Storage method for storing user data into Flash and read method
A user data and data technology, applied in the direction of memory system, electrical digital data processing, memory address/allocation/relocation, etc., can solve the problems of data loss, data Flash usage time is not long, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
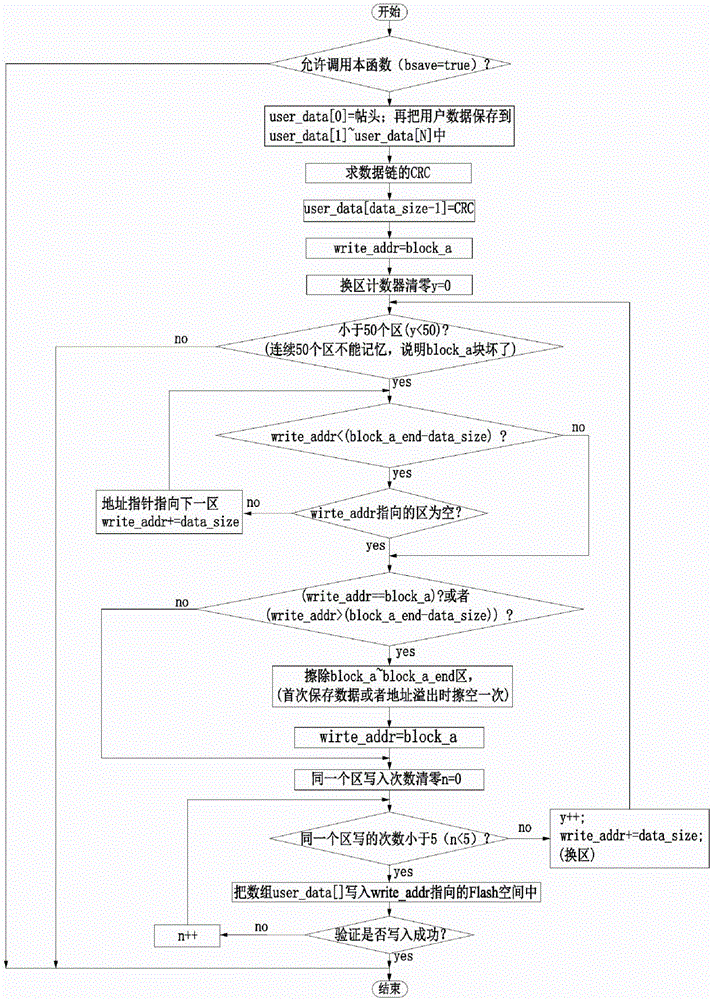
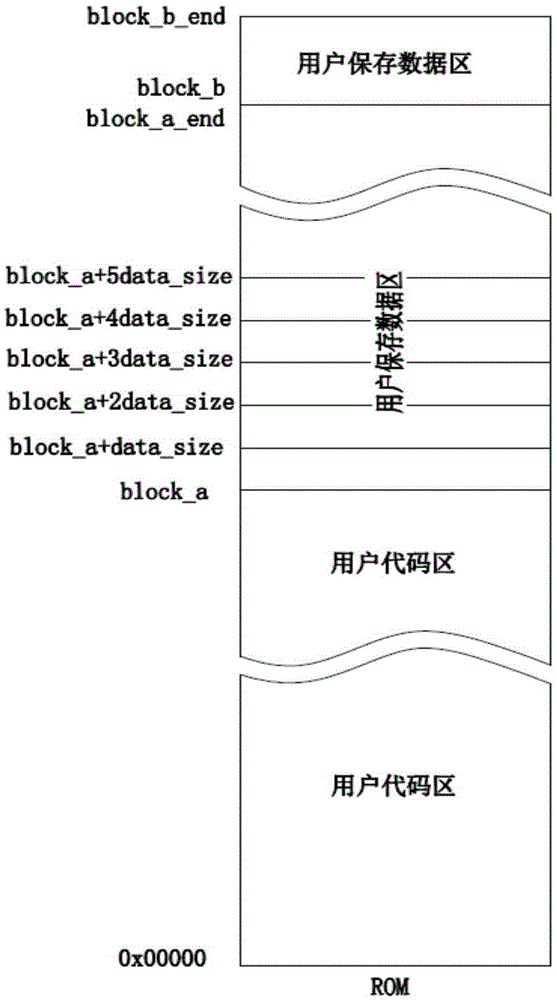
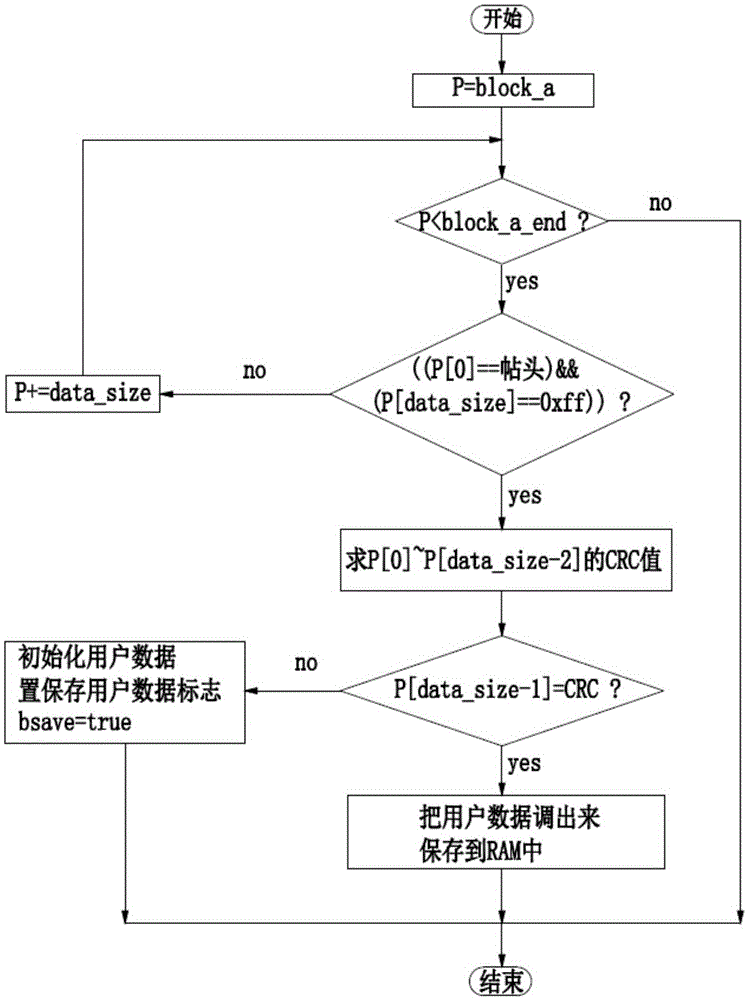
[0035] In this embodiment, the storage method and reading method for storing user data in the Flash are used to store the user data with a fixed length that needs to be saved by the electrical terminal control board in the Flash space of the single-chip microcomputer in the electrical terminal control board. The stored N user data with a fixed length are packed into data according to the following method, each data packet includes header, N user data and check code in sequence from front to back; when the user data length is not fixed, each data packet From front to back, it includes the header, M user data, reserved words, tail and check code; M changes within a predetermined range, and M is less than or equal to the predetermined length N of the longest user data, and the header or tail can be It is used to judge the integrity of the data link. We agree that the length of the stored data packets is fixed, so we agree on a 1byte length header and a 1byte length tail. The conte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com