Thumper circuit
A buzzer and circuit technology, applied to instruments, sound-generating devices, etc., can solve problems such as instability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and preferred embodiment the present invention is described in further detail:
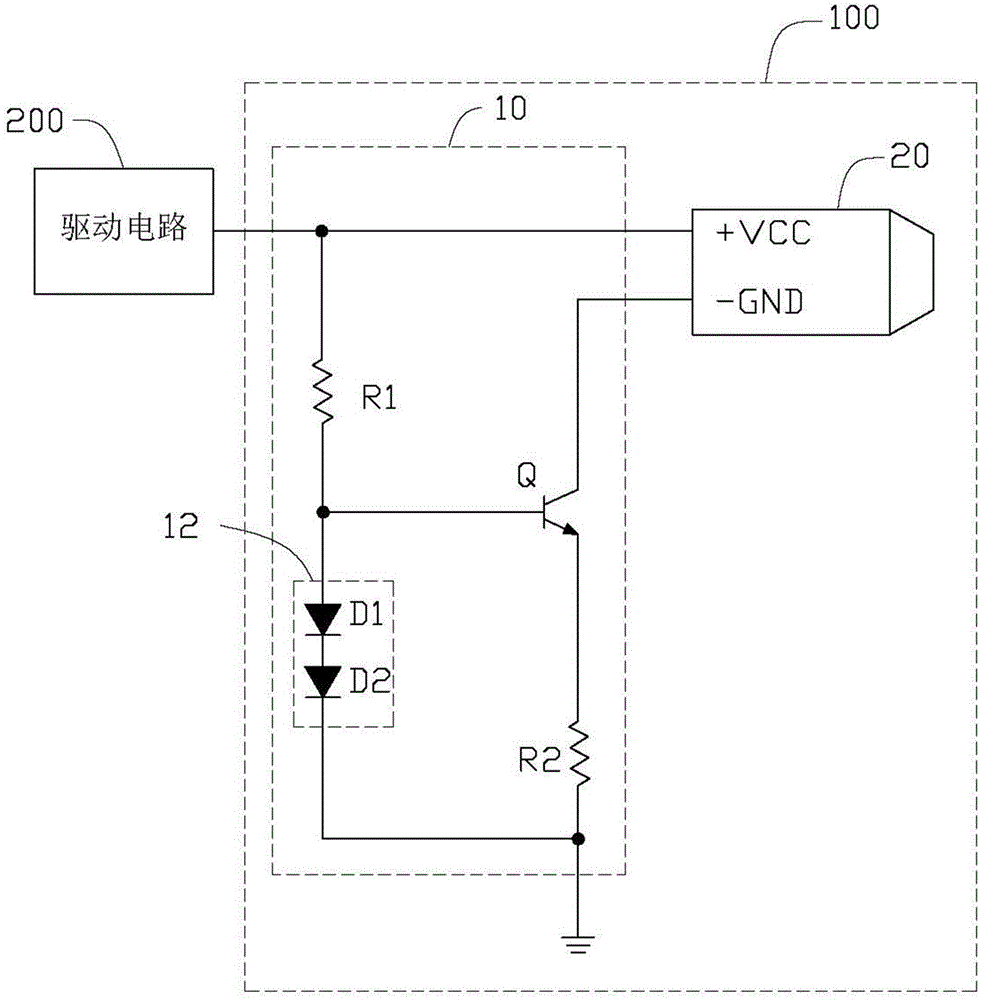
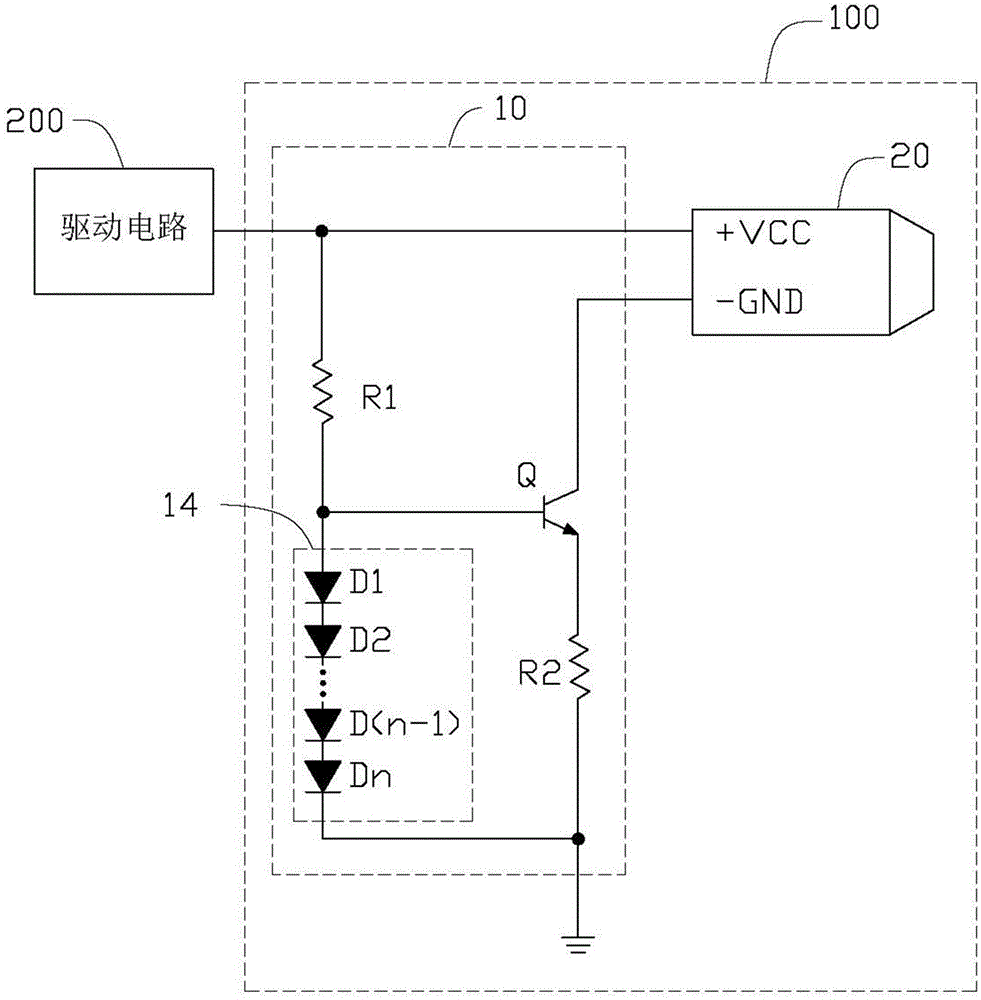
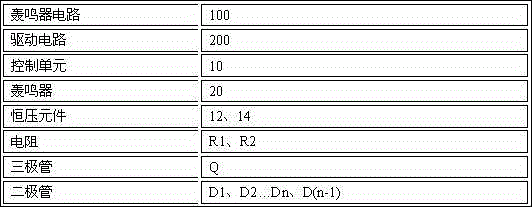
[0014] Please refer to figure 1 , The first preferred embodiment of the buzzer circuit 100 of the present invention is connected to a driving circuit 200 , and the driving circuit 200 is used to drive the buzzer circuit 100 . The buzzer circuit 100 includes a control unit 10 and a buzzer 20 .
[0015] The control unit 10 includes a first resistor R1 , a second resistor R2 , a transistor Q and a constant voltage element 12 . The constant voltage element 12 includes two diodes D1 and D2 connected in series. The buzzer 20 includes a power pin VCC and a ground pin GND. The power supply pin VCC is connected to the driving circuit 200 . The base of the triode Q is connected to the power pin VCC of the buzzer 20 through the first resistor R1. The collector of the transistor Q is connected to the ground pin GND of the buzzer 20 . The emitter of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com