Food safety risk prediction method based on hidden Markov model
A risk prediction and food safety technology, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, resources, etc., can solve the problems of slow learning speed, unsuitable for large sample data analysis and processing, and cannot change the evaluation results, etc., to achieve the effect of strong scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
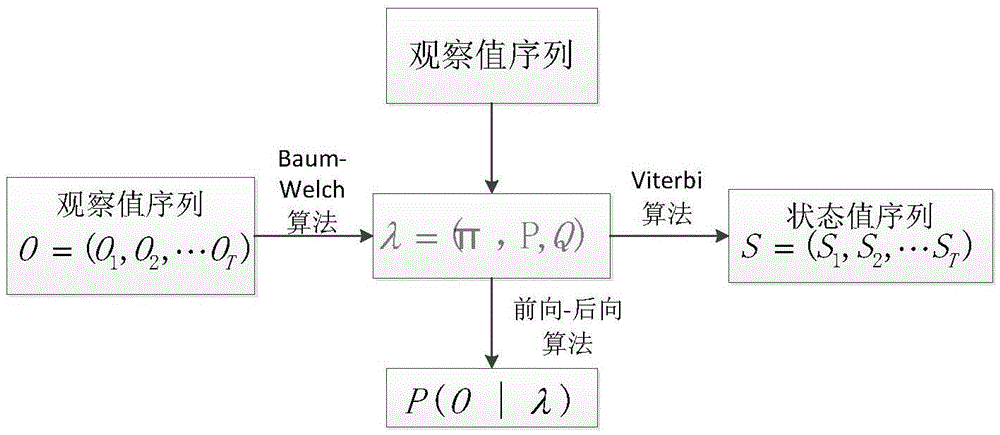
[0034] 1. Description of Hidden Markov Model (HMM):
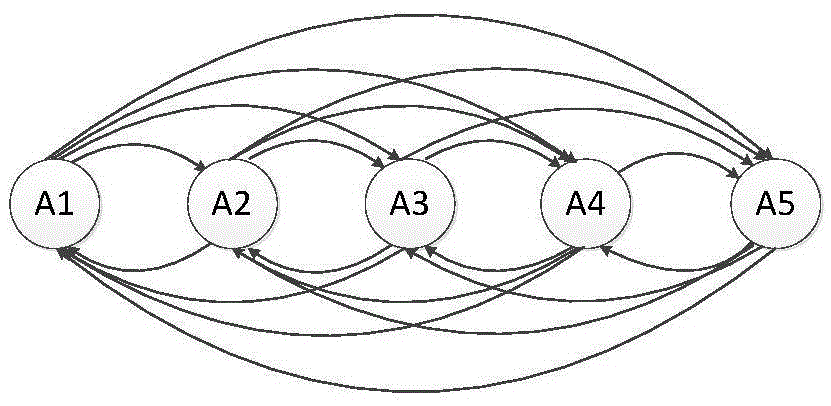
[0035] The basic theory of HMM was founded by Baum et al. in the 1970s and spread and developed in the mid-1980s. Hidden Markov Model (HMM) is developed on the basis of Markov chain. The observed events in an HMM are random functions of the state, so the model is a double stochastic process, one observed state and one hidden state. From the perspective of the observer, only the observation value can be seen, unlike the one-to-one correspondence between the observation value and the state value in the Markov chain model.
[0036] The mathematical expression of HMM is:
[0037] λ=(N,M,π,P,Q)(1)
[0038] It can also be simply expressed as:
[0039] λ=(N,M,π)(2)
[0040] Among them: N is the number of states in the HMM; M is the number of observations corresponding to the HMM; π is the distribution vector of the initial state,
[0041] π=(π 1 , π 2 ,…,π N ),
[0042] 0 ≤ π ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com