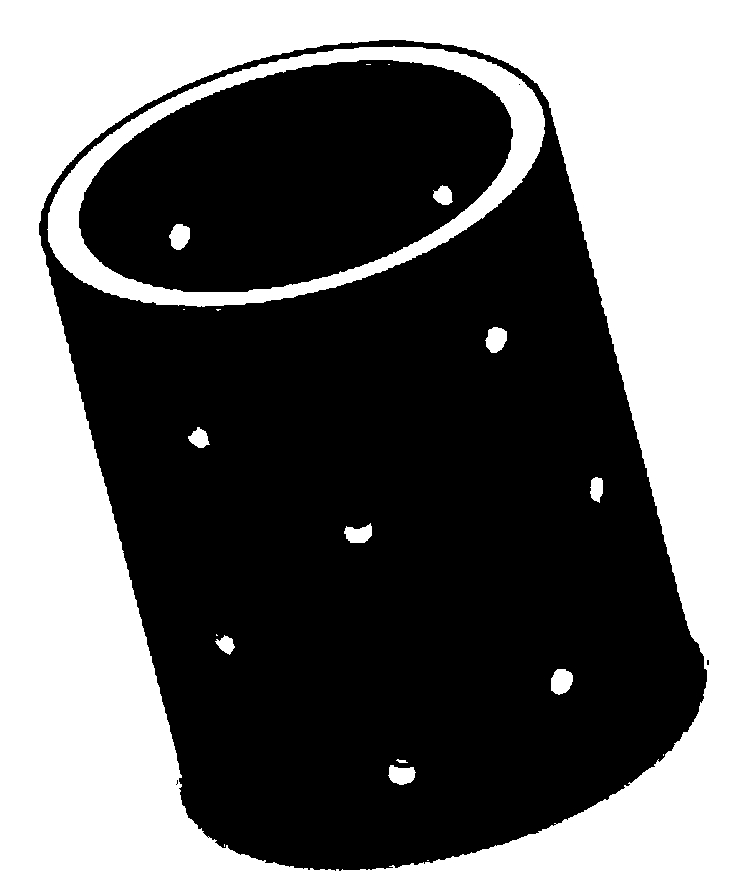
A method for preparing a degradable magnesium cage implant with an antibacterial and corrosion-resistant graphene/apatite composite coating
A technology for composite coatings and implants, applied in coatings, metal material coating processes, prostheses, etc., can solve the problem of mechanical integrity loss, poor bonding strength of apatite film substrate, low corrosion potential of magnesium metal, high Corrosion rate and other issues, to achieve the effects of inhibiting bacterial growth, improving bone fusion speed, corrosion resistance and enhanced membrane-base bonding strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: A method of preparing a degradable magnesium cage implant with an antibacterial and corrosion-resistant graphene / apatite composite coating in this embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0030] Step 1. Process the magnesium metal into a cage-shaped implant. After cleaning the cage-shaped implant with 20-100ml of acetone at room temperature (room temperature is 15-25°C) for 5-20 minutes, use 20-100ml of absolute ethanol in the Ultrasonic cleaning of the cage implant at 15-25°C for 5-20 minutes;
[0031] Step 2: Use deionized water at a temperature of 15 to 25°C to clean the cage-like implant after ultrasonic cleaning with absolute ethanol for 3 to 5 minutes, then dry it at a temperature of 20 to 50°C for 10 to 20 minutes to obtain pretreatment Magnesium metal material; (this deionized water is designated by the International Organization for Standardization ISO / TC)
[0032] Step 3, carry out hydrothermal treatment to the pretr...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that the magnesium metal described in Step 1 is pure magnesium, magnesium-aluminum alloy, magnesium-zinc alloy, magnesium-zirconium alloy, rare earth magnesium alloy or magnesium-calcium alloy. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0048] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the inside of the cage-shaped implant described in step 1 is filled with collagen, autologous granular bone, allogeneic granular bone, active factors for promoting bone fusion, or antibacterial sustained release One or more of the factors. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com