A system for predicting the prognosis of locally advanced gastric cancer
A technology for gastric cancer and prognosis, applied in the direction of measuring devices, microbiological determination/testing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient information used in treatment plans, inability to apply clinically, and genetic characteristics are unlikely to be reproduced
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0133] [Example 1] Investigation of the gene expression profile of NO patients with gastric cancer
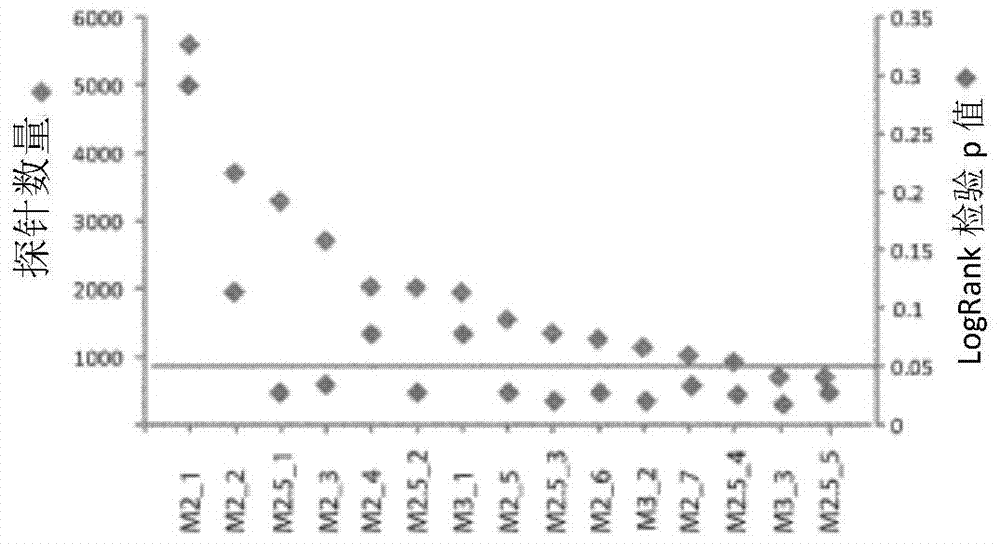
[0134] Scatter filtering was performed sequentially by varying the filtering criteria, generating 15 clusters consisting of unique two main clusters. After dispersive filtering, most genes have 701-5612 probes, which are diverse, and the p-values based on dispersive filtering criteria in the log rank test have various values, among which the maximum value is 0.291 (M2_1: by pair with Genes with at least one probe showing a 2-fold or more increase or decrease compared to the median were selected and had a cluster of 5612 probes after scatter filtering), while the minimum value was 0.0181 (M3_3: pairs with at least 3 genes showing a 3-fold or more increase or decrease in probes when compared to the median were selected and had clusters of 706 probes after scatter filtering). Of the 15 clusters, 11 of them generated 2 major categories in unsupervised hierarchical cluster analys...
Embodiment 2
[0140] [Example 2] The biological characteristics of two main clusters
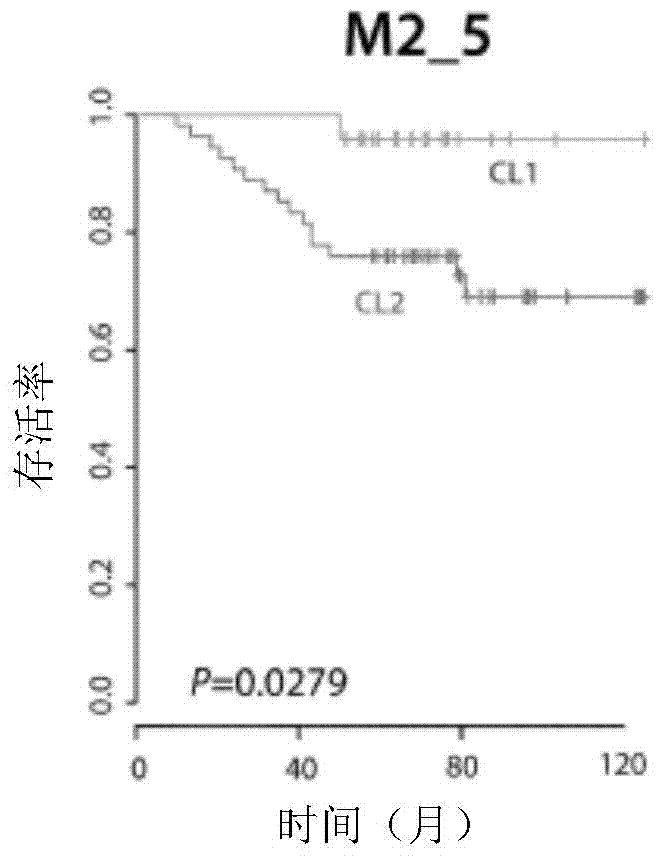
[0141] To define the main gene identity of the two classifications showing this difference in prognostic outcome, t-tests were performed on 2 samples. 2886 significantly different probes (p<0.001 ) were generated by comparison between the 2 taxa showing two major clusters of M2_5 after unsupervised cluster analysis.
[0142] image 3 A shows a heat map of conditional cluster analysis using probes that were statistically significant (p<0.001) when compared between 2 classifications of M2_5 and showed 2-fold or more differences. The expression of many genes related to immune response (IFNG, GZMA, GZMB, CD8A, STAT1, JAK2, HLADPA1) was significantly increased in the good response group.
[0143] When GSEA analysis was performed on the above two classifications in the Biocarta pathway database, the most significantly improved pathways were Antigen Processing and presentation (MHC pathway) with statistical si...
Embodiment 3
[0148] [Example 3] Formation of prognosis prediction model
[0149] In order to form a prognostic prediction model, 3 different prognostic prediction algorithms can be used, namely the mixed covariate prediction method (CCP), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), and nearest centroid method (NC). To make predictions for taxonomic groups, significantly different genes were used for the two taxa at a significance level of 0.001, and calibrated prediction ratios were calculated by using leave-one-out cross-validation.
[0150] The difference in prognosis between the two predicted groups in the training set (YUSH dataset) relative to the M3_3 classification group was statistically significant (log rank test, CCP: p=0.00933, LDA: p=0.0137 and NC: p = 0.00217), and the calibrated prediction ratios for the M3_3 classification group ranged from 85% to 92% (CCP: 86%, LDA: 85% and NC: 92%) (Fig. 7A-C).
[0151] The MDACC dataset was used to examine the taxonomic groups. The prediction r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com