IP positioning method based on tolerable errors
A positioning method and error technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as large calculation distance radius, center offset, and influence on positioning results, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
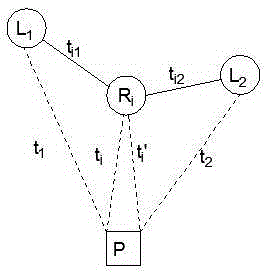
[0023] Such as figure 2 As shown, the IP positioning method based on tolerable error described in the present invention includes the following steps in turn:
[0024] a. According to the path information of the known landmarks and the target IP, obtain the landmark with the nearest common router with the target IP and the position of the nearest common router;
[0025] First, resolve and merge the interface IPs and execution aliases of the intermediate routers that appear on all paths, and then find out the intermediate router that appears on both the known landmarks and the target IP path and is topologically closest to the target IP. This intermediate router That is, the nearest common router, and the landmark connected to the router is the landmark that has the closest common router with the target IP.
[0026] b. For all landmarks connected to the nearest common router, determine the deviation value of each landmark according to the type of the corresponding organization...
Embodiment 2
[0046] In this embodiment, after obtaining the estimated time delay between the estimated position of the landmark and the nearest common router, a nonlinear optimization problem with constraints is used to solve the conversion coefficient and locate the target IP, as follows:
[0047] Such as figure 2 As shown, when the relative delay between the three landmarks A, B, E and the target IP is measurable, the claimed positions of the three landmarks are A, B and E, and the actual positions are marked as A', B' and E', The corresponding deviation values are r 1 、r 2 and r 3 , the estimated delays between the three landmarks and the target T are t 1 , t 2 and t 3 , then the objective function of the optimization problem is shown in formula (1), and the two conditions are shown in formulas (2) and (3) respectively.
[0048] m i n ( ( r 1 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com