Method for fast identifying clinical pathogens based on principal component analysis and Fisher discriminance
A principal component analysis, pathogenic bacteria technology, applied in the analysis of materials, material analysis by optical means, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of high detection cost, lengthy and time-consuming identification, etc., and achieve simple operation and good application prospects. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
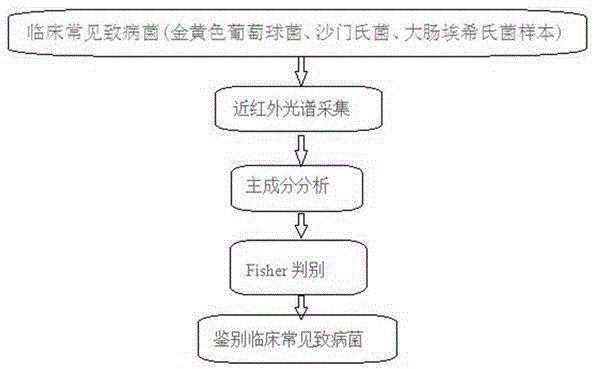
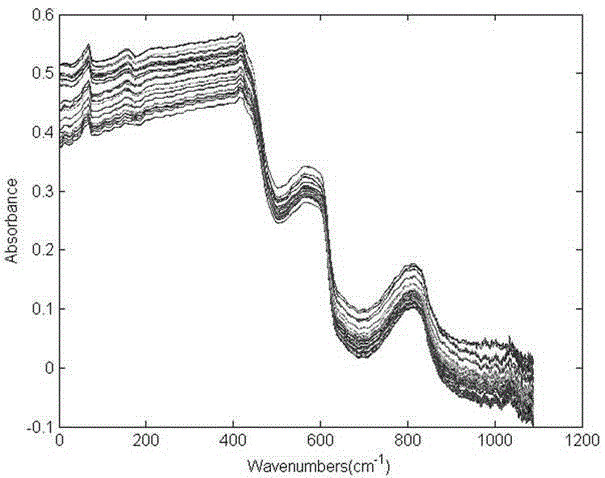
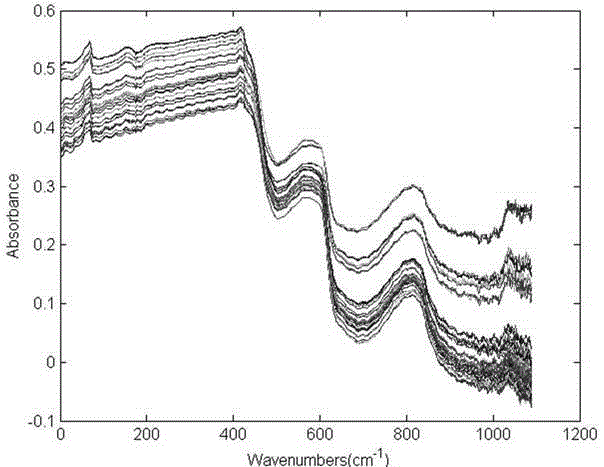
[0020] The present invention adopts the following technical solutions to realize: a method for quickly identifying clinical pathogenic bacteria based on principal component analysis and Fish discriminant method, which is characterized in that: comprising the following steps: step S1: cultivating pathogenic bacteria samples; step S2: carrying out the sample Near-infrared spectrum scanning, collecting the near-infrared spectra of these three bacteria, and eliminating abnormal sample data; Step S3: Select 4003.497~12396.18cm -1 The spectral information under the characteristic band is processed by using multiple scattering correction MSC. The spectral data obtained after scattering correction can effectively eliminate the influence of scattering and enhance the spectral absorption information related to the component content. The use of this method...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com