Fatigue limit rapid prediction method based on strain increment
A fatigue limit and strain increment technology, which is applied in the direction of testing material strength by applying repetitive force/pulsation force, and can solve problems such as narrow application range and poor accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
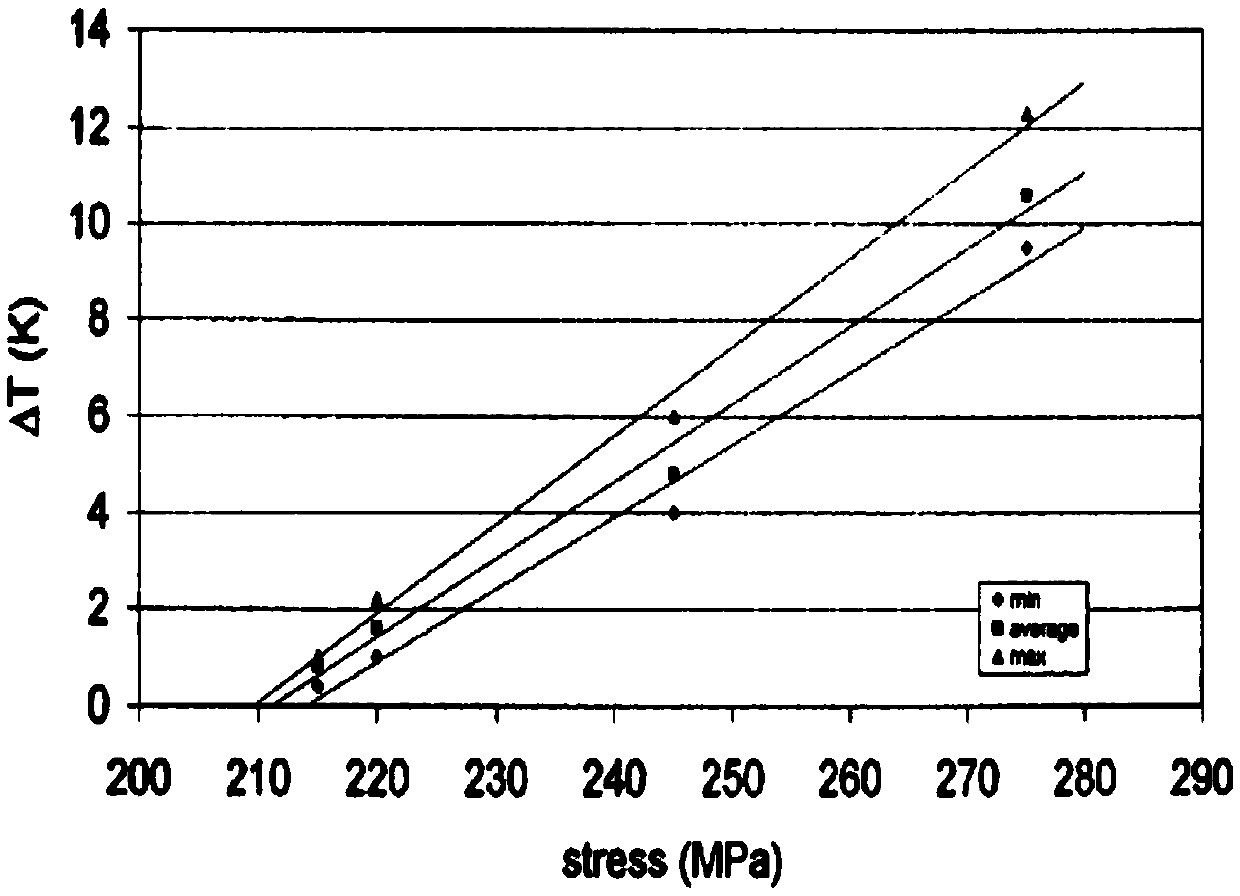
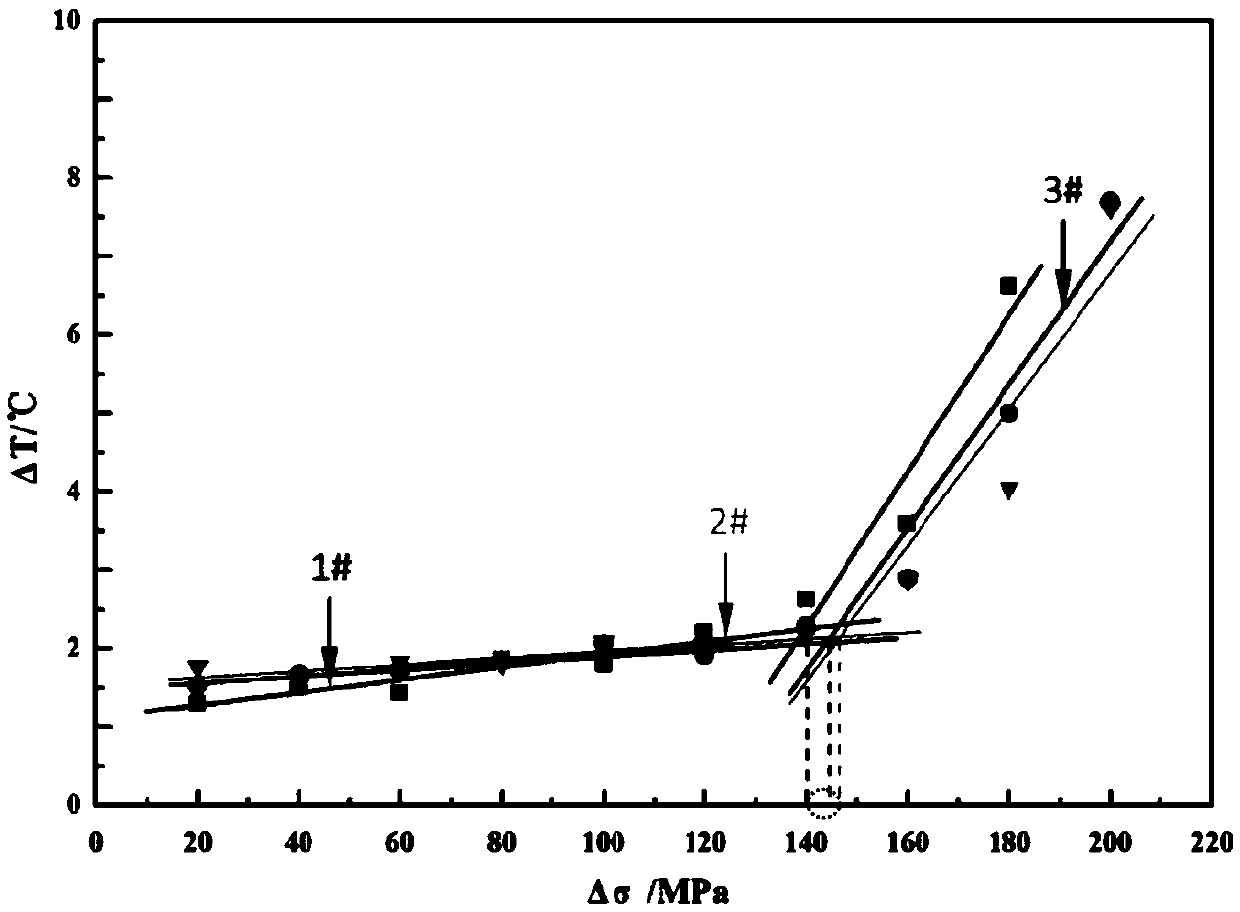
[0064] In order to verify the feasibility and accuracy of the strain-based rapid prediction fatigue limit theory, we carried out strain and infrared experiments on two different common materials for blower impellers (precipitation hardening martensitic stainless steel FV520B and KMN-I) under an average stress of 700MPa. Synchronous online monitoring of thermal signals, comparing and verifying the prediction results of strain-based fatigue limit with the prediction results of Luong method in the currently recognized infrared thermal imaging method. The test results are described in detail below.
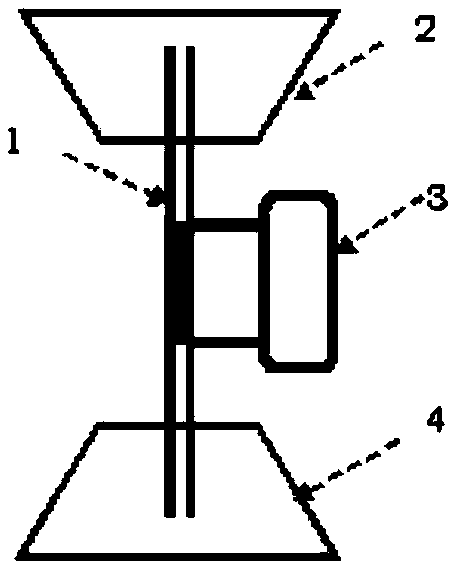
[0065] Two common compressor impeller materials, FV520B and KMN-I, were selected as raw materials and their simulated overspeed preloading process (test average stress σ’ mean Set to 900MPa to simulate ultra-speed centrifugal force, stress amplitude Δσ' to 10MPa to simulate airflow forced vibration, test frequency to 30HZ, and fatigue loading 5000 times) to prepare samples from pre-st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com