Method for quantitatively discriminating nephrite production areas
A technology of origin and nephrite, applied in measurement devices, material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve problems such as research reports
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 2
[0076] Embodiment 1 Binary iterative linear discriminant analysis (IB-LDA) method and distinguishing result
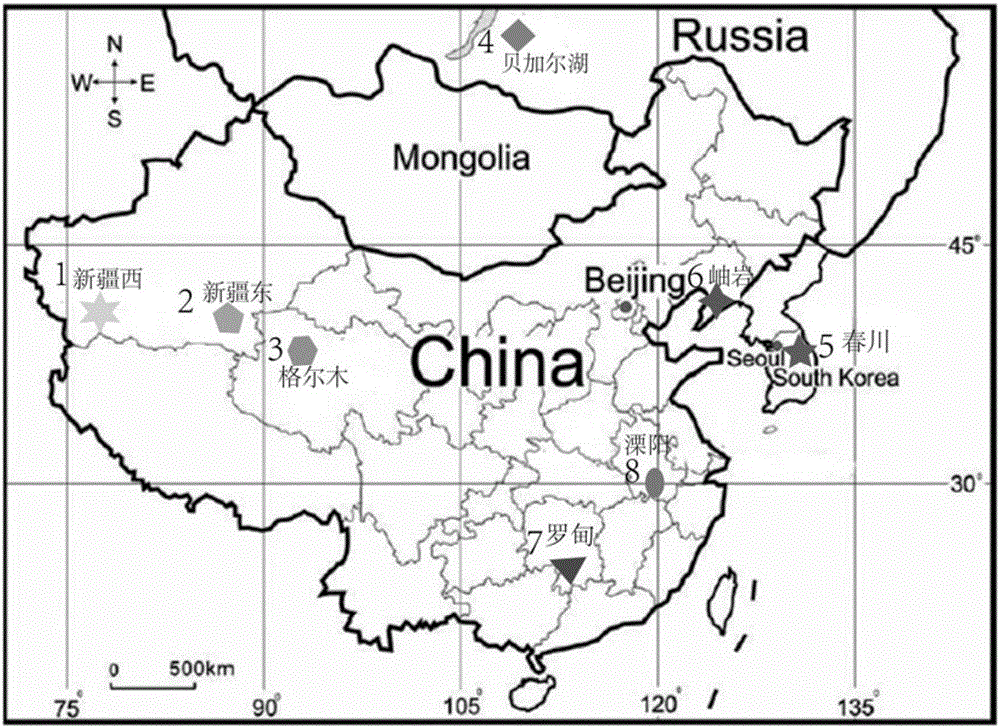
[0077] 1) The samples in the examples are a large number of nephrite samples collected on-the-spot by the research team of the inventor who went to various mining areas of marble-type nephrite in East Asia for many years. Taking the eight most common nephrite jade origins as the research objects, the origin discrimination model was established by using the IB-LDA method. The geographic location of the 8 origins is as follows: figure 2 shown. figure 2 The nephrite produced in the central Xinjiang area is divided into Xinjiang West and Xinjiang East, which is determined based on the significant differences in geological and metallogenic conditions between the two (Tang Yanling et al., 1994). Numbers 1-8 represent Xinjiang West (the ore sites in western Xinjiang, China, including the famous Hotan, Yecheng, and Moyu River areas, etc.), Xinjiang East (the ore sites in e...
Embodiment 2
[0099] The test of embodiment 2 unknown place of origin sample
[0100]In this example, the "sample to be tested" of unknown origin is tested, and the origin discriminant analysis is carried out on two nephrite samples that are said to come from the Xinjiang region (the origin of which has not been determined). As in step 2) of Example 1, first select a smooth and flat area of the sample surface for LA-ICP-MS testing, test 3 points for each sample, and obtain 6 test points in total. The trace element content is brought into Step 4 of Example 1 in turn. IB-LDA is based on the classification function established by 8 production areas, which group has a higher score in the classification function, and which production area the "test sample" belongs to.
[0101] The result of the discrimination is that after 7 rounds of IB-LDA analysis, the classification function scores of these 6 test points all fall within the range of East Xinjiang. or7 Both are 89.6%.
Embodiment 3
[0102] Embodiment 3 traditional linear discriminant analysis (LDA) method producing area distinguishing result
[0103] This example is used to compare the distinguishing effect of traditional LDA and IB-LDA. In traditional LDA analysis, the samples and trace element contents used are the same as in Example 1, that is, statistical linear discriminant analysis is carried out on 480 sample test points from 8 production areas. The difference from IB-LDA is that traditional LDA regards samples from each origin as a group and conducts multiple comparisons at the same time. The discriminant result is the result of a round of discriminant analysis of 8 origins, and the discrimination probability of all origins is the same, while IB-LDA can give the maximum discriminant probability of each origin relative to other origins.
[0104] The specific analysis steps of traditional LDA are as follows:
[0105] Step 1: Each of the 8 production areas is regarded as an independent group, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com