Parallel hybrid excitation compound motor with outer stator poles
A hybrid excitation and composite motor technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve problems such as small output torque, improve overload capacity, achieve brushless, and facilitate installation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
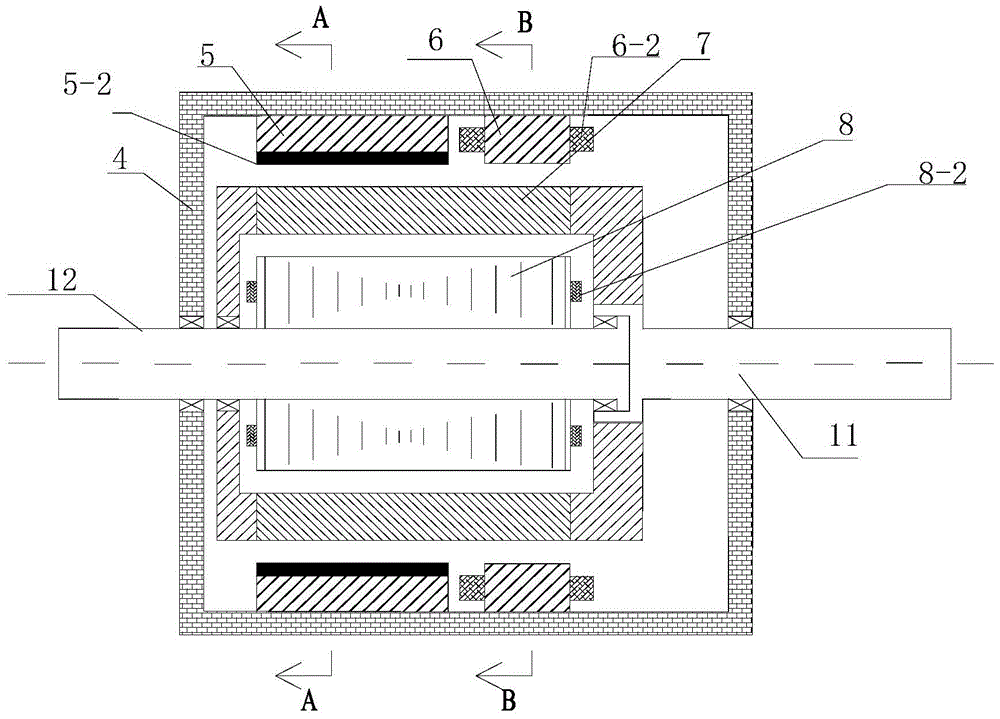
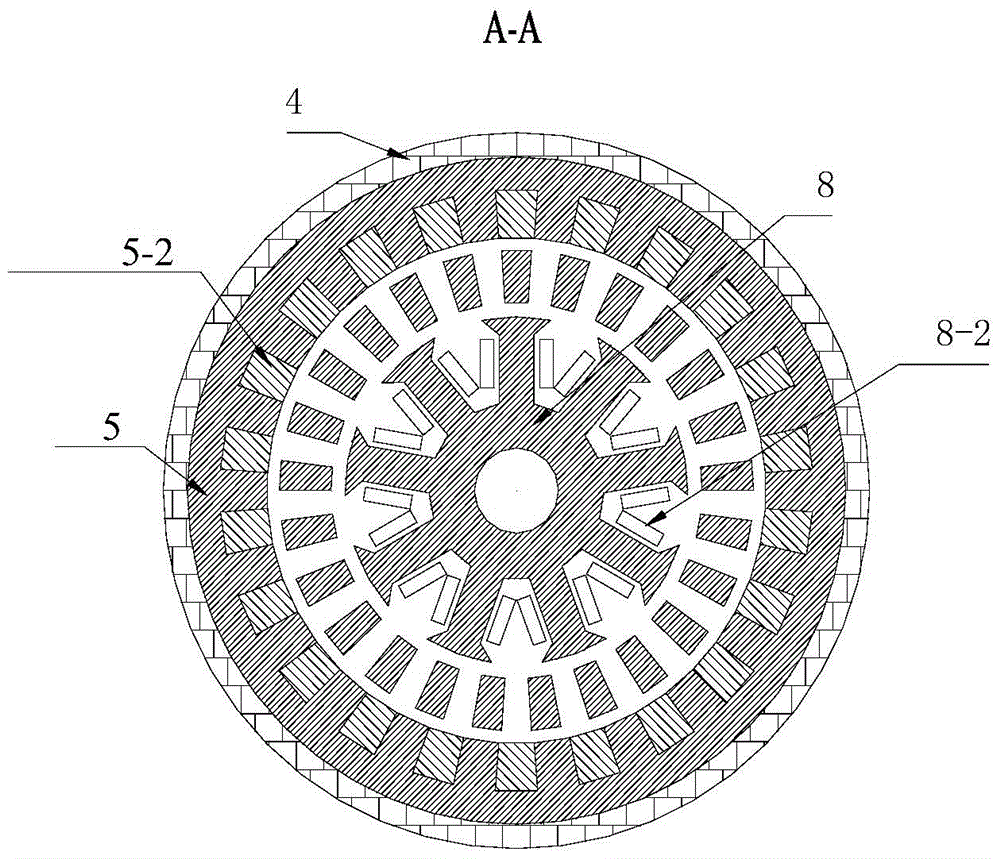
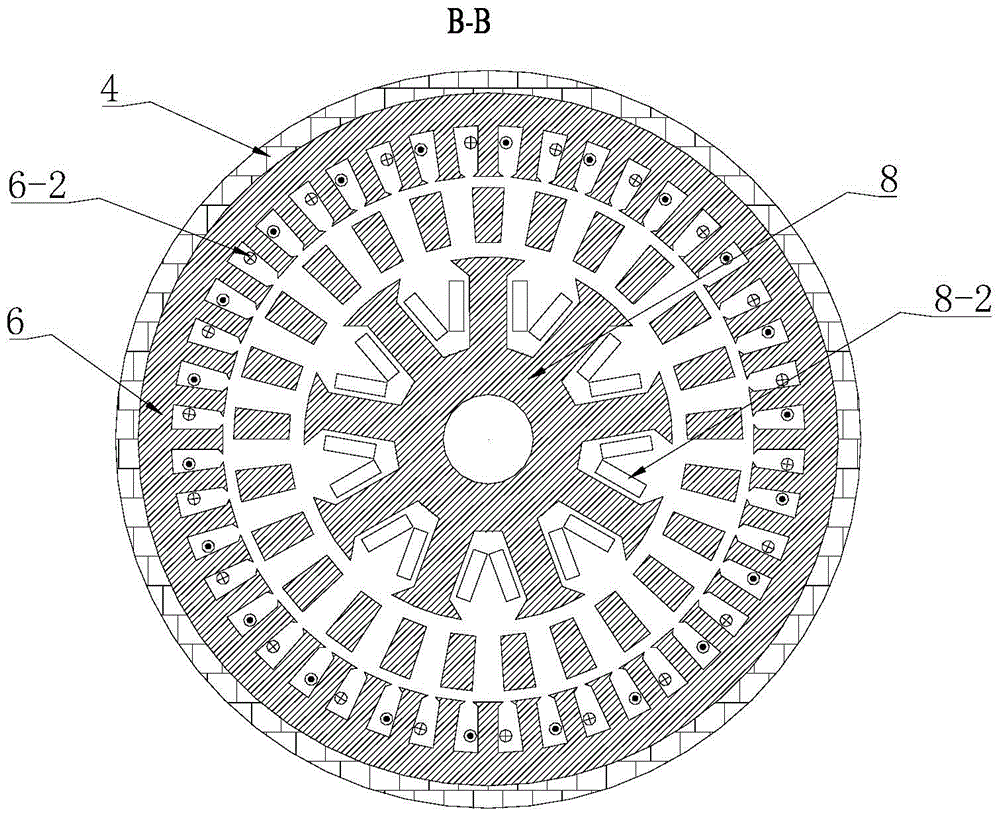
[0019] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 Describe this specific embodiment, the outer stator magnetic pole parallel type hybrid excitation composite motor described in this specific embodiment includes an inner stator 8, an outer stator and a magnetic flux ring rotor 7, and the magnetic flux ring rotor 7 is located between the inner stator 8 and the outer stator , and fixed on one end of the output shaft 11 of the magnetic ring rotor through a bracket, the other end of the output shaft 11 of the magnetic ring rotor passes through the right end cover of the motor casing 4, and is connected to it through a bearing for rotation, the magnetic ring The rotor 7 is separated from the inner stator 8 and the outer stator by a radial air gap;
[0020] The inner stator 8 is fixed on the inner stator output shaft 12, and one end of the inner stator output shaft 12 passes through the left end cover of the motor casing 4, and is connected to it in rotation th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the outer stator pole-parallel hybrid excitation compound motor described in Embodiment 1 is that both the permanent magnet 5-2 and the excitation winding 6-2 are of C-shaped structure.
[0029] In this embodiment, the permanent magnets 5-2, the outer stator yoke and the outer stator teeth are arranged in a C-shaped structure, and the Halbeck 90° magnetization method is used to cut each permanent magnet into three parts, and the middle part is radially filled. Magnetic, both sides are magnetized in the circumferential direction and a non-magnetic material is inserted between it and the core to reduce magnetic flux leakage and improve the utilization rate of the permanent magnet or adopt a radial magnetization method, such as Figure 8 and Figure 9 shown.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Specific Embodiment 3. The difference between this specific embodiment and the outer stator pole-parallel hybrid excitation composite motor described in specific embodiment 1 is that the permanent magnet outer stator 5 adopts a built-in tangential magnetic steel structure or a surface-mounted magnetic steel Structural realization.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com