A multi-factor authentication method to prevent credential stuffing attacks
An identity authentication, multi-factor technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve the problems of low security, no participation in the user-generated password calculation process, lack of practicality, etc., to enhance security, enhance the ability to verify the identity of logged-in users, avoid Easily stolen effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
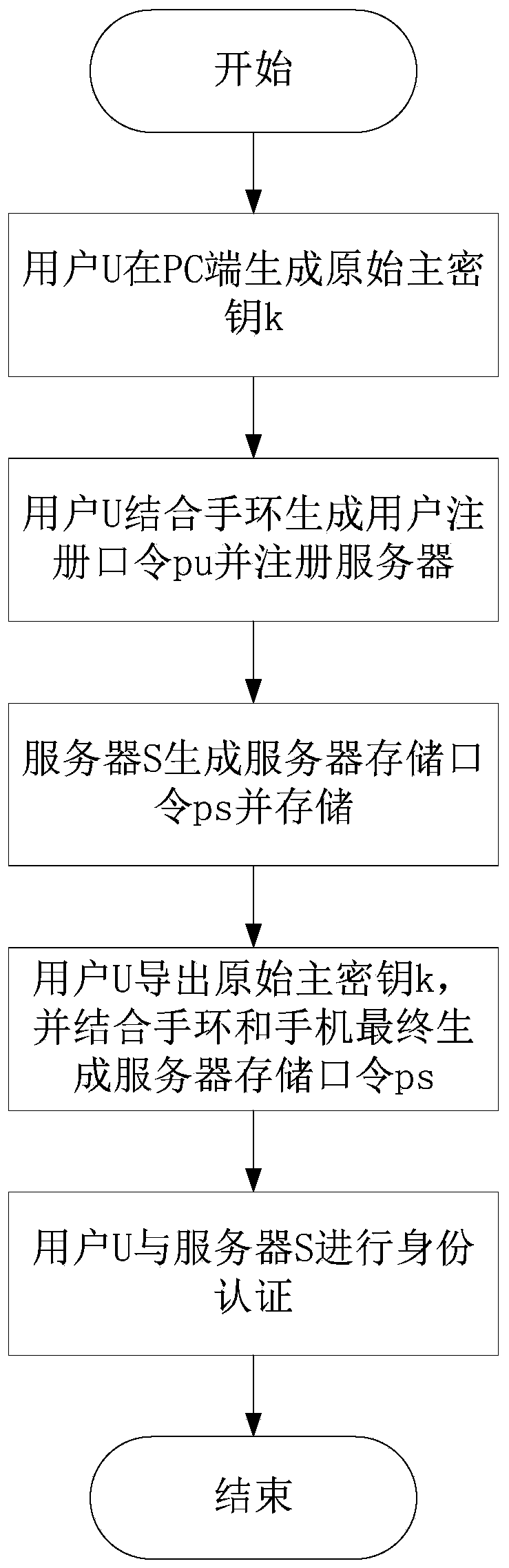
[0032] The present invention is a multi-factor identity authentication method for preventing credentialing attacks. In the present invention, the multi-factors include user password, mobile phone and wristband, all of which are indispensable, and multi-factors jointly participate in the completion of user registration and login. Refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention include:
[0033] (1) Initialization phase:
[0034] 1a) Complete the bracelet initialization: register and activate the bracelet, and bind it to the mobile phone specified by user U, to ensure that the bracelet has Bluetooth function and can connect with the associated mobile phone via Bluetooth.
[0035] 1b) Ensure that the PC used by user U during the registration phase is safe and trusted.
[0036] (2) Registration stage:
[0037] User U uses the short password pwd that he can easily remember on the PC side to generate the original master key k and the verification str...
Embodiment 2
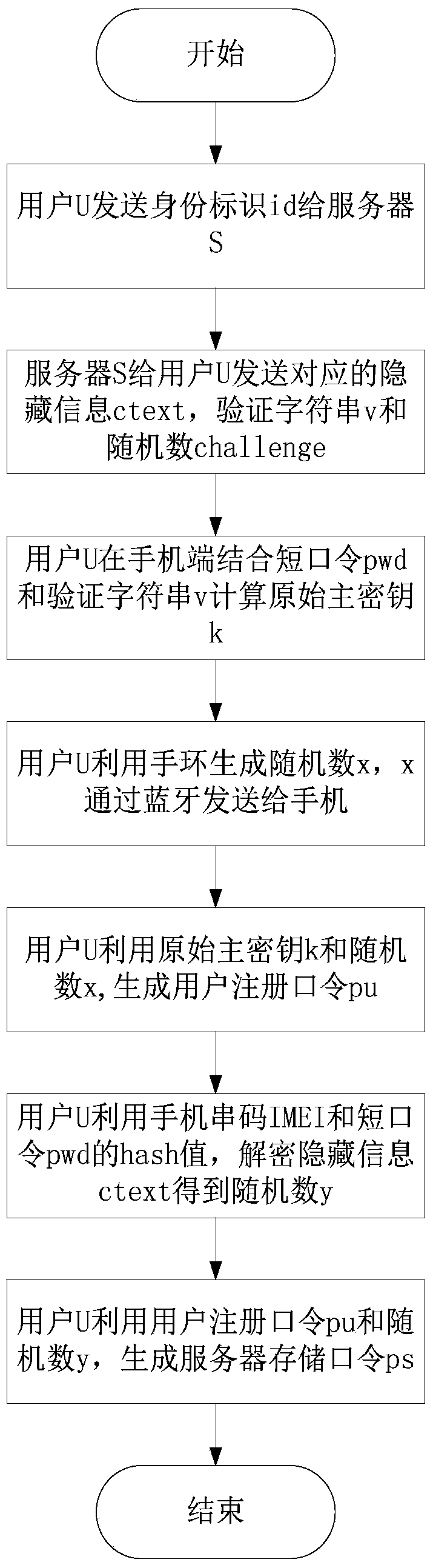
[0055] The multi-factor authentication method for preventing credential stuffing attacks is the same as that in Embodiment 1, refer to figure 2 , the specific implementation of the user registration phase is as follows:
[0056] 2a) User U chooses a random number r, an iteration number t and a short password pwd that he can easily remember for the target server S that he currently wants to register, and uses HKDF to calculate and generate a public verification string v and a definite password on the PC side. The original master key k, ie HKDF.Prepare(r, t, pwd) → (v, k).
[0057] When generating the original master key k, the user U can choose the complexity of generating the original master key k according to the security level by using the characteristics of the HKDF function, that is, choose the number of iterations t: for ordinary users, the number of iterations can be selected Fewer key generation operations; for enterprises or individuals that require a higher level of...
Embodiment 3
[0067] The multi-factor identity authentication method to prevent credential stuffing attacks is the same as that in Embodiment 1-2, the random number x generated in step 2b) of the registration phase is obtained by shaking the bracelet of one of the multi-factors by the user, and the shaking of the bracelet by the user has behavioral characteristics Yes, for different users, because of their different behavioral habits, even if the attacker obtains the user’s bracelet during the pre-login stage, it cannot accurately imitate the behavior characteristics of the user U shaking the bracelet when generating the random number x for the first time, and thus cannot accurately generate Matches the random number x in the registration stage, so it has a certain protective effect on the random number x. The random number x is transmitted to the mobile phone bound by the user by using bluetooth at close range. It is difficult for an attacker to obtain the user's mobile phone and bracelet a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com