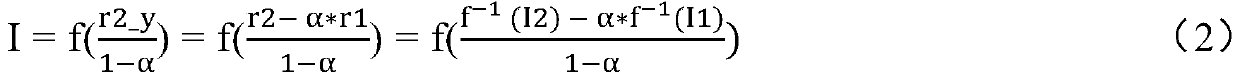Liquid crystal lens imaging method
A technology of liquid crystal lens and imaging method, which is applied in the direction of instruments, nonlinear optics, optics, etc., and can solve the problems of incompletely consistent polarized light propagation behavior, increasing the production cost of liquid crystal lenses, adding liquid crystal lenses or liquid crystal layers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] In order to understand the above-mentioned purpose, features and advantages of the present invention more clearly, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments of the present application and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other.
[0028] In the following description, many specific details are set forth in order to fully understand the present invention, but the present invention can also be implemented in other ways different from those described here, therefore, the present invention is not limited to the specific embodiments disclosed below limit.
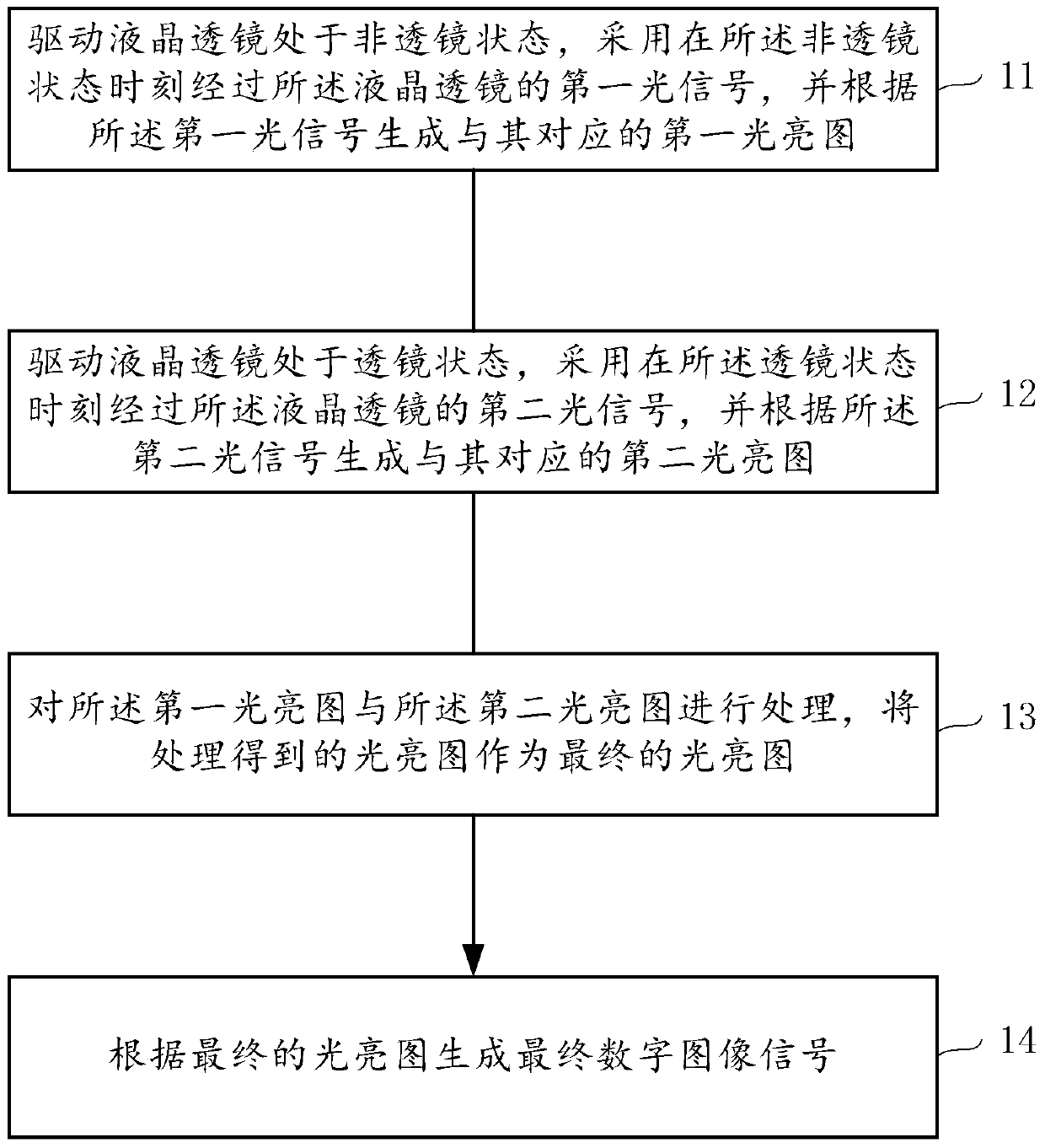
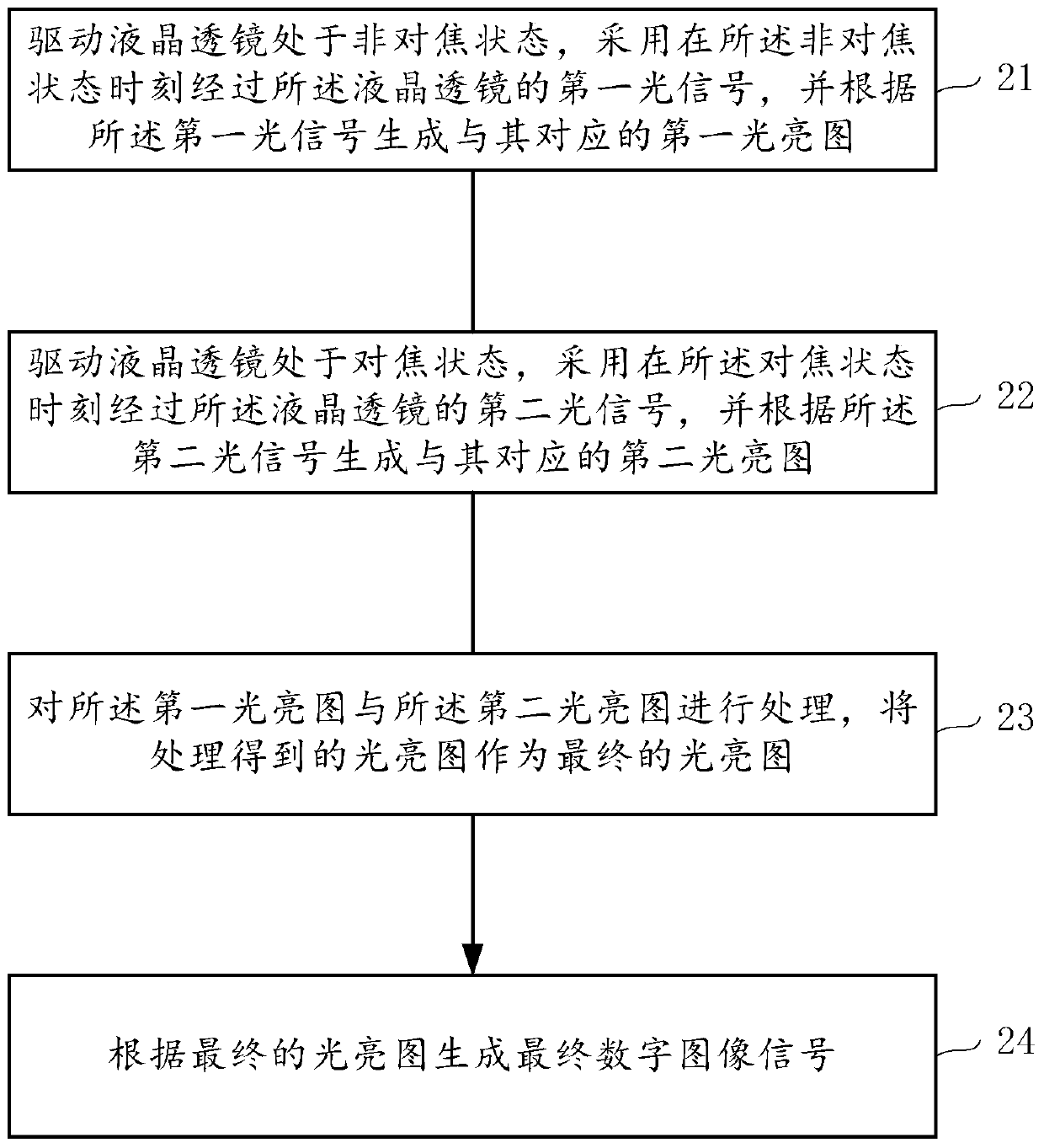
[0029] The liquid crystal lens imaging method provided by the invention comprises the following steps:
[0030] Driving the liquid crystal lens to be in the first state, adopting the first light signal passing through the liquid crystal l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com