Method for monitoring Wi-Fi label through multiple terminals
A multi-terminal and tag technology, applied in key distribution, can solve the problems of hotspot signal strength being easily affected by the surrounding environment, inability to know the status of the target object, limited usage, etc., to achieve high security, power saving, compatibility Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach S20
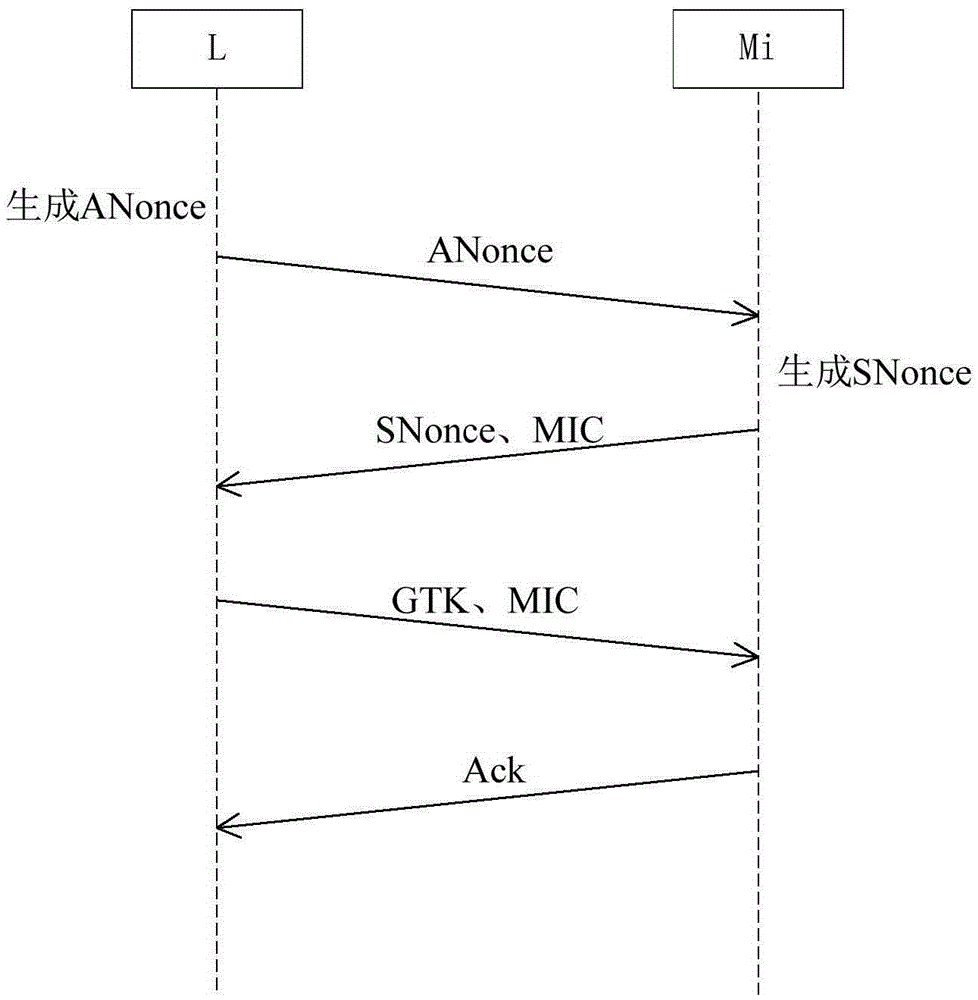
[0069] It is known that monitoring terminals {M1,M2,...,Mi-1} are located within the signal coverage of Wi-Fi label L and have established a long-term monitoring relationship with label L. Label L currently broadcasts random seed s, digital signature d and random number sequence R. At this time, the monitoring terminal Mi tries to access the label L through personal login to verify the authenticity of the label L. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the specific implementation method S20 of the Wi-Fi label L and the monitoring terminal Mi performing four handshakes to update the random seed, digital signature and random number sequence is:
[0070] S201: The tag L broadcasts a random seed s, a digital signature d, and a random number sequence R through the SSID within its signal coverage;
[0071] S202: The monitoring terminal Mi requests the login label L through the personal login method; if the request login fails, then jump to step S208;
[0072] S203: The label L locally recor...
specific Embodiment approach S30
[0081] It is known that the monitoring terminal Mi accesses the Wi-Fi tag L through personal login and verifies that the tag L is true. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the specific implementation method S30 of monitoring the target object by establishing a long-term monitoring relationship between the monitoring terminal Mi and the label L is:
[0082] S301: The monitoring terminal Mi uses a random seed generation method to calculate the random seed s according to the ANonce and SNonce generated during the four-way handshake with the label L;
[0083] In this step, the monitoring terminal Mi generates a random seed s through the random seed generation method used in step S204.
[0084] S302: The monitoring terminal Mi uses a random number generation method to calculate the random number sequence R according to the random seed s and the pre-shared key p and store it locally;
[0085] In this step, the monitoring terminal Mi generates a random number sequence R through the random ...
specific Embodiment approach S40
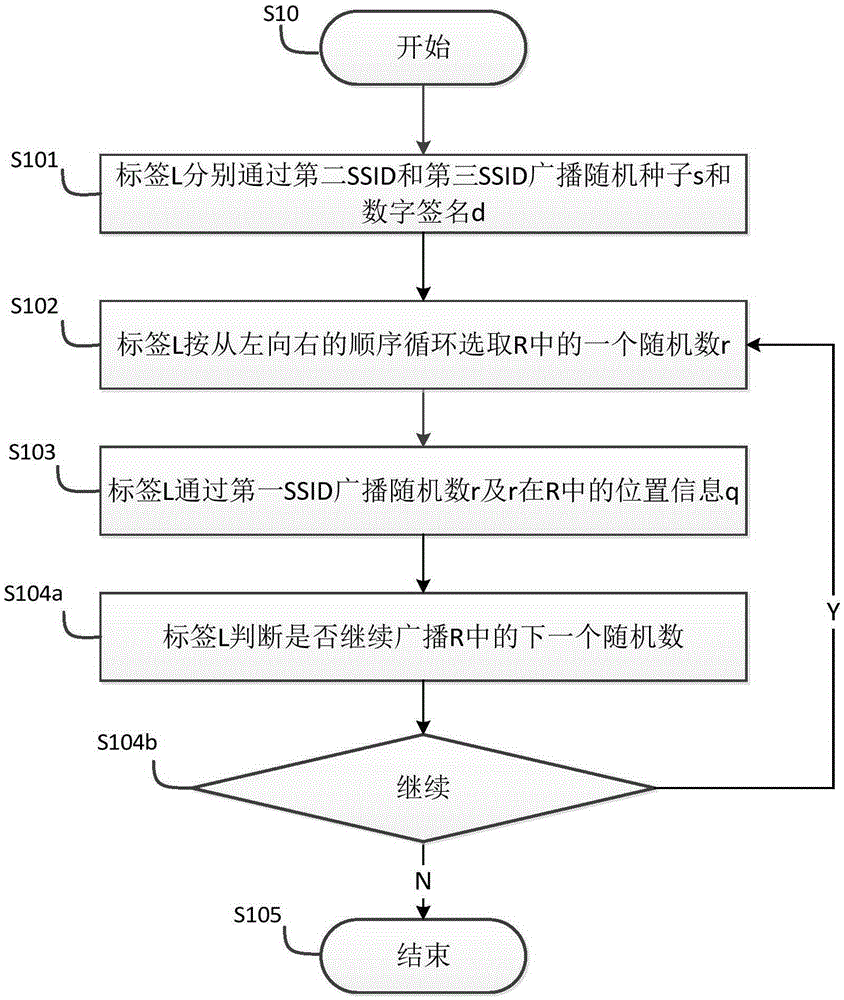
[0092] It is known that the monitoring terminals {M1, M2,...Mi-1} are located within the signal coverage of the Wi-Fi tag L and have established a long-term monitoring relationship with the tag L. Such as Image 6 As shown, any monitoring terminal Mj in {M1, M2, ..., Mi-1} continues to monitor the target object after the label L updates the random seed, digital signature and random number sequence S40 is as follows:
[0093] S401: The monitoring terminal Mj scans the second and third SSIDs broadcast by the label L and extracts a random seed s and a digital signature d therefrom, respectively;
[0094] S402: The monitoring terminal Mj uses a message digest generation method to calculate a digital signature d2 according to the random seed s currently broadcast by the label L, the last random seed s2 broadcast by the label L and the pre-shared key p;
[0095] In this step, the monitoring terminal Mj generates a digital signature d2 through the message digest generation method us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com