Compositions for use in nutrition of dysphagia patients
A technology for dysphagia and composition, which is applied in the field of nutritional composition for patients with dysphagia, and can solve problems such as decreased viscosity of thickened nutrition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0164] Preparation of patient nutrition
[0165] The present disclosure also relates to a method for thickening a patient's food comprising the steps of:
[0166] a. Providing patient food in liquid or fluid form, such as by making a puree;
[0167] b. adding the thickener composition described herein;
[0168] c. Mix the thickener composition with the patient's food.
[0169] soaking solution
[0170] The thickener compositions as described herein can be used to prepare infusion solutions, which are to be delivered or used in cakes, cookies, breads, and the like. A typical infusion solution will include 50-150 milliliters of liquid, such as water, juice or coffee, and about 520 grams of the thickener composition. The soaking solution should be mixed thoroughly, eg by stirring, before use.
[0171] Cakes, cookies, breads or the like can be soaked in the soaking solution and can be placed in the refrigerator for about 2 hours before use.
specific Embodiment approach
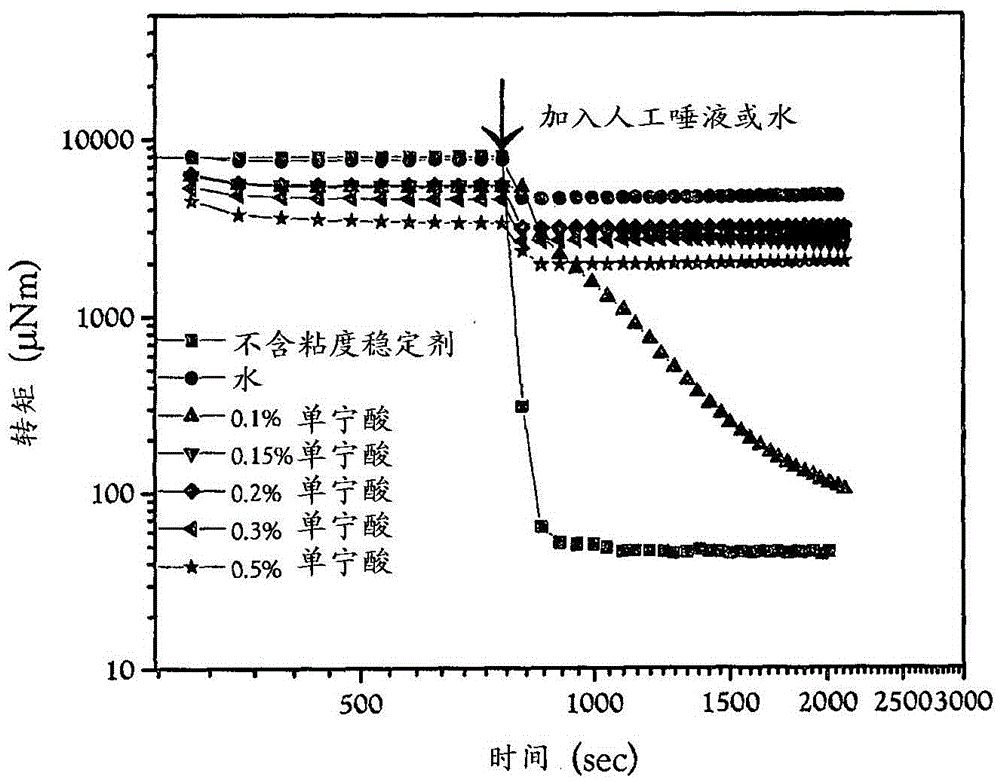
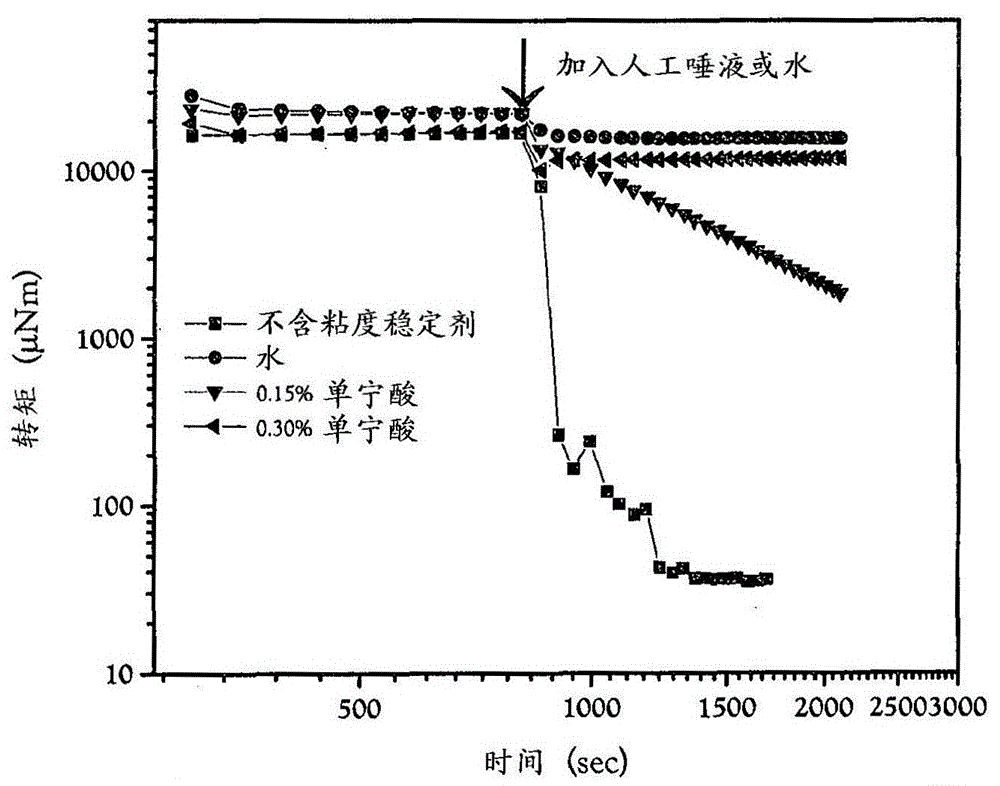
[0172] 1. A food thickener composition for adding nutritional products comprising or consisting of
[0173] a) polyphenol viscosity stabilizers,
[0174] b) starch,
[0175] c) optional cellulose, and
[0176] d) optional one or more additives.
[0177] 2. The thickener composition according to embodiment 1, which comprises cellulose.
[0178] 3. The thickener composition of any preceding embodiment, wherein the weight ratio of polyphenolic viscosity stabilizer to starch is at least 0.001:1, or at least 0.002:1, preferably at least 0.010:1, more preferably at least 0.015:1, even more preferably at least 0.020:1, most preferably at least 0.030:1, eg at least 0.100:1.
[0179] 4. The thickener composition according to any preceding embodiment, wherein the polyphenolic viscosity stabilizer is included in an amount of 0.01-1 wt%, preferably 0.01-0.1 wt%, more preferably 0.05 wt%, based on The total weight of the thickener composition.
[0180] 5. A thickener composition acco...
Embodiment 1
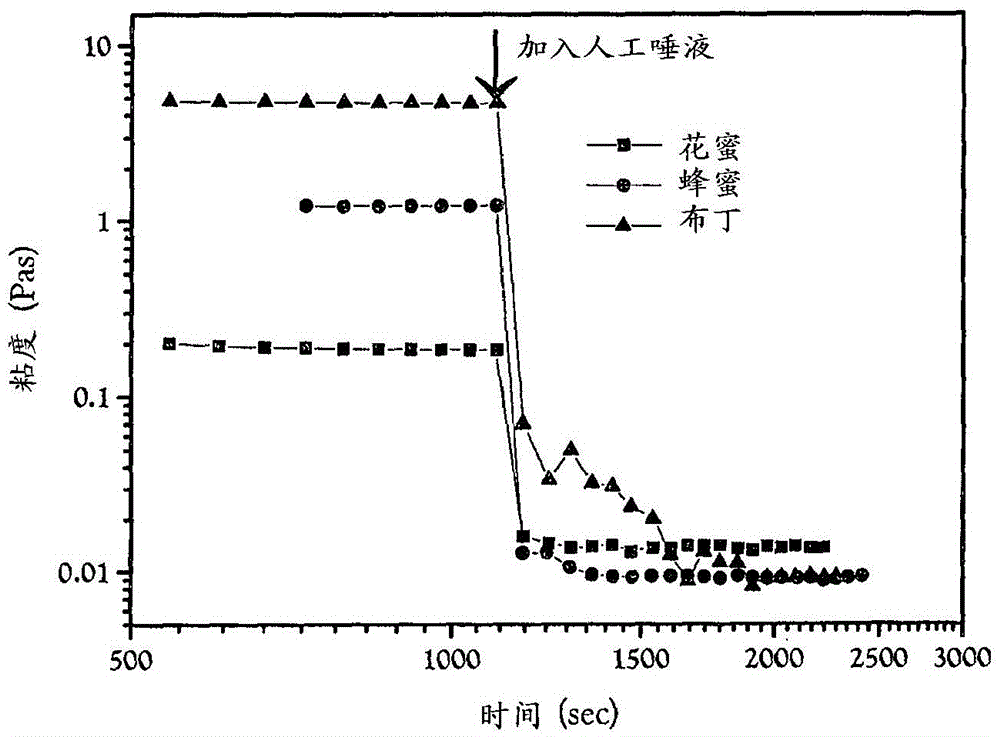
[0230] Example 1: Effect of artificial saliva on solutions thickened with starch-based thickeners
[0231] As shown in Fig. 1, around the swallowing shear rate, the viscosity of three textures (nectar, honey, and pudding) commonly used in the treatment of dysphagia by using 99.7 wt% modified cornstarch and 0.3 wt% The starch-based thickener of maltodextrin was adjusted, and the adjusted viscosity dropped to very low values almost immediately after the addition of artificial saliva. After adding artificial saliva, the viscosity of the thickened solution dropped by up to three orders of magnitude within seconds. The reduced viscosity of such thickened solutions can be problematic for patients with dysphagia because the texture of the prescribed food cannot be maintained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com