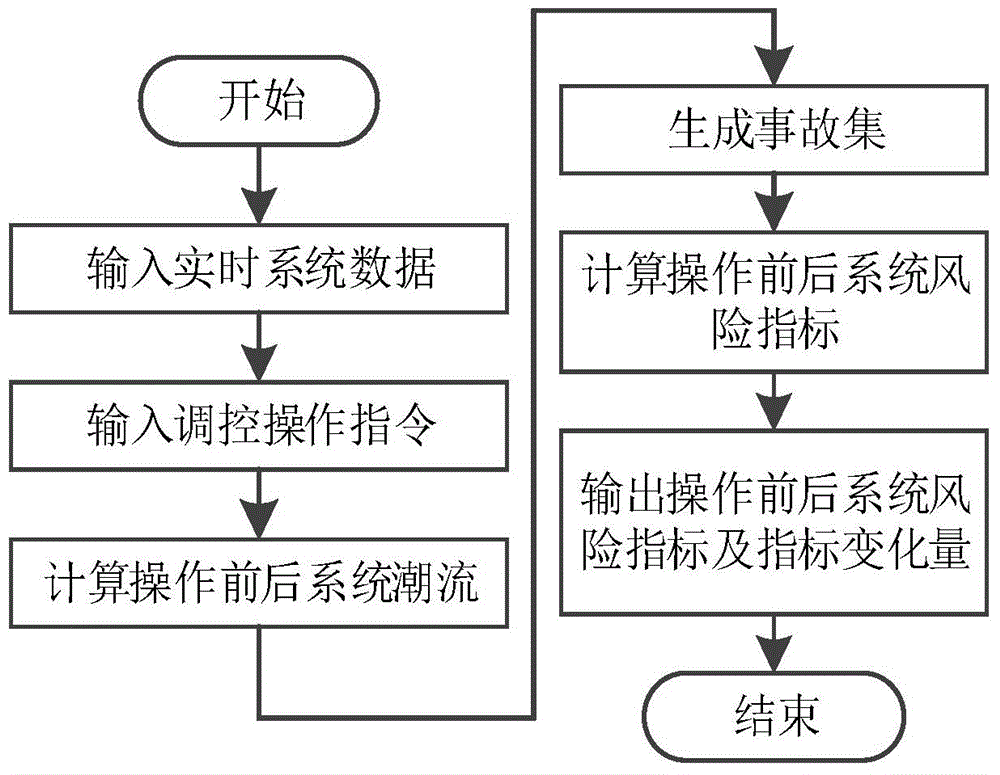
Real-time risk assessment method facing power grid dispatching operation
A technology for risk assessment and power grid dispatching, applied to instruments, data processing applications, information technology support systems, etc., can solve problems such as misoperation, frequent dispatching operations, and suboptimal operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
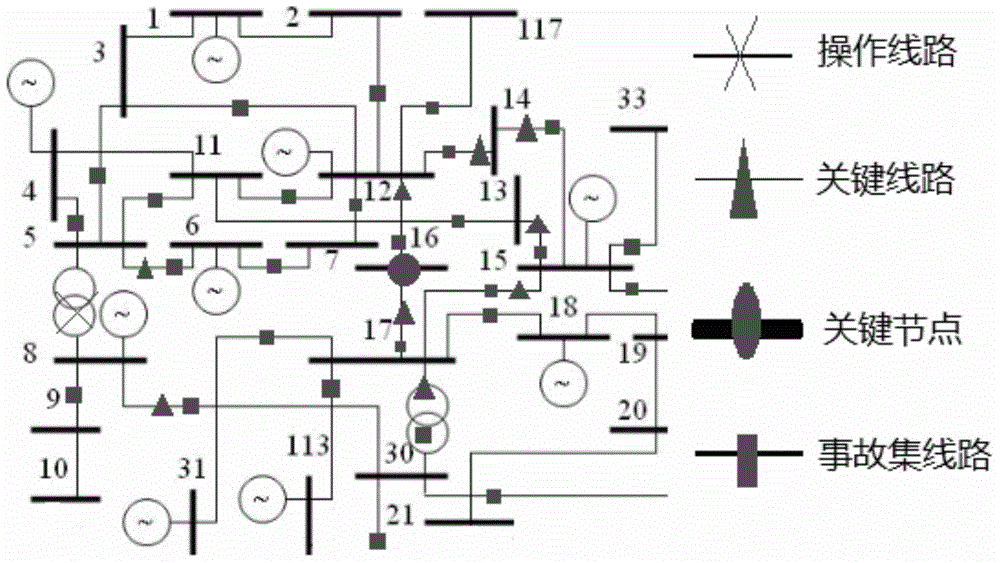
[0125] In Example 1, in order to facilitate the description of the accident set generation method, let δ S = 0.2; δ V =2×10 -2 p.u. Calculate the power flow before and after operation for each line, and |ΔS / S of the line N | and the ΔV(p.u.) of the nodes are sorted, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0126] Table 1
[0127] line
|ΔS / S N |
node
ΔV(p.u.)(×10 -2 )
8-30
1.1338
16
2.2786
16-17
0.4744
30
1.7429
12-16
0.4500
13
1.3620
14-15
0.3770
14
1.0933
15-17
0.3651
5
1.0524
30-17
0.3443
38
0.9214
13-15
0.3305
22
0.5976
12-14
0.2957
17
0.5630
5-6
0.2878
21
0.5618
7-12
0.1855
20
0.3832
[0128] It can be seen from Table 1 that lines 8-30, 16-17, 12-16, 14-15, 15-17, 30-17, 13-15, 12-14 and 5-6 are key lines, and node 16 is a key node .
[0129] Further...
Embodiment 2
[0132] In embodiment 2, in order to illustrate the efficient accuracy of the inventive method better, suppose δ S = 0.3; δ V =2×10 -2 p.u. Figure 4 shows the number of accidents, calculation time at different search depths, Figure 5 The corresponding risk index error is shown, and the calculation error is based on the calculation result of the "N-1" scanning method. It can be seen that when N increases, n c As it increases, the calculation error decreases. The smaller calculation error reveals that the method of the present invention can find out the components that are more sensitive to the scheduling operation, so the selected accident set C 0 It can meet the accuracy and efficiency requirements of dispatching operation risk assessment.
[0133] The risk at N=1 is analyzed.
[0134] Table 2 shows the ranking of the voltage limit indicators of each accident node:
[0135] Table 2
[0136] accident line
ΔR V (×10 -2 )
accident line
ΔR V (×...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com