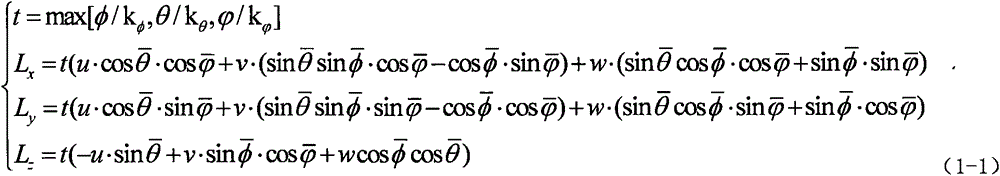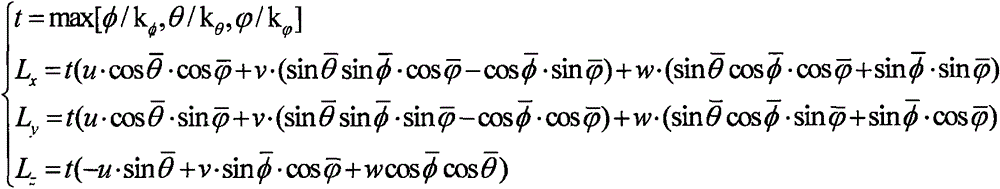Automatic pilot and genetic algorithm-based method for monitoring hovering range of unmanned aerial vehicle
A genetic algorithm and unmanned aerial vehicle technology, applied in the field of monitoring the hovering range of unmanned aerial vehicles, can solve problems such as damage, forced landing, long or touching surrounding objects, etc., to reduce stability, reduce search space, and shorten search the effect of time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The specific embodiment of the present invention is described in further detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
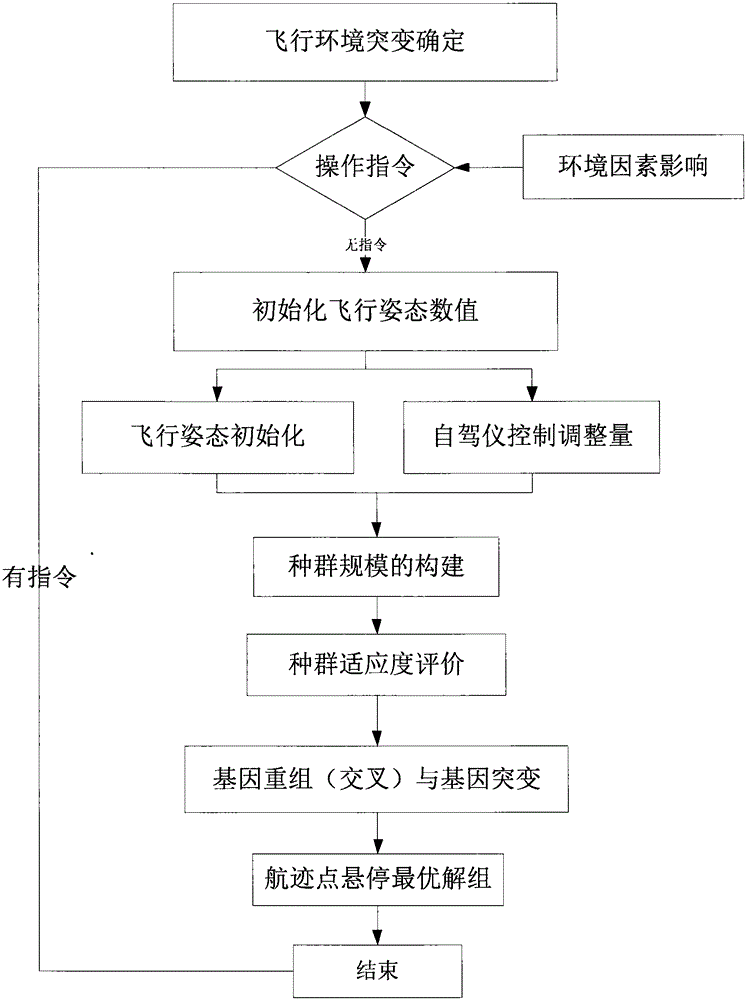
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention, as a method for monitoring the hovering range of the drone based on the autopilot and the genetic algorithm, realizes the flight control of the hovering range of the drone under limited conditions, and the following is combined with specific implementation examples Be explained.
[0034] Step 1: Determine the sudden change of the flight environment
[0035] Rotor UAVs perform tasks in three-dimensional space, and the size of the operating space is 300×300×300 (km). The UAV is affected by strong convective clouds during flight, resulting in a sudden change in the attitude of the UAV. When the autopilot detects that no control command is issued for this change, it determines that the sudden change in flight attitude is affected by external environmental factors; if When a flight contro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com