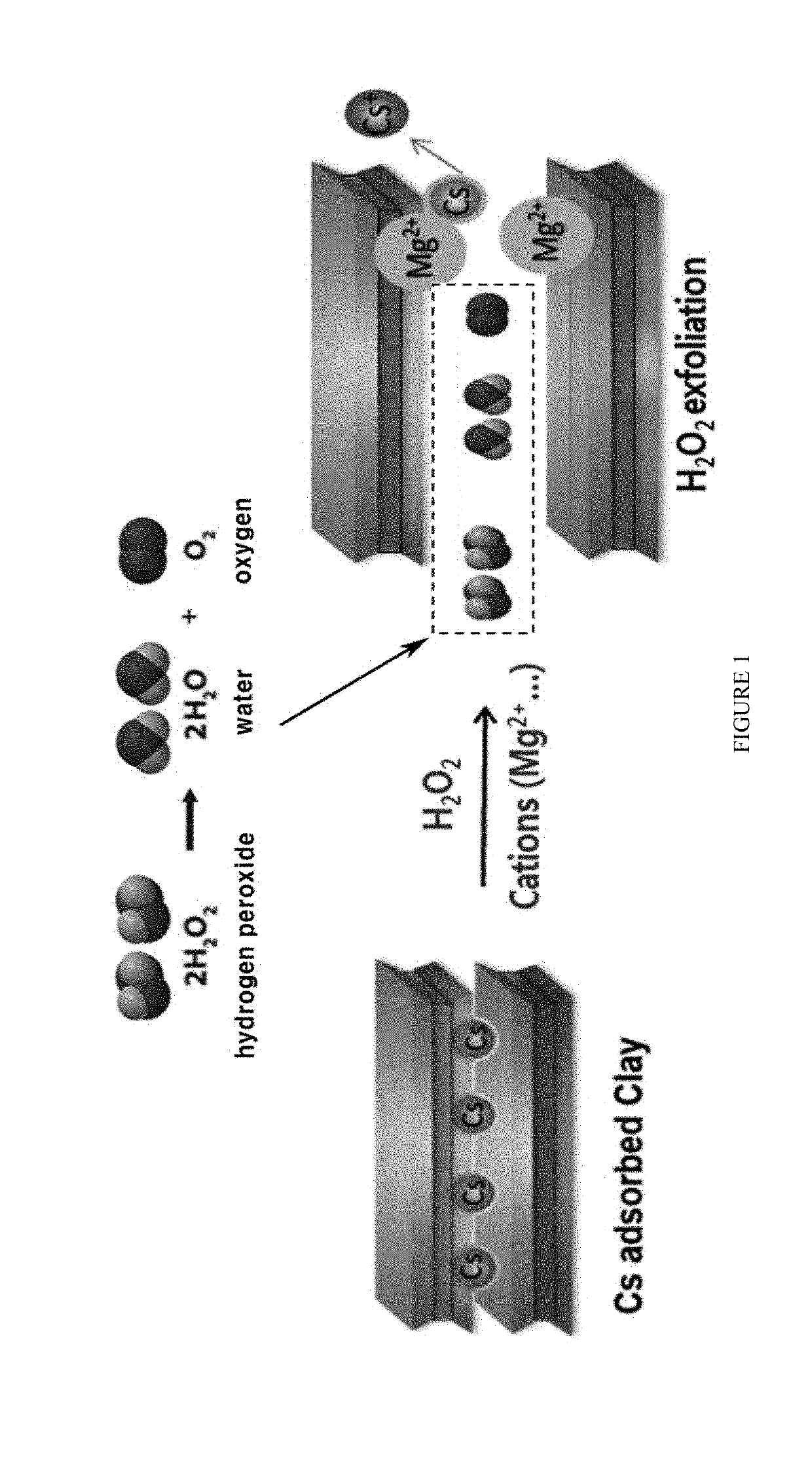
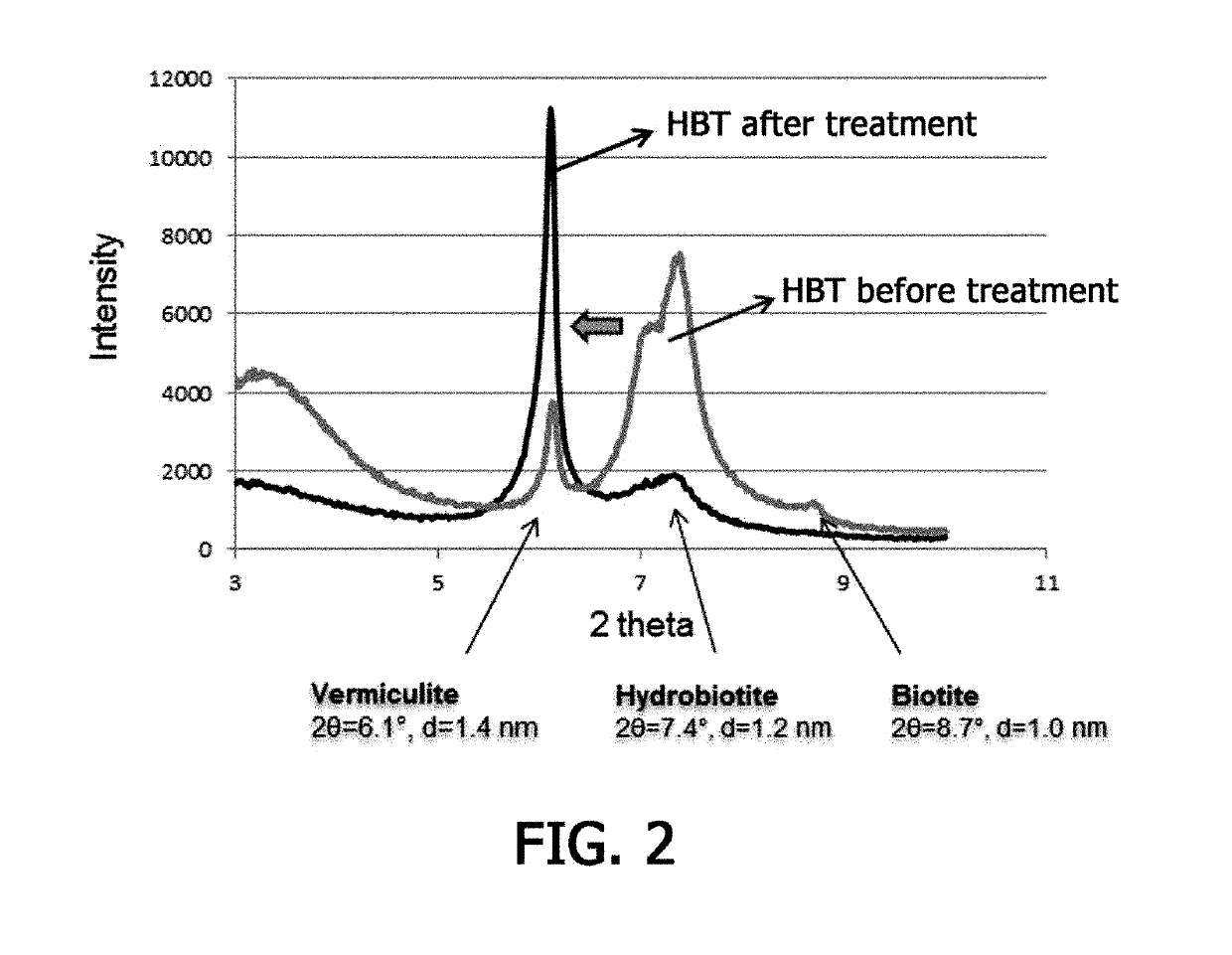
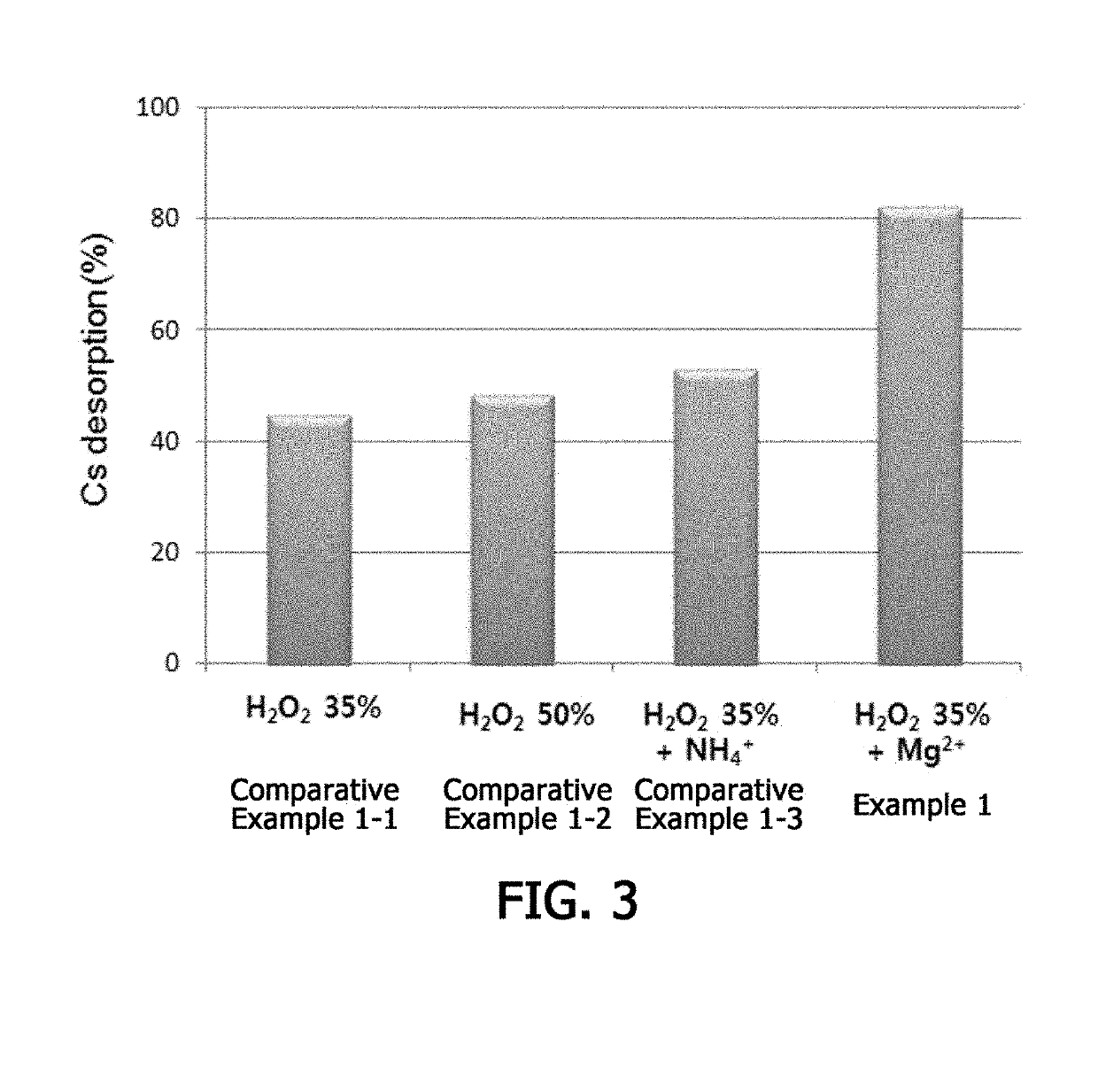
Method for Removing Cesium in Clay Mineral Using Hydrogen Peroxide
ActiveUS20190275573A1Contaminated soil reclamationNuclear engineering problemsFukushima Nuclear AccidentClay minerals
The present invention relates to a method for removing cesium in a clay mineral using hydrogen peroxide. According to the present invention, cesium in a clay mineral is removed using hydrogen peroxide, which serves to induce interlayer expansion of the clay mineral to allow a cation to easily enter an interlayer of the clay mineral, and thus cesium desorption efficiency can be further improved. Also, the method according to the present invention can be efficiently used to restore soil in residential areas widely contaminated with a radionuclide when a major accident such as Fukushima nuclear accident occurs as well as various sites of atomic energy facilities contaminated with a radionuclide. Also, since radiation-contaminated soil is treated with only hydrogen peroxide and cations, secondary environmental pollution caused by wastes can be significantly reduce and the waste disposing cost can also be saved.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Graphite thermal decontamination with reducing gases
Providing a roaster that operates at temperatures in the range of 800° Celsius to 2000° Celsius with inert, optional oxidizing and reducing gases to treat graphite contaminated with radionuclides including tritium, carbon-14, and chlorine-36. The combination of temperatures and gases allow for the removal of most to substantially all the carbon-14 within the graphite while substantially limiting gasifying the bulk graphite.
Owner:ELECTRICITE DE FRANCE
Method for reducing glass solidification melting temperature of sandy soil polluted by radionuclides
ActiveCN109994240AIncrease packing capacityUniform physical and chemical propertiesRadioactive decontaminationMass ratioSodium phosphates
The invention belongs to the field of radioactive waste treatment, and relates to a method for reducing the glass solidification melting temperature of sandy soil polluted by radionuclides. Accordingto the method, raw materials are composed of 40-80 parts of sandy soil, 10-20 parts of boron oxide, 0-10 parts of sodium phosphate and 0-50 parts of waste glass powder. The method comprises the stepsof first putting 50-80 parts of sandy soil into a high-temperature-resistant crucible, and then laying 10-20 parts of boron oxide (or converted into boric acid containing a same mass ratio of boron oxide), 0-10 parts of sodium phosphate And 0-50 parts of waste glass powder sequentially on the surface layer of the sandy soil from bottom to top; putting the crucible into a high-temperature smeltingfurnace or other heating devices, conducting heating to 1400 DEG C, and keeping the temperature for 3-6 hours, and conducting cooling to obtain a uniform glass solidified body. According to the method, the melting temperature of sandy soil radioactive waste glass solidification is reduced, the melting time is shortened, the step of easily generating secondary pollution is avoided, the cost is reduced by utilizing waste glass powder, the capacity of waste is improved, and the glass solidified body with uniform physical and chemical properties is obtained.
Owner:63653 FORCES PLA
Preparation method of protonated titanate nanotubes and adsorption application of protonated titanate nanotubes to uranium and cesium
InactiveCN109174051AOvercoming large particlesOvercoming controllabilityOther chemical processesSeawater treatmentPorosityRadioactive decay
The invention relates to the field of ocean radionuclide contamination management and enrichment and detection and in particular relates to a preparation method of serial protonated titanate nanotubeswith different H<+> / Na<+> ratios and application of the protonated titanate nanotubes to rapid and efficient adsorption to remove low-concentration nuclide uranium and cesium ions in seawater. The titanate nanotubes are prepared by adopting a hydrothermal method and the content of H<+> in the titanate nanotubes is increased through protonated modification; the porosity and specific surface area of a material are increased; and the adsorption and removal capability of the titanate nanotubes on the low-concentration nuclide ions in the seawater is greatly improved. By adopting the preparation method provided by the invention, the application range of a titanate nanotube series material is expanded and technical supports are provided for adsorption and removal and rapid enrichment and detection of uranium and cesium nuclides in the seawater with a low radioactive level.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
On-line measuring device and measuring method for radioactivity in drinking water
PendingCN113568029AOvercome the shortcomings of not being able to continuously monitor radioactive contamination of water systemsImplement filter shapingFluorescence/phosphorescenceX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting ratePotable water
The invention discloses an on-line measurement method for radionuclides in drinking water. The method comprises three parts of water sample collection, radioactivity measurement and data processing. The water sample collecting part can be used for continuously collecting drinking water into the measuring chamber; the radioactive measurement part can rapidly and accurately measure alpha, beta and gamma radionuclide pollutants in drinking water; and the data processing part is used for processing the obtained nuclear signals in real time, selecting interested signal amplitude spectrums for analysis, and automatically giving an alarm when the counting rate of the signals exceeds a threshold value or the counting rate exceeds a certain degree along with time change. The online measurement method solves the problems that a conventional monitoring method of a water system cannot detect short-term pollution, cannot continuously monitor radioactive pollution of the water system and cannot directly judge whether drinking water is polluted or not. The invention further provides a device for measuring the radioactivity in the drinking water on line.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF ENG
Suppression method of radionuclide deposition on reactor component of nuclear power plant and ferrite film formation apparatus
ActiveUS7811392B2Efficiently suppress radionuclide depositionNuclear energy generationSolid state diffusion coatingNuclear plantNuclear power
It is an object of the present invention to efficiently suppress radionuclide deposition on a reactor component of nuclear power plant. Radionuclide deposition on the surface of a metallic reactor component of nuclear power plant is suppressed by forming a ferrite film on the component, wherein the film is formed, after decontamination for removing radionuclides contaminants from the component surface is completed and before the plant is started up, by contacting a treatment solution which mixes a first agent containing the iron (II) ions, a second agent for oxidizing the iron (II) ions into the iron (III) ions and a third agent for adjusting pH level of a solution to 5.5 to 9.0 in this order with the reactor component surface.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Process for the accurate characterization of low level nuclear waste
ActiveUS9779841B2Accurate representationSufficient informationNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorIsotope
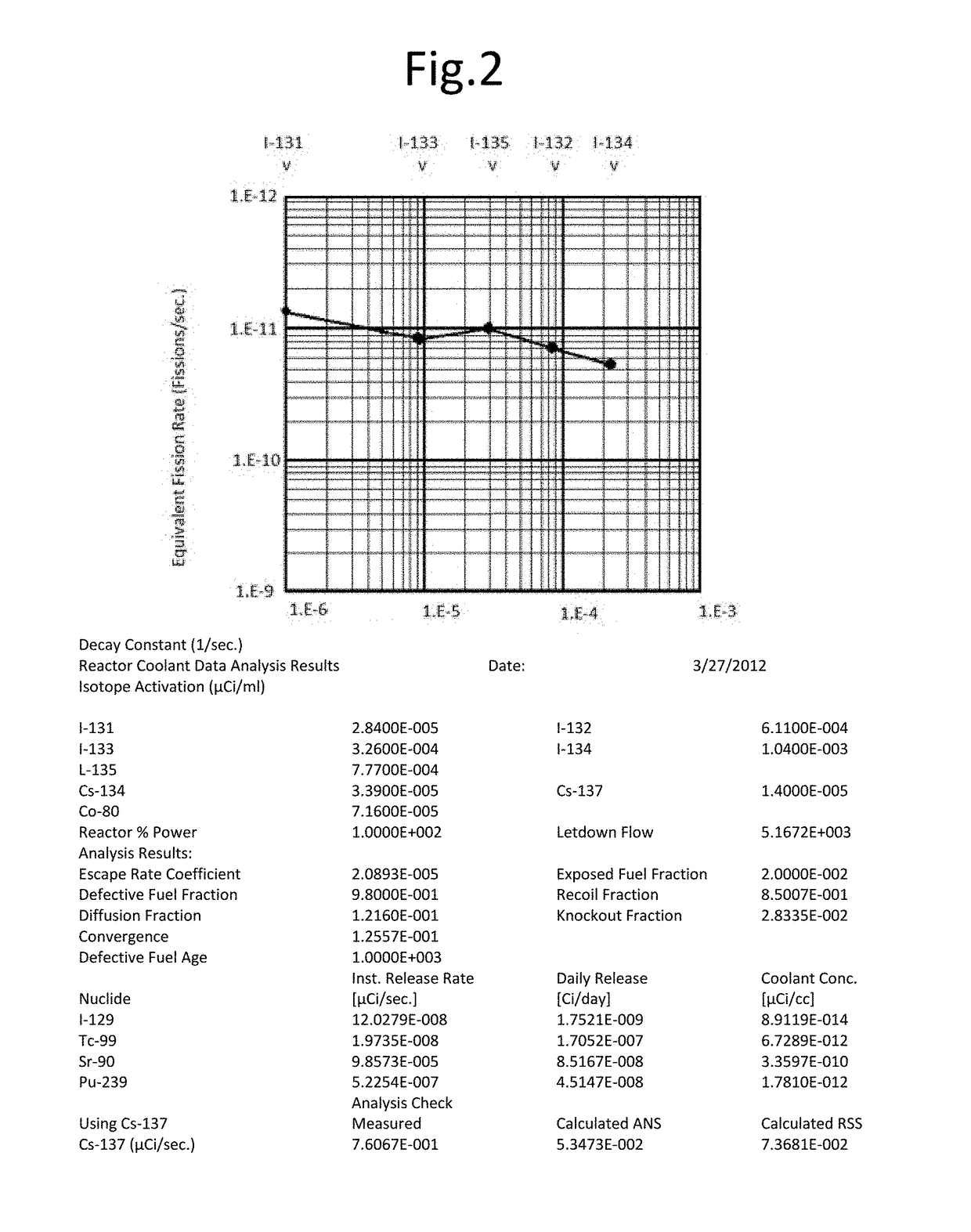
A method of determining and quantifying the presence and concentration of regulated radionuclides present in filter material used to remove radionuclide contaminants from the cooling water of a nuclear reactor. Multiple samples of the reactor cooling water are taken and the presence and concentration of directly measurable fission and activation produced radionuclides are determined through gamma spectroscopy. The release rate of radioactivity from the reactor as a function of the removal rate of the filter material is determined at equilibrium. The presence and the concentration of the indirectly measured fission regulated radionuclides are determined as a function of release rates of the directly measurable fission produced isotopes.
Owner:DW JAMES CONSULTING LLC
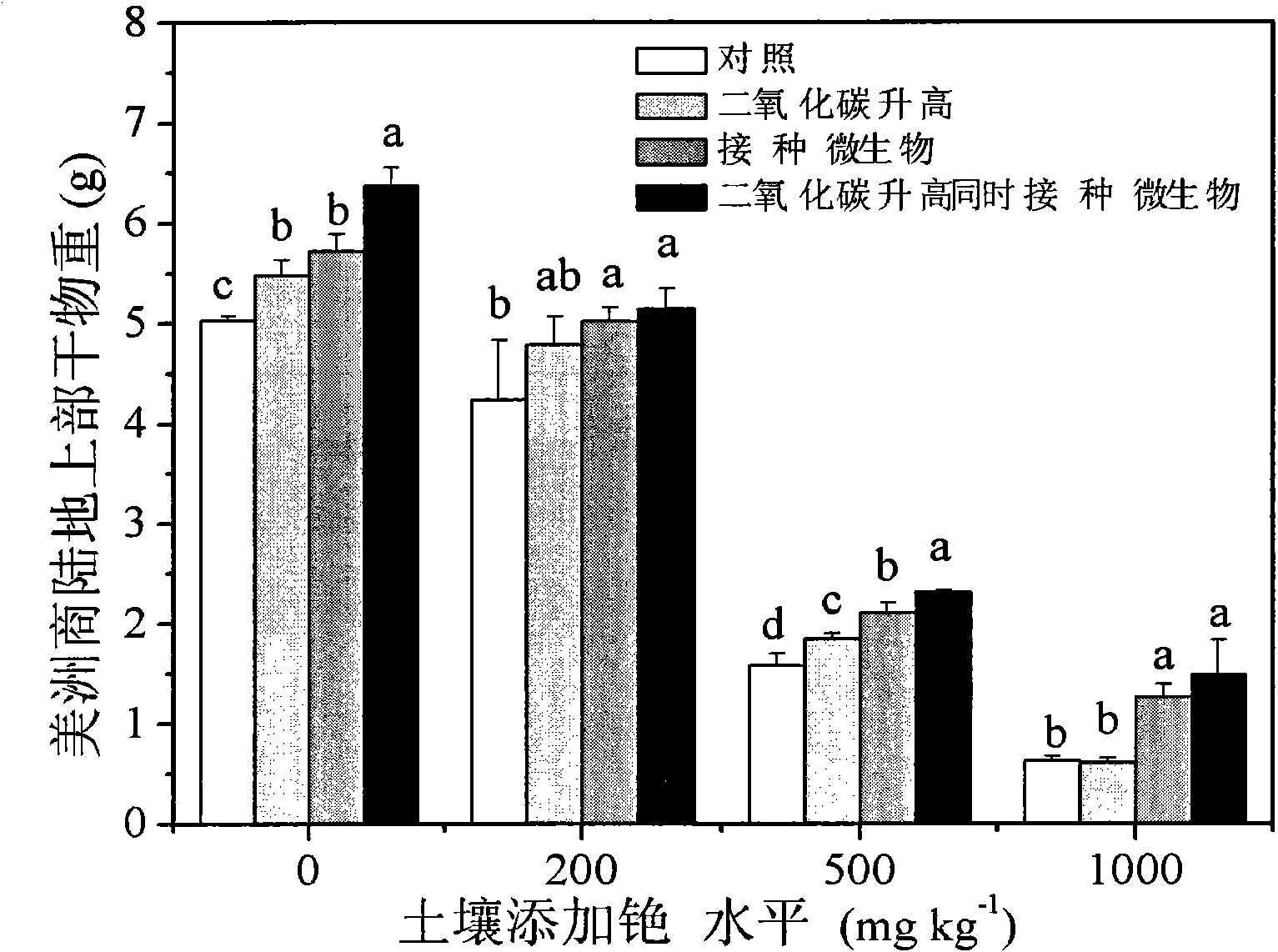
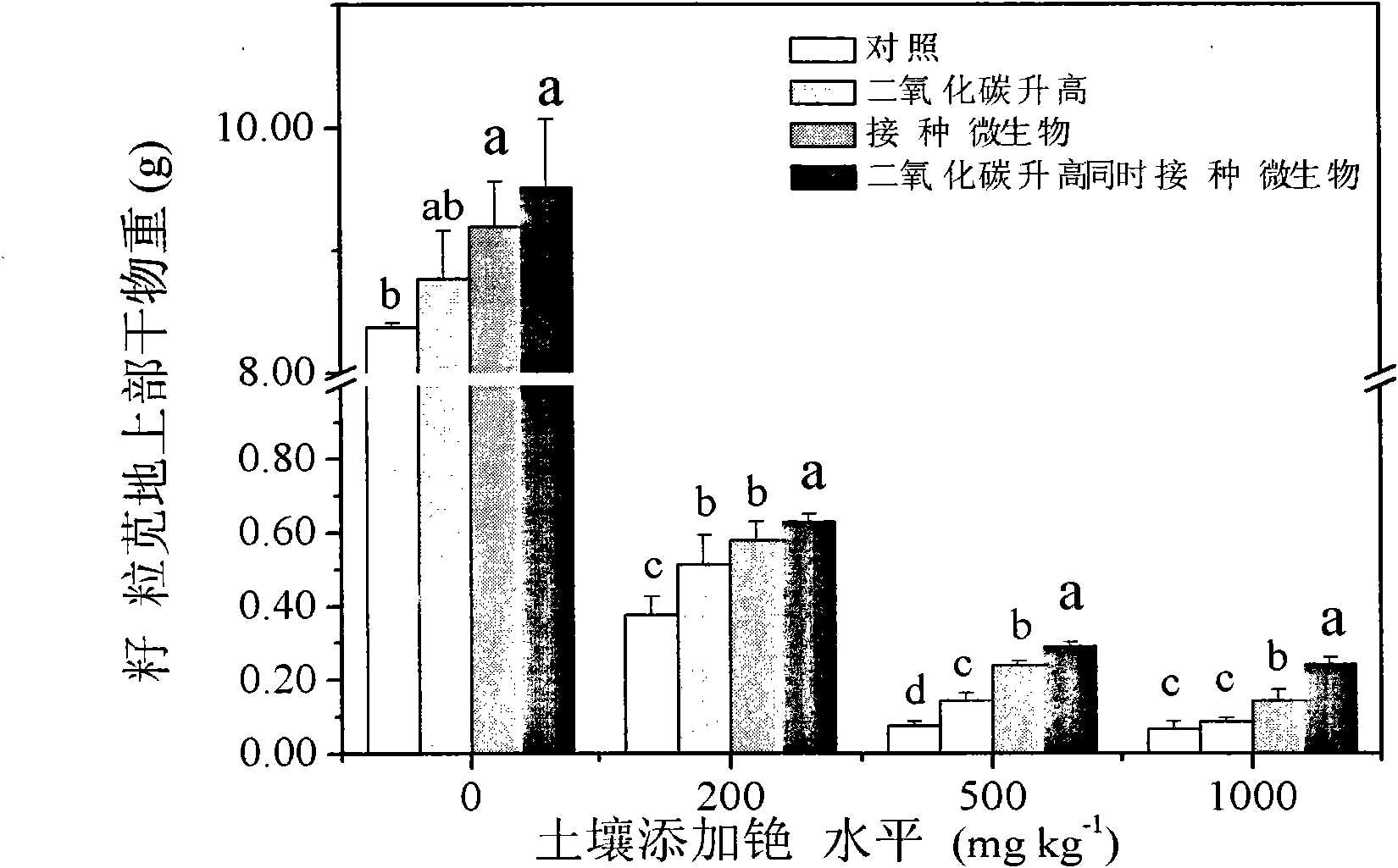
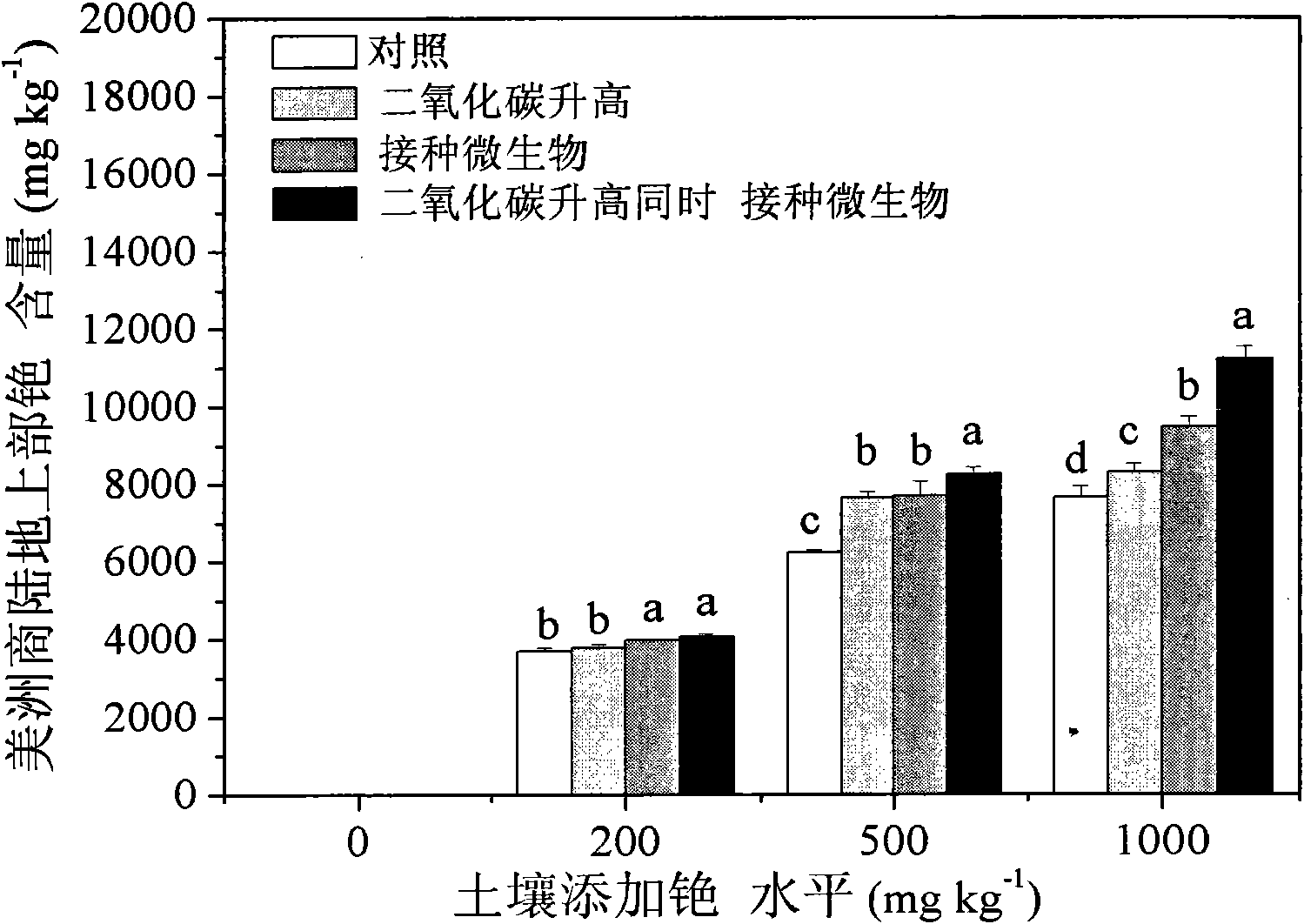
Method for increasing photoremediation efficiency of plants by utilizing joint action of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and CO2
InactiveCN102165899AIncrease aboveground biomassImprove repair efficiencyCarbon dioxide producing fertilisersHorticulture methodsHigh concentrationRhizobacteria
The invention discloses a method for increasing the photoremediation efficiency of plants by utilizing the joint action of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and CO2, belonging to the technical field of bioremediation for radionuclide polluted environments, in particular to a method for increasing the photoremediation radionuclide cesium of plants by utilizing the joint action of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and carbon dioxide fertilization. The method comprises the steps of: when phytolacca americana and grain amaranth are utilized to remediate radionuclide cesium polluted soil, carrying out carbon dioxide manure and simultaneously vaccinating the plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria which can resist high-concentration cesium to promote the growth of the phytolacca americana and the grain amaranth by utilizing carbon dioxide induction and microorganism joint action, remarkably improve the overground biomass liveweight of the phytolacca americana and the grain amaranth used for remediating soil and also increasing the absorptive amount of overground cesium of the phytolacca americana and the grain amaranth so as to accelerate photoremediation of the radionuclide cesium polluted soil, increase the photoremediation efficiency, and finally achieve the long-term target of recovering the productivity of land and promoting harmonious and ecological balance and sustainable development of district landscape.
Owner:AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION INST OF MIN OF AGRI
Novel method for evaluating potential of soil contaminated by phytoremediation radionuclide
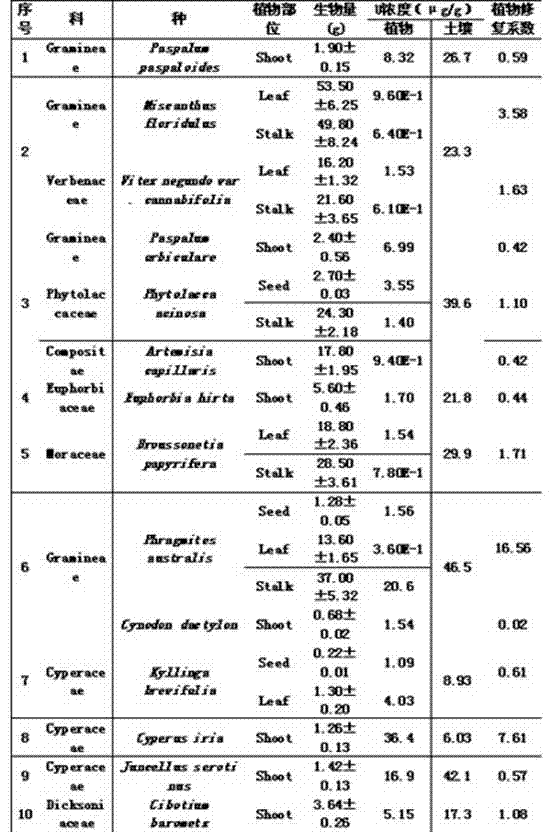
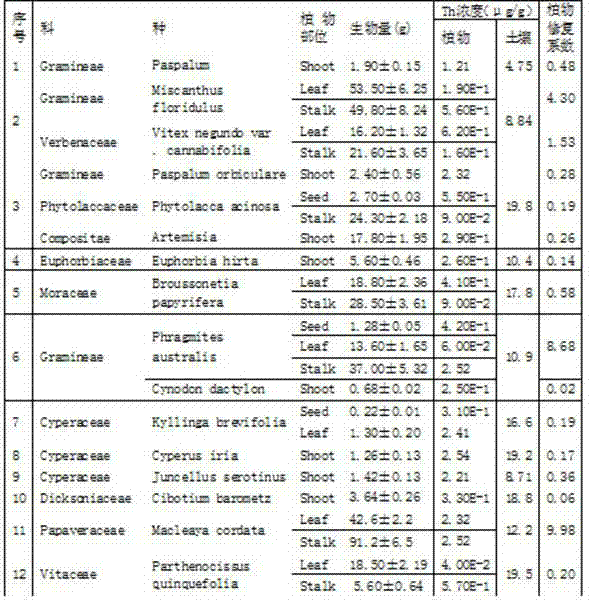
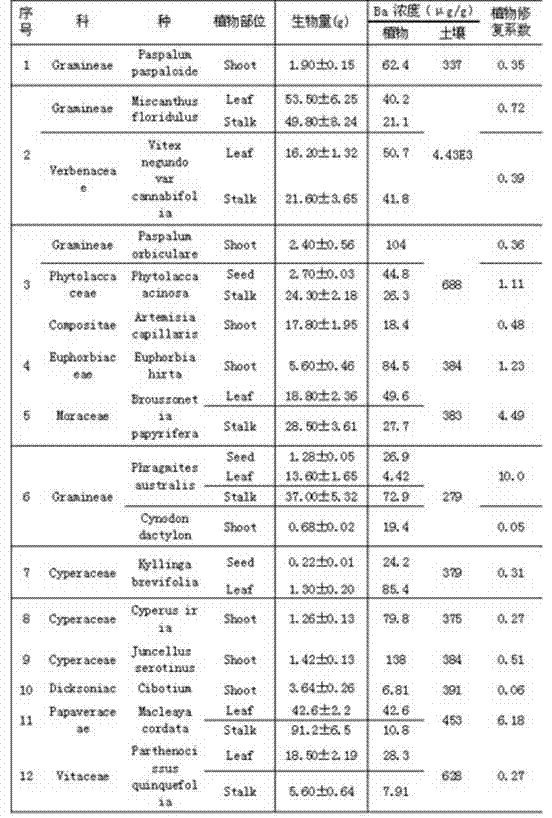
The invention relates to a novel method for evaluating the potential of soil contaminated by phytoremediation radionuclide. The phytoremediation coefficient is defined as the product of the above-ground biomass of plants and the concentration of the radionuclide divided by the concentration of the radionuclide in soil; the potential of soil contaminated by the phytoremediation radionuclide is evaluated by the phytoremediation coefficient. The method comprehensively considers the three factors including the above-ground biomass of plants, the concentration of above-ground radionuclide of plants and the concentration of radionuclide in the contaminated soil, and is reasonable in evaluating the potential of the soil contaminated by phytoremediation radionuclide. Compared with the existing evaluation method, the novel method has the advantages of simplicity, intuition and reasonable result.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
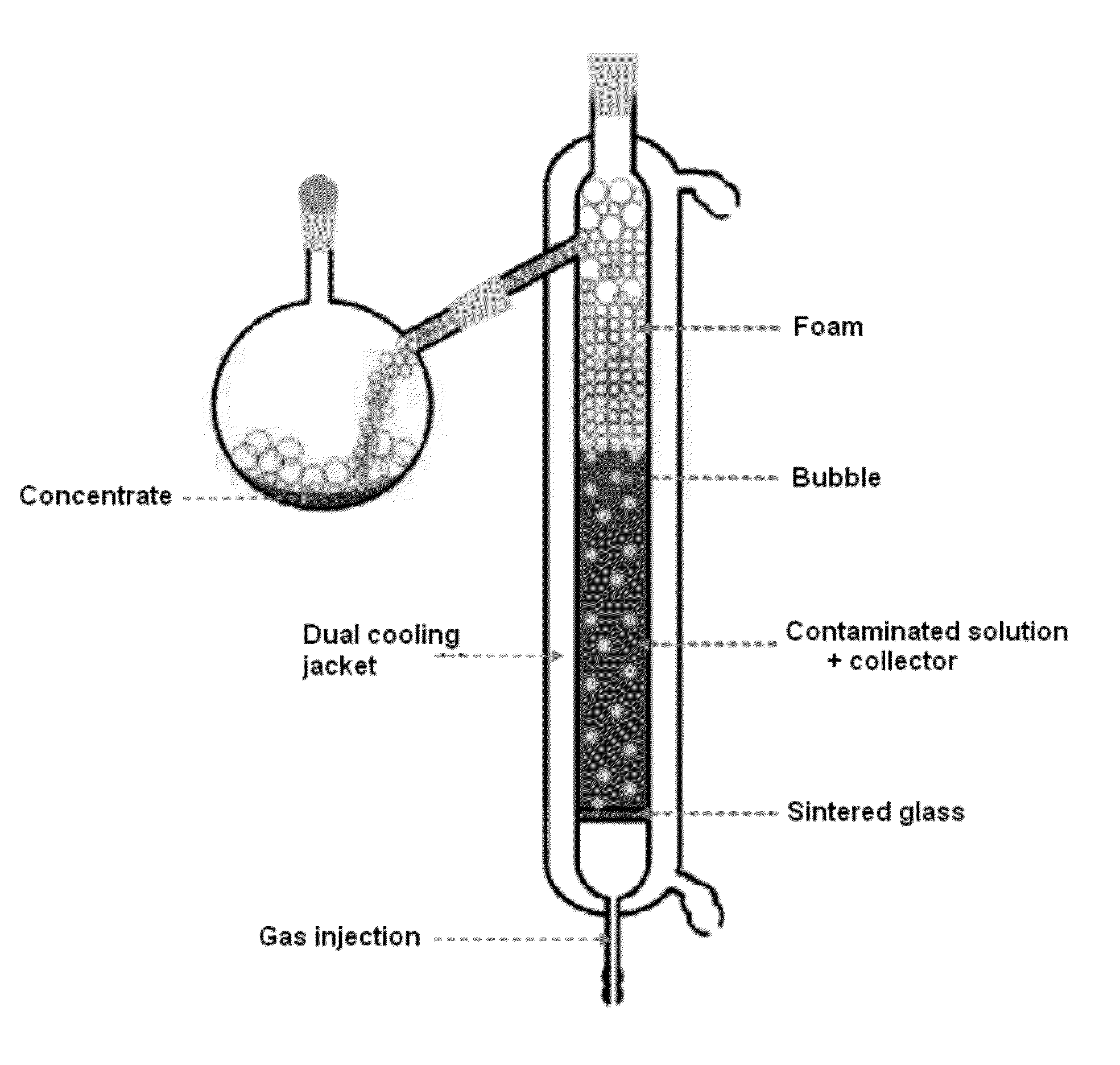
Method for the radioactive decontamination of soil by dispersed air flotation foam and said foam
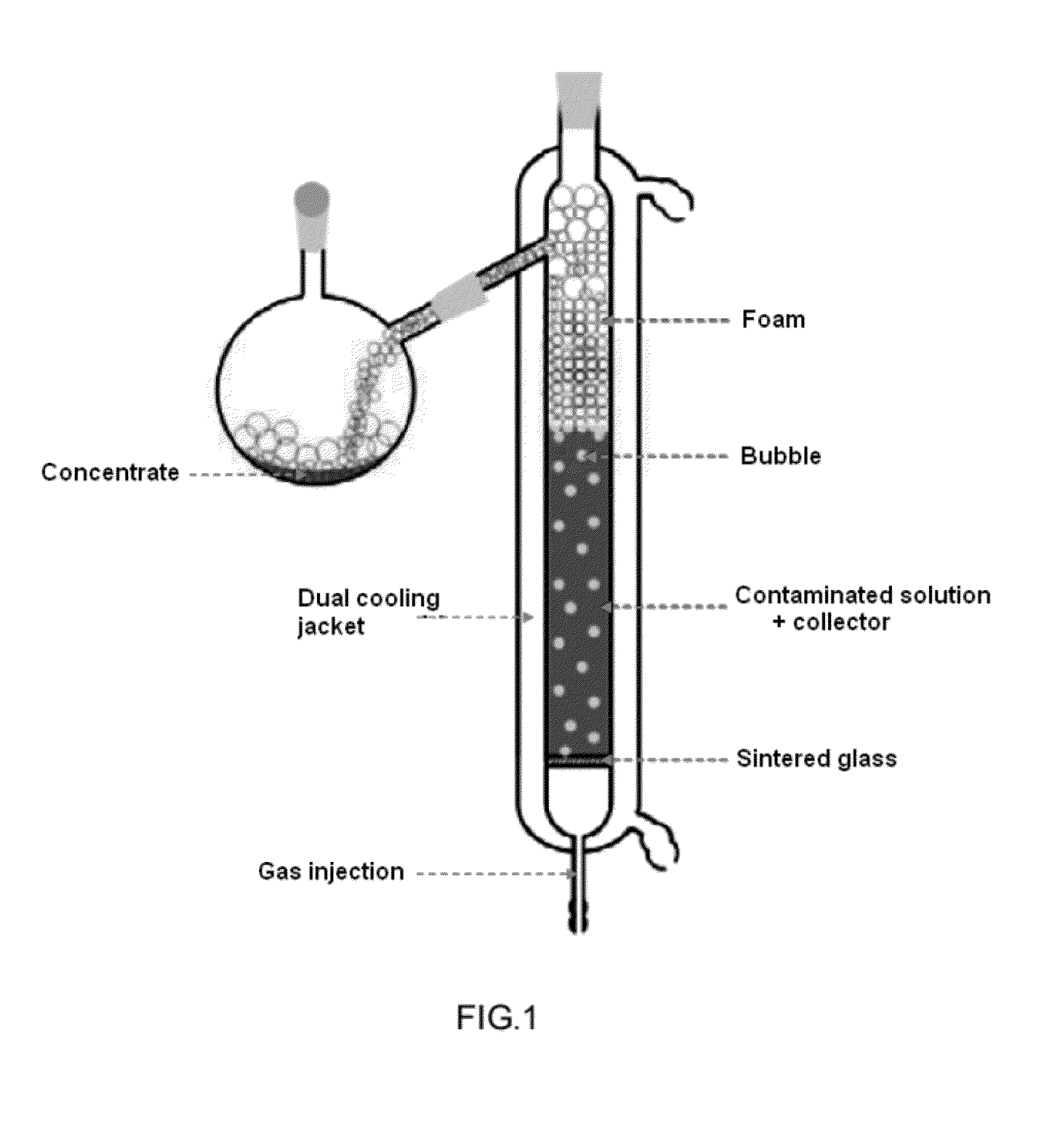
The present invention relates to a process for treating an earth contaminated by at least one radionuclide such as cesium 137Cs comprising at least one step of separating said radionuclide by dispersed air flotation foam produced by blowing air bubbles in a suspension comprising said earth and at least one collector. The present invention also relates to the flotation foam obtained by implementing such a process.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
A kind of modified clinoptilolite and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109809429BIncreased adsorption sitesImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesAluminium silicatesPharmaceutical drugStrontium
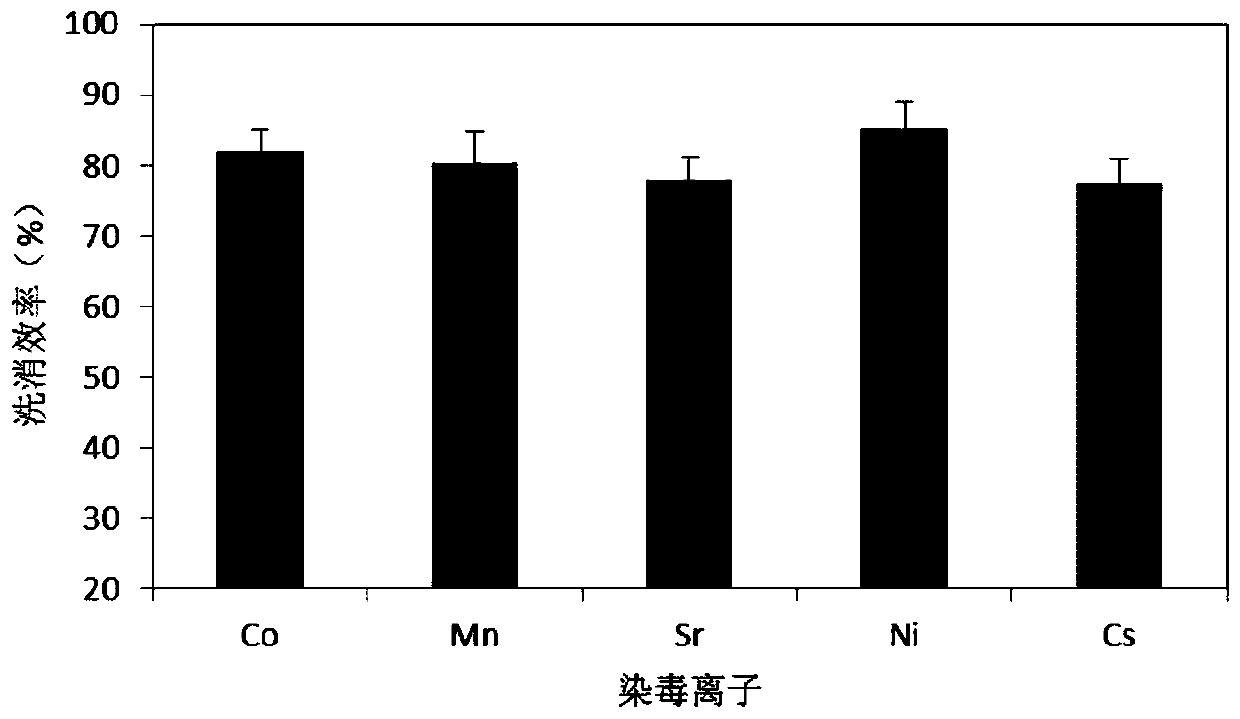
A modified clinoptilolite and its preparation method and application. The modified clinoptilolite is prepared by the following steps: pulverizing the natural clinoptilolite, washing with water, and drying; drying the dried clinoptilolite at 450-600°C React at low temperature for 2‑4h, and cool naturally; add the high-temperature-treated clinoptilolite powder into 1‑2mol / L NaOH solution, and control the solid-liquid ratio to 1:10~20, g / mL; at 80‑100°C After stirring and heating for 8-24 hours, remove the supernatant, rinse repeatedly with pure water to neutrality, and dry; pass through a mesh screen of more than 400 mesh to obtain modified clinoptilolite. The silicon-aluminum ratio of the modified clinoptilolite n(Si / Al)=2.7-5.0, the Na content is higher than 4wt%, the Ca content is higher than 3.5wt%, the particle size is less than or equal to 400 mesh, and it is resistant to radioactive cesium, strontium, cobalt, Manganese, nickel, etc. have large adsorption capacity, and can be used to prepare drugs for promoting excretion of radionuclide pollution in vivo.
Owner:中国人民解放军海军特色医学中心
Starch-base material capable of achieving fertilizer slow release and enriching radionuclide and preparation method of material
InactiveCN102936169BBioabsorbableWith slow release functionFertilizer mixturesPlasticizerMixed materials
The invention discloses a starch-base material capable of achieving fertilizer slow release and enriching radionuclide and a preparation method of the material. The method comprises the steps of weighing, by weight 1-99 parts of starch, 1-99 parts of a fertilizer, 0-50 parts of plasticizer and 0-50 parts of fortifier and mixing and stirring for 5-20 min to obtain a mixed material; and adding the mixed material into a twin screw extruder, conducting melt blending for 5-10min under the condition that the temperature is 80-180 DEG C and the pressure is 0.1-1 MPa, extruding, molding, and pelleting after cooling to obtain the starch-base material capable of achieving fertilizer slow release and enriching radionuclide. According to the starch-base material, good mechanical performances are achieved, the slow release speed can be controlled, when the fertilizer is subjected to slow release, the radionuclide can be enriched, and the material can be widely applied to fertilizer slow release and purification of heavy metal in water and organisms which are polluted by the radionuclide.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
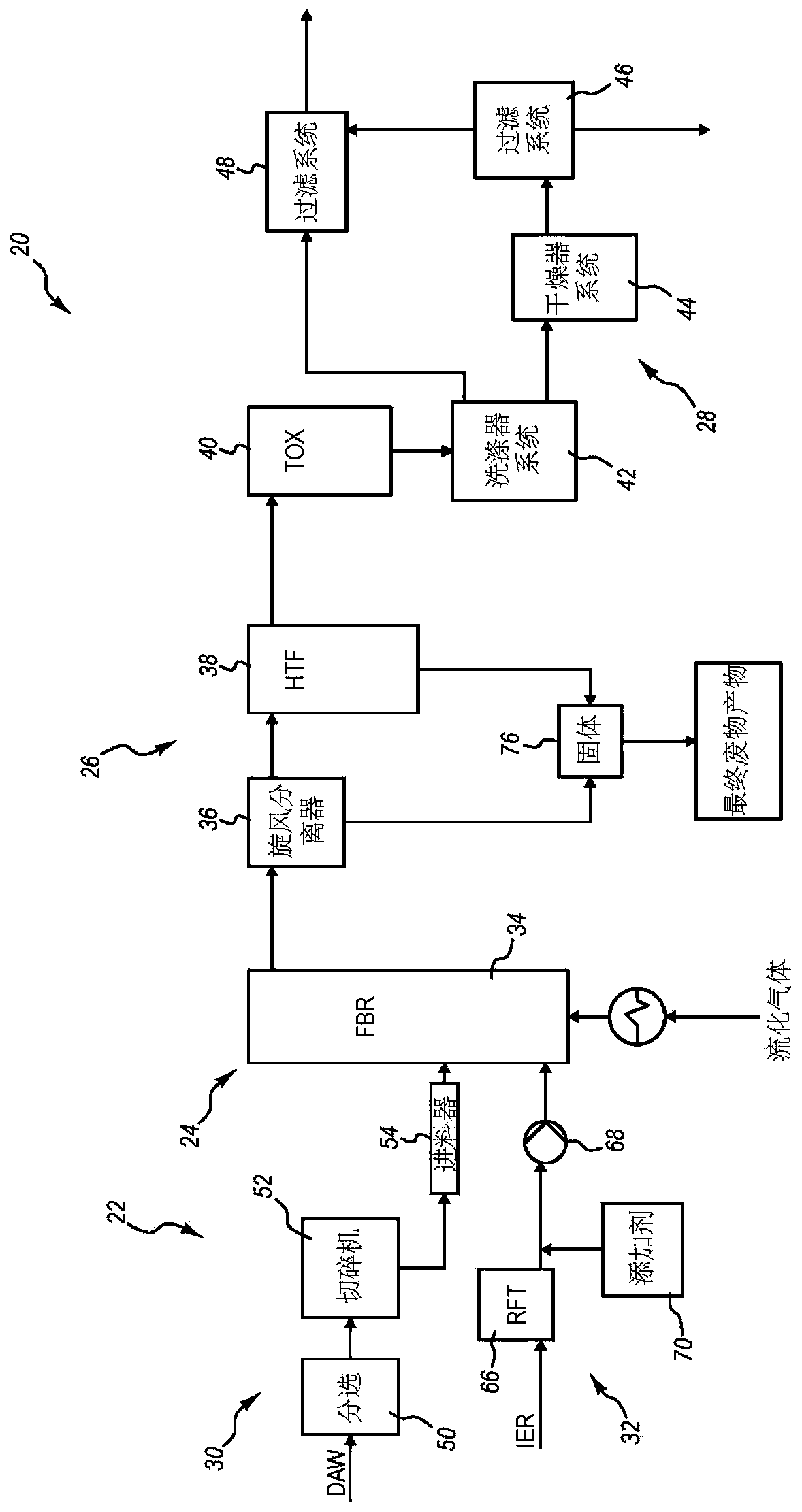
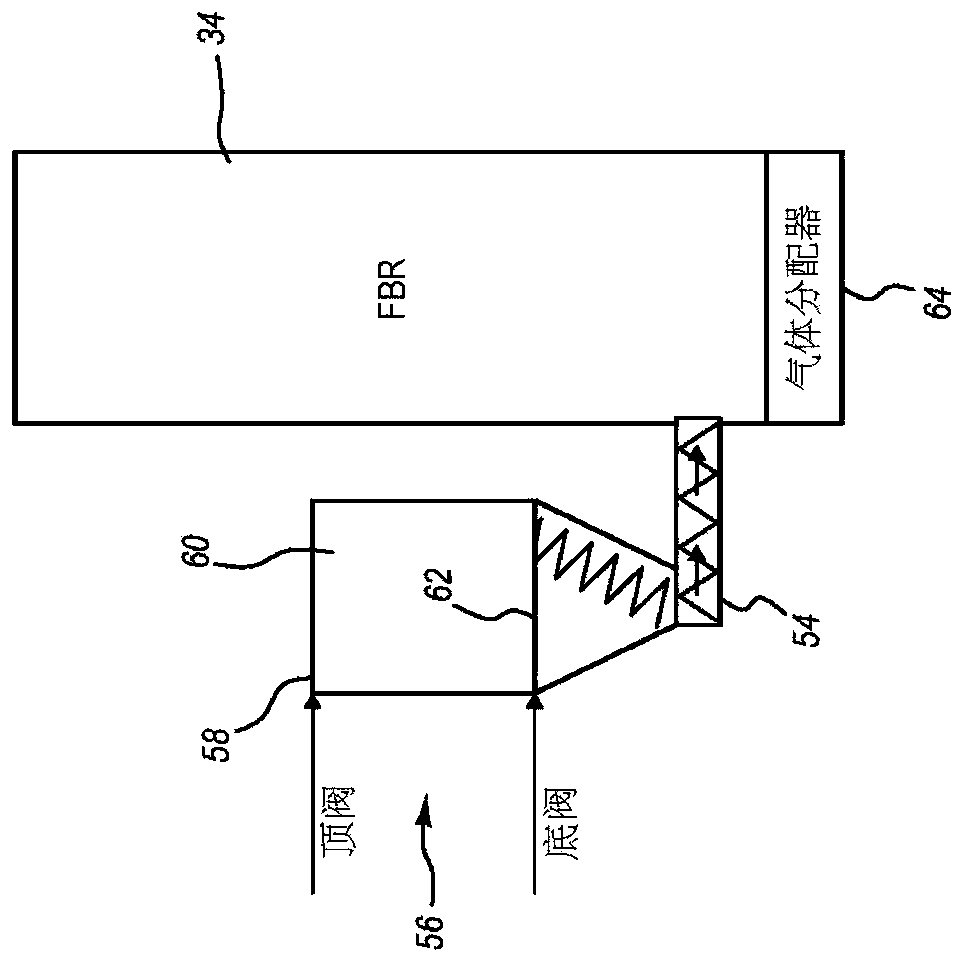
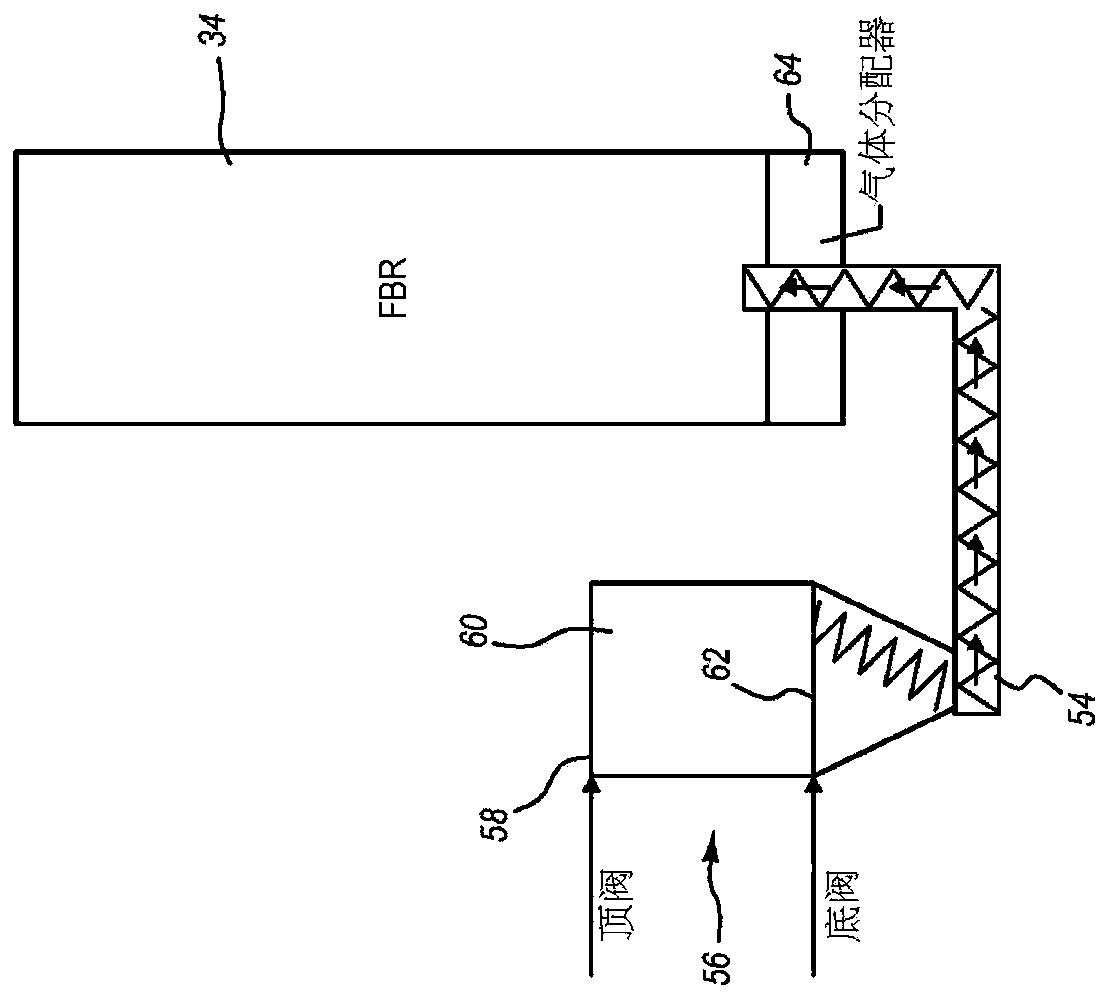
Thermal volume reduction of radioactive wastes
A method for thermal volume reduction of waste material contaminated with radionuclides includes feeding the waste material into a fluidized bed reactor, injecting fluidizing gas into the fluidized bed reactor to fluidize bed media in the fluidized bed reactor, and decomposing the waste material in the fluidized bed reactor. A system for thermal volume reduction of the waste material includes oneor more of a feedstock preparation and handling system, a fluidized bed reactor system, a solids separation system, and an off-gas treatment system. The method and system may be used to effectively reduce the volume or radioactive wastes generated from the operation of nuclear facilities such as nuclear power plants including wastes such as spent ion exchange resin, spent granular activated carbon, and dry active waste. The majority of the organic content in the waste material is converted into carbon dioxide and steam and the solids, including the radionuclides, are converted into a waterlessstable final product that is suitable for disposal or long-term storage.
Owner:ATKINS ENERGY GLOBAL SOLUTIONS LLC
Novel technical method for DNA and protein interaction research
The present invention relates to a new technical proposal for testing, diagnosing, and studying the biology and the medicine. The present invention is characterized in that the cell protein extract combines into compound earlier than the corresponding antibody molecule, and combines with the null probe into a triple compound of the antibody-albumen-null probe, which can be moved into the non-metamorphic polyacrylamide gel for electrophoresis, and finally an ECL method is used for the irradiance test in darkroom. Compared with the traditional method, the technology has simple and reliable operation without radionuclide element pollution.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Radionuclide decontaminant, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113322134AEasy to cleanDoes not contain corrosive ingredientsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsFiberNuclear plant
The invention discloses a radionuclide decontaminant, and a preparation method and application thereof. The decontaminant comprises, by mass, 8-12% of a surfactant, 2-5% of compound enzyme, 16-20% of a nuclide removing agent, 8-14% of a chelating agent and water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the required components according to the weight percentage; adding water into the container; sequentially adding the chelating agent, the nuclide removing agent, the surfactant and the compound enzyme into the container under stirring; and adding a proper amount of the pH regulator into the container, and fully and uniformly mixing to obtain the decontaminant. The application means that the decontaminant is used for removing radionuclides on the surface of a lifting belt or a safety belt for a nuclear power plant. The decontaminant has an excellent cleaning effect on dust and greasy dirt on the surfaces of the lifting belt and the safety belt, especially has an excellent removal effect on radionuclide contamination, and meanwhile, the detergent does not contain corrosive components, is environment-friendly and does not cause damage to fiber materials.
Owner:YANGJIANG NUCLEAR POWER +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com