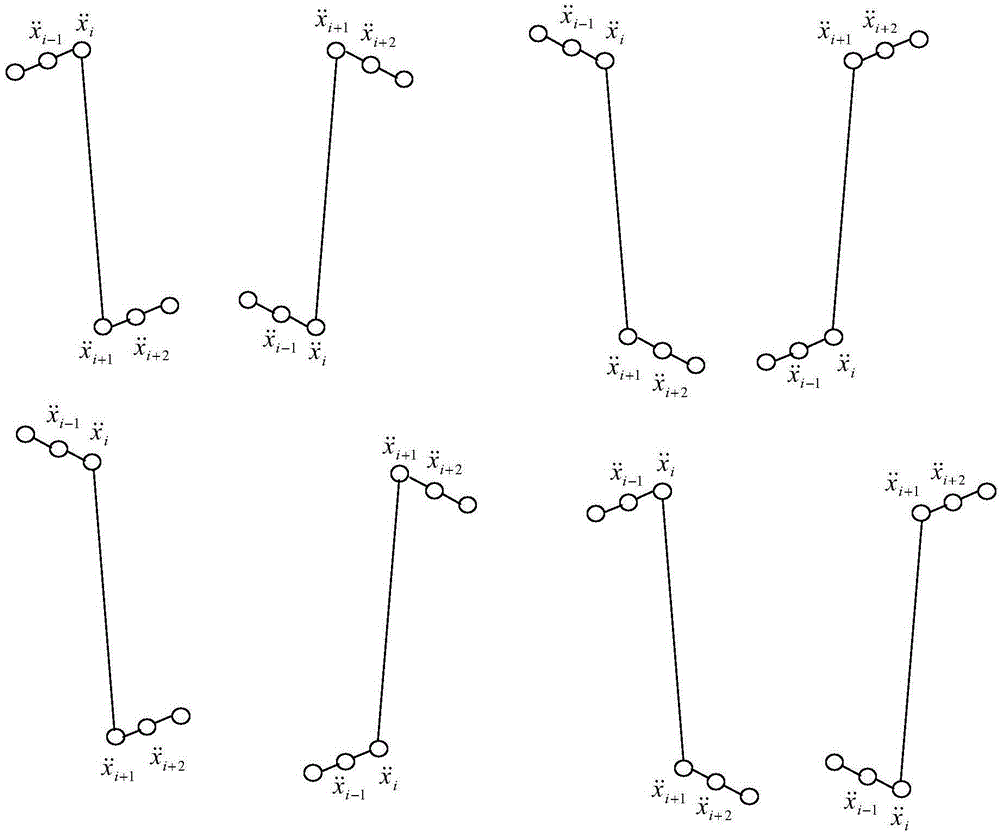Method and system for monitoring rigidity damage of structure based on EMD
A technology for structural stiffness and damage monitoring, applied in the testing, measuring devices, instruments, etc. of machines/structural components. The effect of stability, high monitoring accuracy and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0193] The content of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
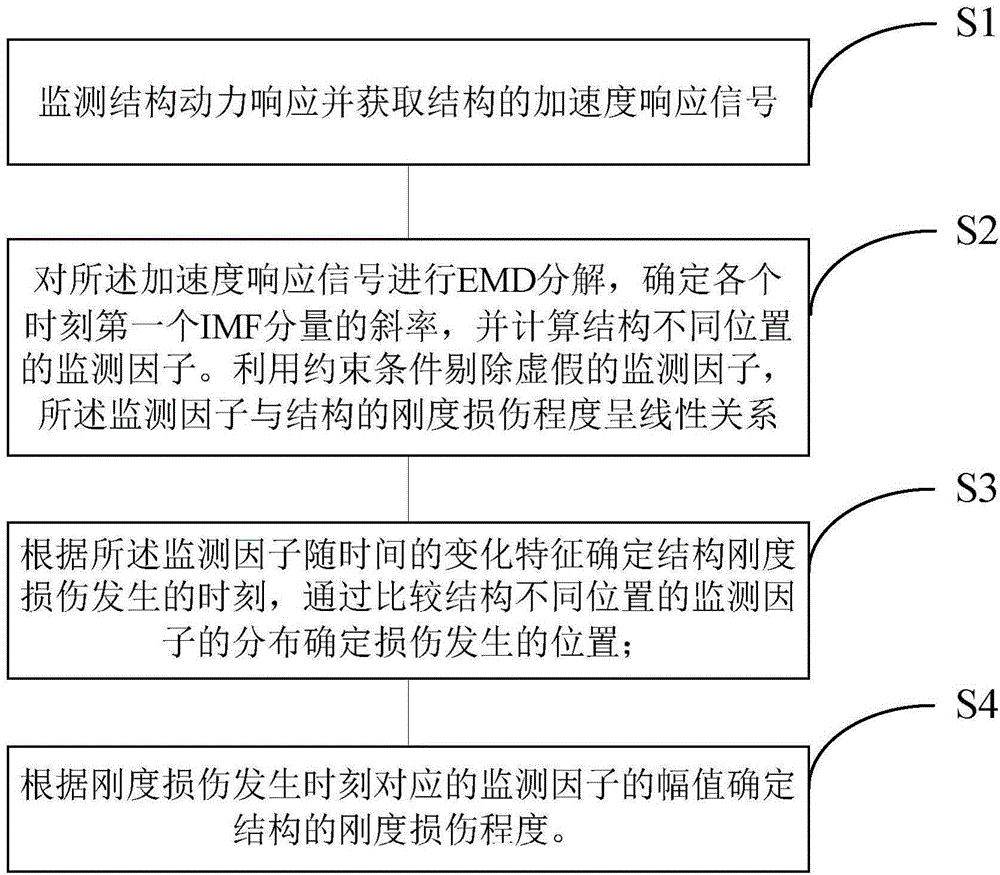
[0194] Such as figure 1 Shown is the embodiment of the EMD-based structural stiffness damage monitoring method of the present invention, and its specific process is as follows:
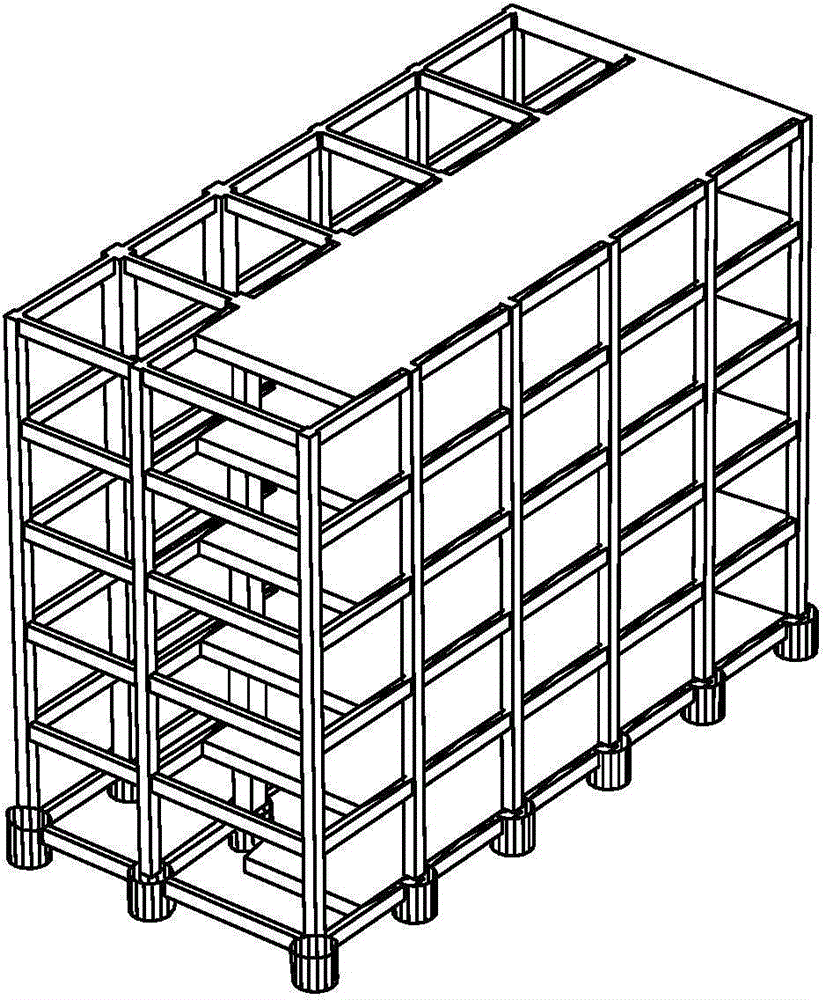
[0195] S1 Install multiple acceleration sensors at different positions of the structure to monitor the dynamic response of the structure in real time, monitor the vibration response of the structure, and obtain acceleration response signals at different positions of the frame structure;
[0196] S2 performs EMD decomposition on the acceleration response signals at different positions of the structure, and determines the slope of the first IMF component at each moment;
[0197] S3 calculates the slope of the IMF component at each moment, and calculates the monitoring factors at different positions of the structure;
[0198] S4 uses constraints...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com